
It has become compulsory for modern medical (or scientifically-relevant) shows to rely on a team of advisors and experts for maximal technical accuracy and verisimilitude on screen. Many of these shows have become so culturally embedded that they’ve changed people’s perceptions and influenced policy. Even the Gates Foundation has partnered with popular television shows to embed important storyline messages pertinent to public health, HIV prevention and infectious diseases. But this was not always the case. When Neal Baer joined ER as a young writer and simultaneous medical student, he became the first technical expert to be subsumed as an official part of a production team. His subsequent canon of work has reshaped the integration of socially relevant issues in television content, but has also ushered in an age of public health awareness in Hollywood, and outreach beyond it. Dr. Baer sat down with ScriptPhD to discuss how lessons from ER have fueled his public health efforts as a professor and founder of UCLA’s Global Media Center For Social Impact, including storytelling through public health metrics and leveraging digital technology for propelling action.
Neal Baer’s passion for social outreach and lending a voice to vulnerable and disadvantaged populations was embedded in his genetic code from a very young age. “My mother was a social activist from as long as I can remember. She worked for the ACLU for almost 45 years and she participated in and was arrested for the migrant workers’ grape boycott in the 60s. It had a true and deep impact on me that I saw her commitment to social justice. My father was a surgeon and was very committed to health care and healing. The two of them set my underlying drives and goals by their own example.” Indeed, his diverse interests and innate curiosity led Baer to study writing at Harvard and the American Film Institute and eventually, medicine at Harvard Medical School. Potentially presenting a professional dichotomy, it instead gave him the perfect niche — medical storytelling — that he parlayed into a critical role on the hit show ER.

During his seven-year run as medical advisor and writer on ER, Baer helped usher the show to indisputable influence and critical acclaim. Through the narration of important, germane storylines and communication of health messages that educated and resonated with viewers, ER‘s authenticity caught the attention of the health care community and inspired many television successors. “It had a really profound impact on me, that people learn from television, and we should be as accurate as possible,” Baer reflects. “[Viewers] believe it’s real, because we’re trying to make it look as real as possible. We’re responsible, I think. We can’t just hide behind the façade of: it’s just entertainment.” As show runner of Law & Order: SVU, Baer spearheaded a storyline about rape kit backlogs in New York City that led to a real-life push to clear 17,000 backlogged kits and established a foundation that will help other major US cities do the same. With the help of the CDC and USC’s prestigious Norman Lear Center, Baer launched Hollywood, Health and Society, which has become an indispensable and inexhaustible source of expert information for entertainment industry professionals looking to incorporate health storylines into their projects. In 2013, Baer co-founded the Global Media Center For Media Impact at UCLA’s School of Public Health, with the aim of addressing public health issues through a combination of storytelling and traditional scientific metrics.
Soda Politics
One of Baer’s seminal accomplishments at the helm of the Global Media Center was convincing public health activist Marion Nestle to write the book Soda Politics: Taking on Big Soda (And Winning). Nestle has a long and storied career of food and social policy work, including the seminal book Food Politics. Baer first took note of the nutritional and health impact soda was having on children in his pediatrics practice. “I was just really intrigued by the story of soda, and the power that a product can have on billions of people, and make billions of dollars, where the product is something that one can easily live without,” he says. That story, as told in Soda Politics, is a powerful indictment on the deleterious contribution of soda to the United States’ obesity crisis, environmental damage and political exploitation of sugar producers, among others. More importantly, it’s an anthology of the history of dubious marketing strategies, insider lobbying power and subversive “goodwill” campaigns employed by Big Soda to broaden brand loyalty.
Even more than a public health cautionary tale, Soda Politics is a case study in the power of activism and persistent advocacy. According to a New York Times expose, the drop in soda consumption represents the “single biggest change in the American diet in the last decade.” Nestle meticulously details the exhaustive, persistent and unyielding efforts that have collectively chipped away at the Big Soda hegemony: highly successful soda taxes that have curbed consumption and obesity rates in Mexico, public health efforts to curb soda access in schools and in advertising that specifically targets young children, and emotion-based messaging that has increased public awareness of the deleterious effects of soda and shifted preference towards healthier options, notably water. And as soda companies are inevitably shifting advertising and sales strategy towards , as well as underdeveloped nations that lack access to clean water, the lessons outlined in the narrative of Soda Politics, which will soon be adapted into a documentary, can be implemented on a global scale.
ActionLab Initiative
Few technological advancements have had an impact on television consumption and creation like the evolution of digital transmedia and social networking. The (fast-crumbling) traditional model of television was linear: content was produced and broadcast by a select conglomerate of powerful broadcast networks, and somewhat less-powerful cable networks, for direct viewer consumption, measured by demographic ratings and advertising revenue. This model has been disrupted by web-based content streaming such as YouTube, Netflix, Hulu and Amazon, which, in conjunction with fractionated networks, will soon displace traditional TV watching altogether. At the same time, this shifting media landscape has burgeoned a powerful new dynamic among the public: engagement. On-demand content has not only broadened access to high-quality storytelling platforms, but also provides more diverse opportunities to tackle socially relevant issues. This is buoyed by the increased role of social media as an entertainment vector. It raises awareness of TV programs (and influences Hollywood content). But it also fosters intimate, influential and symbiotic conversation alongside the very content it promotes. Enter ActionLab.

One of the critical pillars of the Global Media Center at UCLA, ActionLab hopes to bridge the gap between popular media and social change on topics of critical importance. People will often find inspiration from watching a show, reading a book or even an important public advertising campaign, and be compelled to action. However, they don’t have the resources to translate that desire for action into direct results. “We first designed ActionLab about five or six years ago, because I saw the power that the shows were having – people were inspired, but they just didn’t know what to do,” says Baer. “It’s like catching lightning in a bottle.” As a pilot program, the site will offer pragmatic, interactive steps that people can implement to change their lives, families and communities. ActionLab offers personalized campaigns centered around specific inspirational projects Baer has been involved in, such as the Soda Politics book, the If You Build It documentary and a collaboration with New York Times columnist Nicholas Kristof on his book/documentary A Path Appears. As the initiative expands, however, more entertainment and media content will be tailored towards specific issues, such as wellness, female empowerment in poor countries, eradicating poverty and community-building.
“We are story-driven animals. We collect our thoughts and our memories in story bites,” Baer notes. “We’re always going to be telling stories. We just have new tools with which to tell them and share them. And new tools where we can take the inspiration from them and ignite action.”
Baer joined ScriptPhD.com for an exclusive interview, where he discussed how his medical education and the wide-reaching impact of ER influenced his social activism, why he feels multi-media and cross-platform storytelling are critical for the future of entertainment, and his future endeavors in bridging creative platforms and social engagement.
ScriptPhD: Your path to entertainment is an unusual one – not too many Harvard Medical School graduates go on to produce and write for some of the most impactful television shows in entertainment history. Did you always have this dual interest in medicine and creative pursuits?
Neal Baer: I started out as a writer, and went to Harvard as a graduate student in sociology, [where] I started making documentary films because I wanted to make culture instead of studying it from the ivory tower. So, I got to take a documentary course, and it’s come full circle because my mentor Ed Pinchas made his last film called “One Cut, One Life” recently and I was a producer, before his demise from leukemia. That sent me to film school at the American Film Institute in Los Angeles as a directing fellow, which then sent me to write and direct an ABC after-school special called “Private Affairs” and to work on the show China Beach. I got cold feet [about the entertainment industry] and applied to medical school. I was always interested in medicine. My father was a surgeon, and I realized that a lot of the [television] work I was doing was medically oriented. So I went to Harvard Medical School thinking that I was going to become a pediatrician. Little did I know that my childhood friend John Wells, who had hired me on China Beach, would [also] hire me on “ER” by sending me the script, originally written by Michael Crichton in 1969, and dormant for 25 years until it was discovered in a trunk owned by Steven Spielberg. [Wells] asked me what I thought of the script and I said “It’s like my life only it’s outdated.” I gave him notes on how to update it, and I ultimately became one of the first doctor-writers on television with ER, which set that trend of having doctors on the show to bring verisimilitude.
SPhD: From the series launch in 1994 through 2000, you wrote 19 episodes and created the medical storylines for 150 episodes. This work ran parallel to your own medical education as a medical student, and subsequently an intern and resident. How did the two go hand in hand?
NB: I started writing on ER when I was still a fourth year medical student going back and forth to finish up at Harvard Medical School, and my internship at Children’s Hospital of Los Angeles over six years. And I was very passionate about bringing public health messages to the work that I was doing because I saw the impact that television can have on the audience, particularly the large numbers of people that were watching ER back then.
I was Noah Wylie’s character Dr. Carter. He was a third year [medical student], I was a fourth year. So I was a little bit ahead of him, and I was able to capture what it was like to be the low person on the totem pole and to reflect his struggles through many of the things my friends and I had gone through or were going through. Some of my favorite episodes we did were really drawn on things that actually happened. A friend of mine was sequestered away from the operating table but the surgeons were playing a game of world capitals. And she knew the capital of Zaire, when no one else did, so she was allowed to join the operating table [because of that]. So [we used] that same circumstance for Dr. Carter in an episode. Like you wouldn’t know those things, you had to live through them, and that was the freshness that ER brought. It wasn’t what you think doctors do or how they act but truly what goes on in real life, and a lot of that came from my experience.
SPhD: Do you feel like the storylines that you were creating for the show were germane both to things happening socially as well as reflective of the experience of a young doctor in that time period?
NB: Absolutely. We talked to opinion leaders, we had story nights with doctors, residents and nurses. I would talk to people like Donna Shalala, who was the head of the Department of Health and Human Safetey. I asked the then-head of the National Institutes of Health Harold Varmus, a Nobel Prize winner, “What topics should we do?” And he said “Teen alcohol abuse.” So that is when we had Emile Hirsch do a two-episode arc directly because of that advice. Donna Shalala suggested doing a story about elderly patients sharing perscriptions because they couldn’t afford them and the terrible outcomes that were happening. So we were really able to draw on opinion leaders and also what people were dealing with [at that time] in society: PPOs, all the new things that were happening with medical care in the country, and then on an individual basis, we were struggling with new genetics, new tests, we were the first show to have a lead character who was HIV-positive, and the triple cocktail therapy didn’t even come out until 1996. So we were able to be path-breaking in terms of digging into social issues that had medical relevance. We had seen that on other shows, but not to the extent that ER delved in.
SPhD: One of the legacies of a show like ER is how ahead of its time it was with many prescient storylines and issues that it tackled that are relevant to this very day. Are there any that you look back on that stand out to you in that regard as favorites?
NB: I really like the storyline we did with Julianna Margulies’s character [Nurse Carole Hathaway] when she opened up a clinic in the ER to deal with health issues that just weren’t being addressed, like cervical cancer in Southeast Asian populations and dealing with gaps in care that existed, particularly for poor people in this country, and they still do. Emergency rooms [treating people] is not the best way efficiently, economically or really humanely. It’s great to have good ERs, but that’s not where good preventative health care starts. The ethical dilemmas that we raised in an episode I wrote called “Who’s Happy Now?” involving George Clooney’s character [Dr. Doug Ross] treating a minor child who had advanced cystic fibrosis and wanted to be allowed to die. That issue has come up over and over again and there’s a very different view now about letting young people decide their own fate if they have the cognitive ability, as opposed to doing whatever their parents want done.
SPhD: You’ve had an Appointment at UCLA since 2013 at the Fielding School of Global Health as one of the co-founders of the Global Media Center for Social Impact, with extremely lofty ambitions at the intersection of entertainment, social outreach, technology and public health. Tell me a bit about that partnership and how you decided on an academic appointment at this time in your life.
NB: Well, I’m still doing TV. I just finished a three-year stint running the CBS series Under the Dome, which was a small-scale parable about global climate change. While I was doing that, I took this adjunct professorship at UCLA because I felt that there’s a lot we don’t know about how people take stories, learn them, use them, and I wanted to understand that more. I wanted to have a base to do more work in this area of understanding how storytelling can promote public health, both domestically and globally. Our mission at the Global Media Center for Social Impact (GMI) is to draw on both traditional storytelling modes like film, documentaries, music, and innovative or ‘new’ or transmedia approaches like Facebook, Twitter, Instagram, graphic novels and even cell phones to promote and tell stories that engage and inspire people and that can make a difference in their lives.
SPhD: One of the first major initiatives is a very important book “Soda Politics” by the public health food expert Dr. Marion Nestle. You were actually partially responsible for convincing her to write this book. Why this topic and why is it so critical right now?
NB: I went to Marion Nestle because I was convinced after having read a number of studies, particularly those by Kelly Brownell (who is now Dean of Public Policy at Duke University), that sugar-sweetened sodas are the number one contributor to childhood obesity. Just [recently], in the New York Times, they chronicled a new study that showed that obesity is still on the rise. That entails horrible costs, both emotionally and physically for individuals across this country. It’s very expensive to treat Type II diabetes, and it has terrible consequences – retinal blindness, kidney failure and heart disease. So, I was very concerned about this issue, seeing large numbers of kids coming into Children’s Hospital with Type II diabetes when I was a resident, which we had never seen before. I told Marion Nestle about my concerns because I know she’s always been an advocate for reducing the intake and consumption of soda, so I got [her] research funds from the Robert Wood Johnson Foundation. What’s really interesting is the data on soda consumption really aren’t readily available and you have to pay for it. The USDA used to provide it, but advocates for the soda industry pushed to not make that data easily available. I [also] helped design an e-book, with over 50 actionable steps that you can take to take soda out of the home, schools and community.
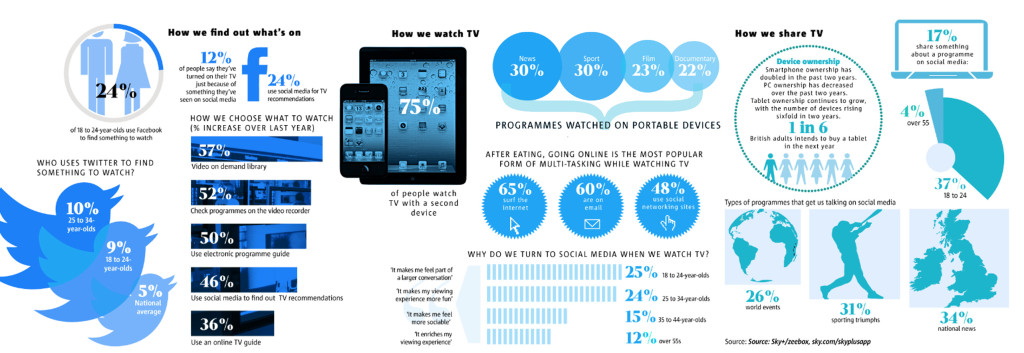
SPhD: How has social media engagement via our phones and computers, directly alongside television watching, changed the metric for viewing popularity, content development and key outreach issues that you’re tackling with your ActionLab initiative?
NB: ActionLab does what we weren’t [previously] able to do, because we have the web platforms now to direct people in multi-directional ways. When I first started on ER in 1994, television and media were uni-directional endeavors. We provided the content, and the viewer consumed it. Now, with Twitter [as an example], we’ve moved from a uni-directional to a multi-directional approach. People are responding, we are responding back to them as the content creators, they’re giving us ideas, they’re telling us what they like, what they don’t like, what works, what doesn’t. And it’s reshaping the content, so it’s this very dynamic process now that didn’t exist in the past. We were really sheltered from public opinion. Now, public opinion can drive what we do and we have to be very careful to put on some filters, because we can’t listen to every single thing that is said, of course. But we do look at what people are saying and we do connect with them in ways they never had access to us before.

This multi-directional approach is not just actors and writers and directors discussing their work on social media, but it’s using all of the tools of the internet to build a new way of storytelling. Now, anyone can do their own shows and it’s very inexpensive. There are all kinds of YouTube shows on now that are watched by many people. It’s a kind of Wild West, where anything goes and I think that’s very exciting. It’s changed the whole world of how we consume media. I [wrote] an episode of ER 20 years ago with George Clooney, where he saved a young boy in a water tunnel, that was watched by 48 million people at once. One out of six Americans. That will never happen again. So, we had a different kind of impact. But now, the media landscape is fractured, and we don’t have anywhere near that kind of audience, and we never will again. It’s a much more democratic and open world than it used to be, and I don’t even think we know what the repercussions of that will be.
SPhD: If you had a wish list, what are some other issues or global obstacles that you’d love to see the entertainment world (and media) tackle more than they do?
NB: In terms of specifics, we really need to talk about civic engagement, and we need to tell stories about how [it] can change the world, not only in micro-ways, say like Habitat For Humanity or programs that make us feel better when we do something to help others, but in a macro policy-driven way, like asking how we are going to provide compulsory secondary education around the world, particularly for girls. How do we instate that? How do we take on child marriage and encourage countries, maybe even through economic boycotts, to raise the age of child marriage, a problem that we know places girls in terrible situations, often with no chance of ever making a good living, much less getting out of poverty. So, we need to think both macroly and microly in terms of our storytelling. We need to think about how to use the internet and crowdsourcing for public policy and social change. How can we amalgamate individuals to support [these issues]? We certainly have the tools now, with Facebook, Twitter and Instagram, and our friends and social networks, to spread the word – and a very good way to spread the word is through short stories.
SPhD: You’ve enjoyed a storied career, and achieved the pinnacle of success in two very competitive and difficult industries. What drives Dr. Neal Baer now, at this stage of your life?
NB: Well, I keep thinking about new and innovative ways to use trans media. How do I use graphic novels in Africa to tell the story of HIV and prevention? How do we use cell phones to tell very short stories that can motivate people to go and get tested? Innovative financing to pay for very expensive drugs around the world? So, I’m very much interested in how storytelling gets the word out, because stories don’t just change minds, they change hearts. Stories tickle our emotions in ways that I think we don’t fully understand yet. And I really want to learn more about that. I want to know about what I call the “epigenetics of storytelling.” I’m writing a book about that, looking into research that [uncovers] how stories actually change our brain and how do we use that knowledge to tell better stories.
Neal Baer, MD is a television writer and producer behind hit shows China Beach, ER, Law & Order SVU, Under The Dome, and others. He is a graduate of Harvard University Medical School and completed a pediatrics internship at Children’s Hospital Los Angeles. A former co-chair of USC’s Norman Lear Center Hollywood, Health and Society, Dr. Baer is the founder of the Global Media Center for Social Impact at the Fielding School of Global Health at UCLA.
*****************
ScriptPhD.com covers science and technology in entertainment, media and advertising. Hire our consulting company for creative content development. Follow us on Twitter and Facebook. Subscribe to our podcast on SoundCloud or iTunes.

On February 28, 1998, the revered British medical journal The Lancet published a brief paper by then-high profile but controversial gastroenterologist Andrew Wakefield that claimed to have linked the MMR (measles, mumps and rubella) vaccine with regressive autism and inflammation of the colon in a small case number of children. A subsequent paper published four years later claimed to have isolated the strain of attenuated measles virus used in the MMR vaccine in the colons of autistic children through a polymerase chain reaction (PCR amplification). The effect on vaccination rates in the UK was immediate, with MMR vaccinations reaching a record low in 2003/2004, and parts of London losing herd immunity with vaccination rates of 62%. 15 American states currently have immunization rates below the recommended 90% threshold. Wakefield was eventually exposed as a scientific fraud and an opportunist trying to cash in on people’s fears with ‘alternative clinics’ and pre-planned a ‘safe’ vaccine of his own before the Lancet paper was ever published. Even the 12 children in his study turned out to have been selectively referred by parents convinced of a link between the MMR vaccine and their children’s autism. The original Lancet paper was retracted and Wakefield was stripped of his medical license. By that point, irreparable damage had been done that may take decades to reverse.
How could a single fraudulent scientific paper, unable to be replicated or validated by the medical community, cause such widespread panic? How could it influence legions of otherwise rational parents to not vaccinate their children against devastating, preventable diseases, at a cost of millions of dollars in treatment and worse yet, unnecessary child fatalities? And why, despite all evidence to the contrary, have people remained adamant in their beliefs that vaccines are responsible for harming otherwise healthy children, whether through autism or other insidious side effects? In his brilliant, timely, meticulously-researched book The Panic Virus, author Seth Mnookin disseminates the aggregate effect of media coverage, echo chamber information exchange, cognitive biases and the desperate anguish of autism parents as fuel for the recent anti-vaccine movement. In doing so, he retraces the triumphs and missteps in the history of vaccines, examines the social impact of rejecting the scientific method in a more broad perspective, and ways that this current utterly preventable public health crisis can be avoided in future scenarios. A review of The Panic Virus, an enthusiastic ScriptPhD.com Editor’s Selection, follows below.

Such fervent controversy over inoculating young children for communicable diseases might have seemed unimaginable to the pre-vaccine generations. It wasn’t long ago, Mnookin chronicles, that death and suffering at the hands of diseases like polio and small pox were the accepted norm. In 18th Century Europe, for example, 400,000 people per year regularly died of small pox, and it caused one third of all cases of blindness. So desperate were people to avoid the illnesses’ ravages, that crude, rudimentary inoculation methods were employed, even at the high risk of death, to achieve life-long immunity. A 1916 polio outbreak in New York City, with fatality rates between 20 and 25 percent, frayed nerves and public health infrastructure to the point of near-anarchy. As the disease waxed and waned in outbreaks throughout the decades that followed, distraught parents had no idea about how to protect their children, who were often far more susceptible to fatality than adults. By the time Jonas Salk’s polio vaccine breakthrough was announced as “safe, effective and potent” on April 12, 1955, pandemonium broke out. “Air raid sirens were set off,” Mnookin writes. “Traffic lights blinked red; churches’ bells rang; grown men and women wept; schoolchildren observed a moment of silence.” Salk’s discovery was hailed as “one of the greatest events in the history of medicine.”

Mnookin doesn’t let scientists off the hook where vaccines are concerned, however, and rightfully so. Starting around World War II, with advances such as the cowpox and polio vaccines, along with the dawning of the Antibiotics Age, eradicating death and suffering from communicable diseases and bacterial infections, a hubris and sense of superiority began to creep into the scientific establishment, with dangerous consequences. Fearing the threat of biological warfare during World War II, a 1941 hastily-constructed US military campaign to vaccinate all US troops against yellow fever resulted in batches contaminated with Hepatitis B, resulting in 300,000 infections and 60 deaths. The first iteration of Salk’s polio vaccine was only 60-90% effective before being perfected and eventually replaced by the more effective Sabin vaccine. Furthermore, dozens of children who had received doses from the first batch of vaccines were paralyzed or killed due to contaminated vaccines that had failed safety tests. In 1976, buoyed by the death of a soldier from a flu virus that bore striking genetic similarity to the 1918 Spanish flu epidemic strain, President Gerald Ford instituted a nation-wide mass vaccination initiative against a “swine flu” epidemic. Unfortunately, although 40 million Americans were vaccinated in three months, 500 developed symptoms of Guillain-Barré syndrome (30 died), seven times higher than would normally be expected as a rare side effect of vaccination. Many people feel that the scars of the 1976 fiasco have incurred a permanent distrust of the medical establishment and have haunted public health influenza immunization efforts to this day.
These black marks on the otherwise miraculous, life-saving history of vaccine development not only instilled a gradual mistrust in public health officials, but laid the groundwork for the incendiary autism-vaccine scandal. The only missing components were a proper context of panic, a snake oil salesman and a compliant media willing to spread his erroneous message.
Enter the autism epidemic and Andrew Wakefield’s hoax. Because this seminal event had such a profound effect on the formation and proliferation of the current anti-vaccine movement, it is chronicled in far greater detail than our introduction above. From precursor incidents that ripened the potential for coercion to the Wakefield’s shoddy methodology and the naive medical community that took him at his word, Mnookin weaves through this case with well-researched scientific facts, interesting interviews and logic. A large chunk of the book is ultimately devoted to the psychology of what the anti-vaccine movement really is: a cognitive bias and a willingness to stay adamant in the belief that vaccines cause harm despite all evidence to the contrary. “If you assume,” he writes, “as I had, that human beings are fundamentally logical creatures, this obsessive preoccupation with a theory that has for all intents and purposes been disproved is hard to fathom. But when it comes to decisions around emotionally charged topics, logic often takes a back seat to a set of unconscious mechanisms that convince us that it is our feelings about a situation and not the facts that represent the truth.”
Given this blog’s objective to cover science and technology in entertainment and media, it would be disingenuous to write about the anti-vaccine movement without recognizing the implicit role played by the media and entertainment industries in exacerbating the polemic. By lending a voice to the anti-vaccine argument, even in a subtle manner or in a journalistic attempt to “be fair to the other side,” over time, an echo chamber of lies turned into an inferno. In 1982, an hour-long NBC documentary called DPT: Vaccine Roulette aired, overemphasizing rare side effects in babies from vaccinations to a nation of alarmed parents and completely undermining their benefits. It was a propaganda piece, but an important hallmark for what would come later. A 2008 episode of the popular ABC hit show Eli Stone irresponsibly aired anti-vaccination propaganda involving a lawyer questioning a pharmaceutical company that manufactures vaccines due to the even then-debunked link to autism. For several recent years, actress and Playboy bunny Jenny McCarthy (who is given an entire chapter by Mnookin) became a tireless advocate against vaccinations, believing that they gave her son autism. She didn’t have any scientific proof for this, but was nevertheless given a platform by everyone from Larry King on CNN to a fawning Oprah Winfrey.

As it turns out, McCarthy’s son never even had autism, but rather a very rare and treatable neurological disorder. In a self-penned editorial for the Chicago Sun-Times, she has officially retroactively denied her anti-vaccine stance, and says she simply wants “more research on their effectiveness.” An extremely sympathetic 2014 eight-page Washington Post magazine article profile of prominent anti-vaccine activist Robert F. Kennedy, Jr. (who believes in the link between vaccines and autism) repeated his talking points numerous times throughout. This, among an endless cycle of interviews and appearances by defiant anti-vaccine proponents, given equal air time side-by-side with frustrated scientists, as if both positions were somehow viable, and worthy of journalistic debate. Once the worm was out of the can, no amount of rational discourse could temper the visceral antipathy that had been created. This is irresponsible, dangerous and flat-out wrong. When the public is confused about an esoteric issue pertaining to science, medicine or technology, influencers in the public eye cannot perpetuate misinformation.
Despite the unanimous medical repudiation of Wakefield’s fraudulent methods and conclusions and the retraction of his Lancet paper, an irreversible and insidious myth had begun permeating, first among the autism community, then spreading to proponents of organic and holistic approaches to health and finally, to mainstream society. In the aftermath of the controversy, epidemiological studies debunking the autism-vaccination “link,” combined with a growing disease crisis, have forced the largest US-based autism advocacy organization to reverse its stance and fully endorse vaccination to a still-divided community. Wakefield remains more defiant than ever, insisting to this day that his research was valid, attempting to sue the British journalism outlet that funded the inquiry into his fraud and peddling holistic treatments for autism as well as his “alternative” vaccine. Sadly, the public health ramifications have nothing short of disastrous, with a dangerous recurrence of several major childhood diseases.
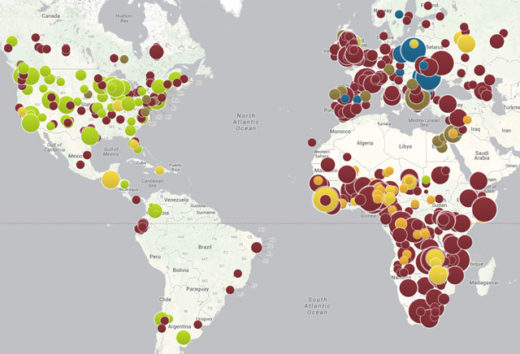
A few examples of the many systemic casualties of the anti-vaccination movement (many occurring just since the publication of Mnookin’s book):
•A summary from the American Medical Association about the nascence of the measles crisis in 2011, when the US saw more measles cases than it had in 15 years
•Immunization rates falling so low that schools in some communities are being forced to terminate personal exemption waivers and, in some cases, legally mandated immunization for public school attendance
•California’s worst whooping cough epidemic in 70 years.
•Most recently, a measles outbreak at Disneyland, resulting in 26 cases spread across four states, after an unvaccinated woman visited the theme park
•Anti-vaccine hysteria has spread to Europe, which has had a measles rise of 348% from 2013 to 2014 (and growing), along with an alarming resurgence of pertussis
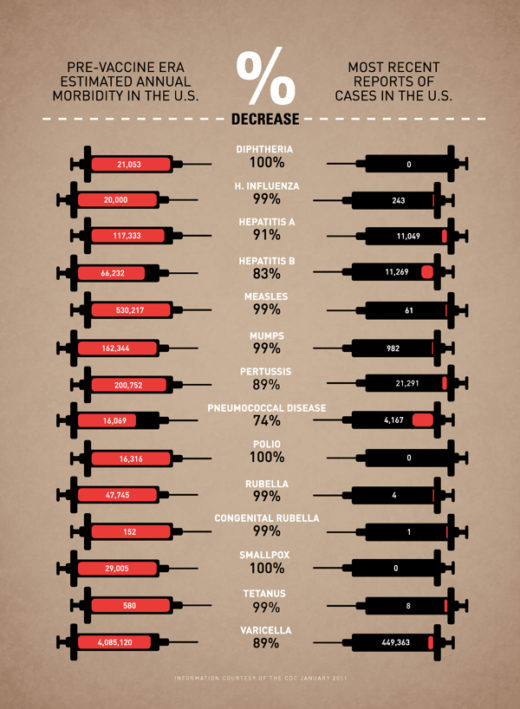
The scientific evidence that vaccines work is indisputable, and as the below infographic summarizes, their impact on morbidity from communicable diseases is miraculous. Sadly, now that the anti-vaccine movement has streamlined into the general population, anxious parents are conflicted as to whether vaccinating is the right choice for their children. We must start by going back to the basics of what a vaccine actually is and how it works. Next, we must reiterate the critical importance that maintaining herd immunity above 92-95% plays in protecting not only those too young or immunocompromised to be vaccinated, but even fully vaccinated populations. If all else fails, try emailing skeptical friends and family a clever graphic cartoon that breaks down digestible vaccine facts. Simply put: getting vaccinated is not a personal choice, it’s a selfish and dangerous choice.
The Panic Virus is first and foremost an incredibly entertaining, well-written narrative of the dawn of an anti-vaccine phenomenon which has reached a critical mass. It is also an important case study and cautionary tale about how we process and disseminate information in the age of the Internet and access to instant information. It is also an indictment on a trigger-happy, ratings-driven, sensationalist media that reports “news” as they interpret it first, and bother to check for facts later. In the case of the anti-vaccine movement of the last few years, the media fueled the fire that Andrew Wakefield started, and once a gaggle of angry, sympathetic parents was released, it was difficult (if-near impossible) to undo the damage. This type of journalism, Mnookin writes, “gives credence to the belief that we can intuit our way through all the various decisions we need to make in our lives and it validates the notion that our feelings are a more reliable barometer of reality than the facts.” Sadly, the autism-vaccine panic movement is not an outlying incident, but rather a disconcerting emblem of a growing anti-science agenda. The UN just released its most dire and alarming report ever issued on man-made climate change impacts, warning that temperature changes and industrial pollution will affect not just the environment, extreme weather events and coastal cities, but even the stability of our global economy itself. Immediate rebuttals from an influential lobbying group tried to undermine the majority of the scientists’ findings. So toxic is the corporate and political resistance to any kind of mitigating action, that some feel we need a technological or political miracle to stave off a certain environmental crisis. At a time when physicists are serious debate on evolution versus creationism and thousands of public schools across the United States use taxpayer funds to teach creationism in the classroom.
Mnookin’s book is an important resource and conversation starter for scientists, researchers and frustrated physicians as they carve out talking points and communication strategies to establish a dialogue with the public at large. When young parents have questions about vaccines (no matter how erroneous or ill-informed), pediatricians should already have materials for engaging in a positive, thoughtful discussion with them. When scientists and researchers encounter anti-science proclivities or subversive efforts to undermine their advocacy for a pressing issue, they should be armed with powerful, articulate communicators — ready and willing to deliberate in the media and convey factual information in an accessible way. When Jenny McCarthy and a gaggle of new-age holistic herbologists were peddling their “mommy instincts” and conspiracy theories against vaccines, far too many scientists and physicians simply thought it was beneath them to even engage in a discussion about something whose certainty and proof of concept was beyond reproach. Now, the newest polling suggests that nothing will change an anti-vaxxer’s mind, not even factual reasoning. Going forward, regardless of the issue at hand, this type of response can never happen again. The cost of complacency or arrogance is nothing short of life or death.
The Panic Virus by Seth Mnookin is currently available on paperback and Kindle wherever books are sold. For further reading on how to deal with the complexities of the anti-vaccine movement aftermath, we suggest the recent book On Immunity: An Inoculation by Northwestern University lecturer Eula Bliss.
*****************
ScriptPhD.com covers science and technology in entertainment, media and advertising. Hire our consulting company for creative content development. Follow us on Twitter and Facebook. Subscribe to our podcast on SoundCloud or iTunes.

Every July, hundreds of thousands of fans descend upon the city of San Diego for a four-day celebration of comics, sci-fi, popular arts fandom and (growingly) previews of mainstream television and film blockbusters. What is this spectacular nexus of nerds? Comic-Con International, of course! From ScriptPhD’s comprehensive past coverage, one can easily glean the diversity of events, guests and panels, with enormous throngs patiently queueing to see their favorites. But who are these fans? Where do they come from? What kinds of passions drive their journeys to Comic-Con from all over the world? And what microcosms are categorized under the general umbrella of fandom? Award-winning filmmaker Morgan Spurlock attempts to answer these questions by crafting the sweet, intimate, honest documentary-as-ethnography Comic-Con Episode IV: A Fan’s Hope. Through the archetypes of five 2009 Comic-Con attendees, Spurlock guides us through the history of the Con, its growth (and the subsequent conflicts that this has engendered), and most importantly, the conclusion that underneath all of those Spider-Man and Klingon costumes, geeks really do come in all shapes, colors and sizes. For full ScriptPhD review, click “continue reading.”
In 1970, comics fan Shel Dorf organized a three-day gathering in San Diego at the US Grant hotel as a fringe gathering for the most enthusiastic amateur comics fans, aspiring artists and writers to interact with comics pros. It drew 300 fans. This was the backdrop against which young Morgan Spurlock grew up in West Virginia, passionately consuming comics and horror films, transported to a different world where everyone was a little bit askew and “weird.” “I wasn’t just a fan,” Spurlock remarks. “I was addicted.” It wasn’t until 2009 that he was able to make his first amateur journey to Comic-Con International San Diego, by now a cultural juggernaut regularly drawing over 150,000 fans, amid a vastly changed (and comics-cultural) landscape. Nevertheless, Spurlock was thrilled. He ran into boyhood idol Marvel animator Stan Lee, and thanked him for all the confidence and creativity he helped to inspire. Stan’s response? “Let’s make a documentary about Comic-Con!” And so, gathering forces with Lee, sci-fi cult icon Joss Whedon, among others, Spurlock embarked on a two-year journey that captured the 2010 Con (the 40th Anniversary edition) in all its glory—including panels, parades, photos, costumes and interviews with notable celebrities that have turned passions into professions. Most of all, however, Spurlock captured the fans.

To winnow down the most compelling stories for the documentary, Spurlock held a casting call online that drew thousands of submissions. Among them was Holly Conrad, a talented, award-winning costume designer from a small town hoping to win the grand prize at the annual Comic-Con costume show. Knowing her slim odds, especially because of where she comes from, and the importance of making a splash for her career to take off, Holly called Comic-Con a “suicide mission for her future.” Also in a pressure cooker was Chuck Rozanski, proprietor of Mile High Comics, Americas largest inventory and dealer of comic books. Chuck uses the hectic, chaotic, crowded Comic-Con exhibit area to sell rare and collectible comics, comprising a substantial portion of his company’s income for the year, but faces a more fractured Con, with a smaller focus on comics every year. If he doesn’t make a killing at this year’s Com, Chuck knows the future of his whole business might be at risk. Sharing the convention floor with Chuck are comics-obsessed bartender Skip Harvey and US Airforce pilot and family man Eric Henson, two amateur graphic artists also putting their destiny on the line in San Diego. Armed with only a portfolio and a dream, Eric and Skip are hoping to get noticed at the portfolio critique sessions and land a professional design contract with one of the comics representatives. One succeeds (to the preview audience’s delight) and one learns he is a very big fish in a very small bowl, and must cultivate his talent for the greater stage. Intermingled for comic relief is the adorable story of James Darling and Se Young Kang, a couple who met and started dating at the previous year’s Con. James is planning to ask Se Young to marry him at this year’s Con, but must overcome a slew of hilarious obstacles to pull of his nerdy romantic feat.

Comic-Con Episode IV: A Fan’s Hope is a terrific purview into the conflicts and dissent of the modern Con. Hidden beneath the popularity of the yearly event is a schism between older fans who have been coming for years (and feel somewhat lost in the shuffle) and the new fans, such as lovebirds James and Se Young, who may not even necessarily be there for comics events. Longtime attendees such as Kevin Smith admitted that the event has become a “beancounter” with tremendous power to preview movies and television, something Hollywood has noticed and latched onto. One can legitimately forget the presence of comics and the graphic arts at Comic-Con altogether without trying very hard. This presents a huge problem for the poignant storyline of Chuck Rozanski, with whom we empathize as he struggles to sell comics through 4-day event. When ScriptPhD.com asked Spurlock at a recent Los Angeles junket about what surprised him the most, he pointed to the sheer volume of what goes on at Comic-Con, especially the job-hunting aspect of the Comic-Con exhibition floor. His favorite moment in the movie is the comparison of Comic-Con to a Russian nesting doll, with events hidden beneath other events. “I showed the movie to people and they responded that they didn’t even know that went on at Comic-Con! There is something for everyone, no matter what your passion.” Spurlock remarked.
The documentary is at its strongest and most successful when the focus turns to what the essence of what Comic-Con is defined by—the fans. “We all weighed in with what we thought were the most important pieces of the story,” Spurlock says. “But in the end it all came back to the fans.” It is the fans whose enthusiasm drives the growth of events like Comic-Con, however much nostalgia for the past may feel threatened. It is the fans whose passion continues to motivate and drive geniuses like Stan Lee to this very day. That very same passion also launches new careers, as Holly Conrad found. Since the filming of this documentary, she has moved to Hollywood and found successful work as a costume designer on several productions. Lastly, and most importantly, it is the fans who create that magical atmosphere where no matter who you are, where you come from, what you look like, how “out there” you behave, you find total acceptance and camaraderie amongst a group of treasured friends just as passionate and devoted as you are. To Spurlock, the Con “reminds us all of the importance of dreams and of wonder. It’s not just an event… it’s a state of mind.”
Trailer for Comic-Con Episode IV: A Fan’s Hope:
“Making of” featurette:
Comic-Con Episode IV: A Fan’s Hope was released in select cities on April 5, and theaters and video on demand on April 6th.
~*ScriptPhD*~
*****************
ScriptPhD.com covers science and technology in entertainment, media and advertising. Hire our consulting company for creative content development.
Subscribe to free email notifications of new posts on our home page.
]]>
Read through any archive of science fiction movies, and you quickly realize that the merger of pop culture and science dates as far back as the dawn of cinema in the early 1920s. Even more surprising than the enduring prevalence of science in film is that the relationship between film directors, scribes and the science advisors that have influenced their works is equally as rich and timeless. Lab Coats in Hollywood: Science, Scientists, and Cinema (2011, MIT Press), one of the most in-depth books on the intersection of science and Hollywood to date, serves as the backdrop for recounting the history of science and technology in film, how it influenced real-world research and the scientists that contributed their ideas to improve the cinematic realism of science and scientists. For a full ScriptPhD.com review and in-depth extended discussion of science advising in the film industry, please click the “continue reading” cut.
Written by David A. Kirby, Lecturer in Science Communication Studies at the Centre for History of Science, Technology and Medicine at the University of Manchester, England, Lab Coats offers a surprising, detailed analysis of the symbiotic—if sometimes contentious—partnership between filmmakers and scientists. This includes the wide-ranging services science advisors can be asked to provide to members of a film’s production staff, how these ideas are subsequently incorporated into the film, and why the depiction of scientists in film carries such enormous real-world consequences. Thorough, detailed, and honest, Lab Coats in Hollywood is an exhaustive tome of the history of scientists’ impact on cinema and storytelling. It’s also an essential and realistic road map of the challenges that scientists, engineers and other technical advisors might face as they seriously pursue science advising to the film industry as a career.
The essential questions that Lab Coats in Hollywood addresses are these—is it worth it to hire a science advisor for a movie production? Is it worth it for the scientist to be an advisor? The book’s purposefully vague conclusion is that it depends solely on how the scientist can film’s storyline and visual effects. Kirby wisely writes with an objective tone here because the topic is open to a considerable amount of debate among the scientists and filmmakers profiled in the book. Sometimes a scientist is so key to a film’s development, he or she becomes an indispensible part of the day-to-day production. A good example of this is Jack Horner, paleontologist at the Museum of the Rockies in Bozeman, MT, and technical science advisor to Steven Spielberg in Jurassic Park and both of its sequels. Horner, who drew from his own research on the link between dinosaurs and birds for a more realistic depiction of the film’s contentious science, helped filmmakers construct visuals, write dialogue, character reactions, animal behaviors, and map out entire scenes. J. Marvin Herndon, a geophysicist at the Transdyne Corporation, approached the director of the disaster film The Core when he learned the plot was going to be based on his controversial hypothesis about a giant uranium ball in the center of the Earth. Herndon’s ideas were fully incorporated into the film’s plot, while Herndon rode the wave of publicity from the film to publish his research in a PNAS paper. The gold standard of science input, however, were Stanley Kubrik’s multiple science and engineering advisors for 2001: A Space Odyssey, discussed in much further detail below.

Kirby hypothesizes that sometimes, a film’s poor reception might have been avoided with a science advisor. He provides the example of the Arnold Schwarzenegger futuristic sci-fi bomb The Sixth Day, which contained a ludicrously implausible use of human cloning in its main plot. While the film may have been destined for failure, Kirby posits that it only could have benefited from proper script vetting by a scientist. By contrast, the 1998 action adventure thriller Armageddon came under heavy expert criticism for its basic assertion that an asteroid “the size of Texas” could go undetected until eighteen days before impact. Director Michael Bay patently refused to take the advice of his advisor, NASA researcher Ivan Bakey, and admitted he was sacrificing science for plot, but Armageddon went on to be a huge box office hit regardless. Quite often, the presence of a science advisor is helpful, albeit unnecessary. One of the book’s more amusing anecdotes is about Dustin Hoffman’s hyper-obsessive shadowing of a scientist for the making of the pandemic thriller Outbreak (great guide to the movie’s science can be found here). Hoffman was preparing to play a virologist and wanted to infuse realism in all of his character’s reactions. Hoffman kept asking the scientist to document reactions in mundane situations that we all encounter—a traffic jam, for example—only to come to the shocking conclusion that the scientist was a real person just like everyone else.
Most of the time, including scientists in the filmmaking process is at the discretion of the studios because of the one immutable decree reiterated throughout the book: the story is king. When a writer, producer or director hires a science consultant, their expertise is utilized solely to facilitate, improve or augment story elements for the purposes of entertaining the audience. Because of this, one of the most difficult adjustments a science consultant may face is a secondary status on-set even though they may be a superstar in their own field. Some of the other less glamorous aspects of film consulting include heavy negotiations with unionized writers for script or storyline changes, long working hours, a delicate balance between side consulting work and a day job, and most importantly, an inconsistent (sometimes nonexistent) payment structure per project. I was notably thrilled to see Kirby mention the pros and cons of programs such as the National Science Foundation’s Creative Science Studio (a collaboration with USC’s school of the Cinematic Arts) and the National Academy of Science’s Science and Entertainment Exchange, which both provide on-demand scientific expertise to the Hollywood filmmaking community in the hope of increasing and promoting the realism of scientific portrayal in film. While valuable commodities to science communication, both programs have had the unfortunate effect of acclimating Hollywood studios to expect high-level scientific consulting for free.
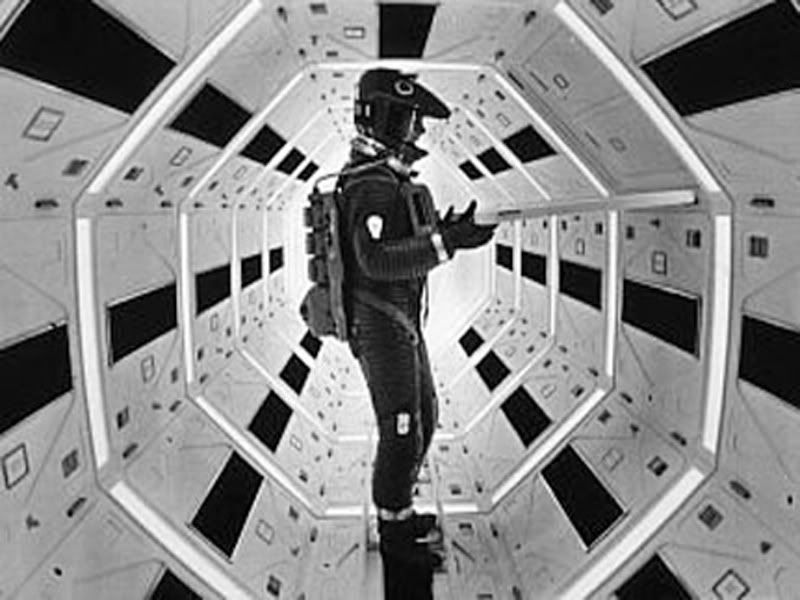

1968’s 2001: A Space Odyssey is widely considered by popular consensus to be the greatest sci-fi movie ever made, and certainly the most influential. As such, Kirby devotes an entire chapter to detailing the film’s production and integration of science. Director Stanley Kubrik took painstaking detail in scientific accuracy to explore complex ideas about the relationship between humanity and technology, hiring a range of advisors from anthropologists, aeronautical engineers, statisticians, and nuclear physicists for various stages of production. Statistician I. J. Good provided advice on supercomputers, aerospace Harry Lange provided production design, while NASA space scientist Frederick Ordway lent over three years of his time to develop the space technology used in the film. In doing so, Kubrik’s staff consulted with over sixty-five different private companies, government agencies, university groups and research institutions. So real was the space technology in 2001 that moon landing hoax supporters have claimed the real moon landing by United States astronauts, taking place in 1969, was taped on the same sets. Not every science-based film has used science input as meticulously or thoroughly since, but Kubrik’s influence on the film industry’s fascination with science and technology has been an undeniable legacy.
One of the real treats of Lab Coats in Hollywood is the exploration of the two-way relationship between scientists and filmmakers, and how film in turn influences the course of science, as we discuss in more detail below. Between film case studies, critiques and interviews with past science advisors are interstitial vignettes of ways scientists have shaped films we know and love. Even the animated feature Finding Nemo had an oceanography advisor to get the marine biology correct. The seminal moment of the most recent Star Trek installation was due to a piece of off-handed scientific advice from an astronomer. The cloning science of Jurassic Park, so thoroughly researched and pieced together by director Steven Spielberg and science advisor Jack Horner, was actually published in a top-notch journal days ahead of the movie’s premiere. Even in rare spots where the book drags a bit with highly technical analysis are cinematic backstories with details that readers will salivate over. (For example, there’s a very good reason all the kelp went missing from Finding Nemo between its cinematic and DVD releases.)
As the director of a creative scientific consulting company based in Los Angeles, one of the biggest questions I get asked on a regular basis is “What does a science advisor do, exactly?” Lab Coats in Hollywood does an excellent job of recounting stories and case studies of high-profile scientist consultants, all of whom contributed their creative talents to their respective films in different ways, what might be expected (and not expected) of scientists on set, and of giving different areas of expertise that are currently in demand in Hollywood. Kirby breaks down cinematic fact checking, the most frequent task scientists are hired to perform, into three areas within textbook science (known, proven facts that cannot be disputed, such as gravity): public science, something we all know and would think was ridiculous if filmmakers got wrong, expert science, facts that are known to specialists and scientific experts outside of the lay audience, and (most problematic) folk science, incorrect science that has nevertheless been accepted as true by the public. Filmmakers are most likely to alter or modify facts that they perceive as expert science to minimize repercussions at the box office.

A science advisor is constantly navigating cinematic storytelling constraints and a filmmaker’s desire to utilize only the most visually appealing and interesting aspects of science (regardless of whether the context is always academically appropriate). Another broad area of high demand is in helping actors look and act like a real scientist on screen. Scientists have been hired to do everything from doctoring dialogue to add realism into an actor’s portrayal (the movie Contact and Jodie Foster’s depiction of Dr. Ellie Arroway is a good example of this), training actors in using equipment and pronouncing foreign-sounding jargon, replicating laboratory notebooks or chalkboard scribbles with the symbols and shorthand of science (such as in the mathematics film A Beautiful Mind), and to recreate the physical space of an authentic laboratory. Finally, the scientist’s expertise of the known is used to help construct plausible scenarios and storylines for the speculative, an area that requires the greatest degree of flexibility and compromise from the science advisor. Uncertainty, unexplored research and “what if” scenarios, the bane of every scientist’s existence, happen to be Hollywood’s favorite scenarios, because they allow the greatest creative freedom in storytelling and speculative conceptualization without being negated by a proven scientific impossibility. An entire chapter—the book’s finest—is devoted to two case studies, Deep Impact and The Hulk, where real science concepts (near-Earth asteroid impacts and genetic engineering, respectively) were researched and integrated into the stories that unfolded in the films. (Side note: if you are ever planning on being a science advisor read this section of the book very carefully).
In years past, consulting in films didn’t necessarily bring acclaim to scientists within their own research communities; indeed, Lab Coats recounts many instances where scientists were viewed as betraying science or undermining its seriousness with Hollywood frivolity, including many popular media figures such as Carl Sagan and Paul Ehrlich. Recently, however, consultants have come to be viewed as publicity investments both by studios that hire high-profile researchers for recognition value of their film’s science content and by institutes that benefit from branding and exposure. Science films from the last 10-15 years such as GATTACA, Outbreak, Armageddon, Contact, The Day After Tomorrow and a panoply of space-related flicks have attached big-name scientists as consultants (gene therapy pioneer French Anderson, epidemiologist David Morens, NASA director Ivan Bekey, SETI institute astronomers Seth Shostak and Jill Tartar and climatologist Michael Molitor, respectively). They also happened to revolve around the research salient to our modern era: genetic bioengineering, global infectious diseases, near-earth objects, global warming and (as always) exploring deep space. As such, a mutually beneficial marketing relationship has emerged between science advisors and studios that transcends the film itself resulting in funding and visibility to individual scientists, their research, and even institutes and research centers. The National Severe Storms Laboratory (NSSL) promoted themselves in two recent films, Twister and Dante’s Peak, using the films as a vehicle to promote their scientific work, to brand themselves as heroes underfunded by the government, and to temper public expectations about storm predictions. No institute has had a deeper relationship with Hollywood than NASA, extending back to the Star Trek television series, with intricate involvement and prominent logo display in the films Apollo 13, Armageddon, Mission to Mars, and Space Cowboys. Some critics have argued that this relationship played an integral role in helping NASA maintain a positive public profile after the devastating 1986 Challenger space shuttle disaster. The end result of the aforementioned promotion via cinematic integration can only benefit scientific innovation and public support.

Accurate and favorable portrayal of science content in modern cinema has an even bigger beneficiary than specific research institutes, and that is society itself. Fictional technology portrayed in film – termed a “diegetic prototype” – has often inspired or led directly to real-world application and development. Kirby offers the most impactful case of diegetic prototyping as the 1981 film Threshold, which portrayed the first successful implantation of a permanent artificial heart, a medical marvel that became reality only a year later. Robert Jarvik, inventor of the Jarvik-7 artificial heart used in the transplant, was also a key medical advisor for Threshold, and felt that his participation in the film could both facilitate technological realism and by doing so, help ease public fears about what was then considered a freak surgery, even engendering a ban in Great Britain. Of the many obstacles that expensive, ambitious, large-scale research faces, Kirby argues that skepticism or lack of enthusiasm from the public can be the most difficult to overcome, precisely because it feeds directly into essential political support that makes funding possible. A later example of film as an avenue for promotion of futuristic technology is Minority Report, set in the year 2054, and featuring realistic gestural interfacing technology and visual analytics software used to predict crime before it actually happens. Less than a decade later, technology and gadgets featured in the film have come to fruition in the form of multi-touch interfaces like the iPad and retina scanners, with others in development including insect robots (mimics of the film’s spider robots), facial recognition advertising billboards, crime prediction software and electronic paper. A much more recent example not featured in the book is the 2011 film Limitless, featuring a writer that is able to stimulate and access 100% of his brain at will by taking a nootropic drug. While the fictitious drug portrayed in the film is not yet a neurochemical reality, brain enhancement is a rising field of biomedical research, and may one day indeed yield a brain-boosting pill.
No other scientific feat has been a bigger beneficiary of diegetic prototyping than space travel, starting with 1929’s prophetic masterpiece Frau im Mond [Woman in the Moon], sponsored by the German Rocket Society and advised masterfully by Hermann Oberth, a pioneering German rocket research scientist. The first film to ever present the basics of rocket travel in cinema, and credited with the now-standard countdown to zero before launch in real life, Frau im Mond also featured a prototype of the liquid-fuel rocket and inspired a generation of physicists to contribute to the eventual realization of space travel. Destination Moon, a 1950 American sci-fi film about a privately financed trip to the Moon, was the first film produced in the United States to deal realistically with the prospect of space travel by utilizing the technical and screenplay input of notable science fiction author Robert A. Heinlein. Released seven years before the start of the USSR Sputnik program, Destination Moon set off a wave of iconic space films and television shows such as When Worlds Collide, Red Planet Mars, Conquest of Space and Star Trek in the midst of the 1950s and 1960s Cold War “space race” between the United States and Russia. What theoretical scientific feat will propel the next diegetic prototype? A mission to Mars? Space colonization? Anti-aging research? Advanced stem cell research? Time will only tell.
Ultimately, readers will enjoy Lab Coats in Hollywood for its engaging writing style, detailed exploration of the history of science in film and most of all, valuable advice from fellow scientists who transitioned from the lab to consulting on a movie set. Whether you are a sci-fi film buff or a research scientist aspiring to be a Hollywood consultant, you will find some aspect of this book fascinating. Especially given the rapid proliferation of science and technology content in movies (even those outside of the traditional sci-fi genre), and the input from the scientific community that it will surely necessitate, knowing the benefits and pitfalls of this increasingly in-demand career choice is as important as its significance in ensuring accurate portrayal of scientists to the general public.
~*ScriptPhD*~
***************
ScriptPhD.com covers science and technology in entertainment, media and advertising. Hire our consulting company for creative content development.
Subscribe to free email notifications of new posts on our home page.
]]>
Battlestar Galactica is one of the defining, genre-changing science fiction shows of its, or perhaps any, time. The remake of the 1970s cult classic was sexy, sophisticated, and set a new standard for the science fiction shows and movies that will follow in its path. In addition to exploring staple concepts such as life, survival, politics and war, BSG reawakened its audience to science and its role in moral, ethical, and daily impact in our lives, especially given the technologically-driven era that we live in. “Writers were not allowed to jettison science for the sake of the story,” declares co-executive producer Jane Espenson in her foreword to the book. “Other than in specific instances of intentionally inexplicable phenomena, science was respected.” In an artful afterword, Richard Hatch (the original Apollo and Tom Zarek in the new series) concurs. “BSG used science not as a veneer, but as a key thematic component for driving many of the character stories… which is the art of science fiction.” The sustained use of complex, correct science as a plot element to the degree that was done in Battlestar Galactica is also a hallmark first. This is the topic of the new book The Science of Battlestar Galactica, newly released from Wiley Books, and written by Kevin R. Grazier, the very science advisor who consulted with the BSG writing staff on all things science, with a contribution from Wired writer Patrick DiJusto. Now, for the first time, everyone from casual fans to astrophysicists can gain insight into the research used to construct major stories and technology of the show—and learn some very cool science along the way. Our review of The Science of Battlestar Galactica (and our 100th blog post!) under the “continue reading” cut.

What is life? Seriously. I’m not asking one of those hypothetical existential questions that end up discussed ad nauseum in a dorm room at 3 AM. I’m asking the central question that Battlestar Galactica, and much of science fiction, is based around. The shortest section of The Science of Battlestar Galactica, “Life Began Out Here,” is its most poignant. No matter the conflict, subplot or theme explored on BSG, they ultimately reverted back to the idea of what constituted a living being, and what rights, if any, those beings possessed. It all boils down to cylons. What are they made of? How do their brains (potentially) work? How much information can they contain, and how is it processed from one dead cylon to its next incarnation? How could a cylon and a human mate successfully, and is their offspring (Hera Agathon) the Mitochondrial Eve of that society? How did they evolve? What is the biological difference between raiders, centurions, and humanoid cylons? Who can forget the ew gross factor of Boomer plugging her arm into the cylon computer system, but how could she do that, especially when she was made to act, feel and think as a human being? A brief, smart discussion on spontaneous evolution and basic biology gives way to a thoughtful evocation of our own efforts with artificial intelligence, and the responsibilities that it engenders. Take a look at the website of the MIT iGem Program, an annual competition to design biological systems that will operate in living cells from standard toolkits. Do some of their creations, including bacteria that eat industrial pollutants and treat lactose intolerance, constitute life, and are our own Cybernetic Life Nodes not too far away? The section ends in a fascinating debate over who we are more akin to—the humans of the Battlestar universe (as is widely assumed) or cylons. The answer would surprise you.
The middle of The Science of Battlestar Galactica, composed of “The Physics of Battlestar Galactica” and “The Twelve Colonies and The Rest of Space” reads largely like my college physics textbook, only with far cooler sample problems. If Apollo and Starbuck both launch their vipers at the same time and Starbuck coasts past Apollo, according to special relativity, who is moving? In perhaps the greatest implementation of Einstein’s famous theory in science fiction, special relativity explains how Starbuck could explain that she wasn’t a Cylon when she returned unharmed from the dead, and why her viper looked brand new. A special look at radiation particularly interested me, with a chemistry background, as it thoroughly delved into the chemistry and physics of radiation, heat-seeking missile weapons, DNA damage, and the power of nuclear weapons, both with fictional examples (the destruction of Caprica) and real (Japan and Chernobyl). The chapters on relativity (E=mc2) and the Lorentz Contraction reminded me of a seminar on dark energy that we covered at the Hollywood Laserium presented a year ago by Dr. Charles Baltay (NOT Baltar!), the man who was responsible for Pluto losing its planetary status. At the time, a lot of the concepts seemed a bit esoteric, but having read this book, are now elementary. Did you know, for example, that a supernova explosion is so powerful, it can briefly cause iron and other atoms remaining in the star to fuse into every naturally occurring element in the periodic table? Nifty, eh? Astronomy buffs, amateur and experienced, will enjoy the section on space, with a preamble on the formation of our galaxy and star systems to the 12 different planets of the Colonies, and how that many habitable planets could all be packed into such a dense area (see companion map below).
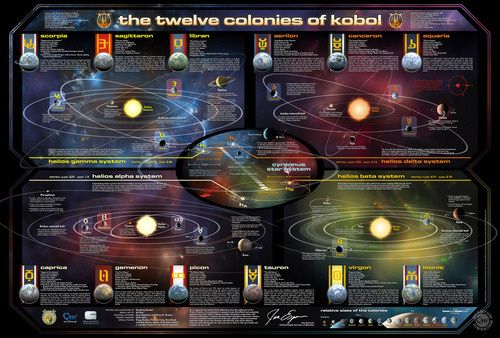
With perfect timing for the publication of The Science of BSG, Kevin R. Grazier and co-executive producer Jane Espenson have teamed up to create a plausible astronomy map of the 12 colonies of Battlestar Galactica. Find a larger, interactive version here.

One of the more fun aspects to watching BSG was the cornucopia of weapons, toys, and other electronics used by both humans and Cylons, a subject explored in the most meaty section of the whole book, “Battlestar Tech.” This includes a discussion of propulsion and how the Galactica’s jump drive might work, artificial gravity, a great chapter on the vipers and raptors as effective weapons, and positing how it is that Six was able to infiltrate the colonial computer infrastructure… besides the obvious, that is. I really enjoyed learning about Faraday cages, tachyon particles, brane cosmology, and what a back door is in computer programming, terms you can bet I will be throwing out casually at my next hoity-toity dinner party. The next time you rewatch an episode, and hear Mr. Gaeta utter a directive such as “We have a Cylon raider, CBDR, bearing 123 carom 45,” not only will you know exactly what he’s saying relative to the cartesian coordinates of the BSG space universe, but how this information is used to operate the complicated three-dimensional space system that the pilots have to operate in. Finally, critics such as myself of the dilapidated corded phones used aboard the Galactica will be interested to find out why they may have actually been a good idea in protecting the fleet from Cylon detection.

The ultimate selling point of this book is its ability to present material that will appeal to all fractions of a very diverse audience. The writing style is fluid, clever, informative and appropriately humorous in the way one would expect of a geeky sci-fi book (highlighted by a chapter on Cylon composition and detection thereof by Dr. Baltar written in dialogue format between an omniscient scientist and a smart-aleck fanboy). In fact, the co-authors merge their styles well enough so as to imagine that only one person wrote the book. Part textbook, part entertainment, part series companion, The Science of Battlestar Galactica is concomitantly smart, complicated, approachable and difficult—it does not surprise us one bit that in the couple of short months since its wide release, talk of numerous literary awards has already been circling. In between lessons on basic biology, astrophysics, energy and basic engineering are sprinkled delightful vignettes of actual on-set problem solving involving science. My favorites included plausible ways Cylons could download their information as they’re reborn (get ready for some serious computer-speak here!), an excellent explanation of Dr. Baltar’s mysterious Cylon detector, radiation and the difference between uninhabitable ‘dead Earth’ and barely habitable New Caprica, and the revelation by Dr. Grazier of how he had to—in a frantic period of 24 sleepless hours—construct a theory as to how the FTL drive works for an episode-specific reason. Much like the show it is based on, this book asks as many questions as it answers, most notably on social parables within our own world. Are we on our way to building Cylon artificial intelligence? Could our computer infrastructure ever get compromised like the ones on Caprica? Would we ever be able to travel to parallel universes, and what would be the implications of life forms besides our own? How might they even detect our presence?
Read our in-depth interview with Kevin R. Grazier here
Join our our Facebook fan page for a special giveaway commemorating the release of The Science of Battlestar Galactica and our 100th blog post. Now if you’ll excuse me, having read and absorbed this illuminating volume, I have been inspired to go and watch the entire series from start to finish all over again!
~*ScriptPhD*~
*****************
ScriptPhD.com covers science and technology in entertainment, media and advertising. Hire our consulting company for creative content development.
Subscribe to free email notifications of new posts on our home page.
]]>
One of the most captivating books of 2010 was not a gory science-fiction thriller or a gripping end-of-the world page-turner, though its subject matter is equally engrossing and out of the ordinary. It is about somewhat crazy people doing crazy things as seen through the lenses of the man that has been treating them for decades. The Naked Lady Who Stood On Her Head is the first psych ward memoir, a tale of a curious doctor/scientist and his most extreme, bizarre, and sometimes touching cases from the nation’s most prestigious neurology centers and universities. Included in ScriptPhD.com’s review is a podcast interview with Dr. Small, as well as the opportunity to win a free autographed copy of his book. Our end-of-the year science library pick is under the “continue reading” cut.

Gary Small is a very unlikely candidate for the chaos that many of us confuse with a psych ward. Whether it was the frantic psych consults on ER or fond remembrance of Jack Nicholson and his cohorts in One Flew Over The Cuckoo’s Nest, most of us have a natural association of psychiatry with insanity or pandemonium. Meeting Dr. Small in real life is the antithesis of these scenarios. Warm, welcoming, serene and genuinely affable, his voice translates directly from the pages of his latest book. Told in chronological order—starting with
a young, curious, inexperienced intern at Harvard’s Massachussetts General Hospital to his tenure as a world-renowned neuroscientist at UCLA—The Naked Lady Who Stood On Her Head feels like an enormous learning and growing experience for Dr. Small, his patients, and the reader.
The scene plays out like a standard medical drama or movie. In the beginning, the young, bright-eyed, bushy-tailed, trepidatious doctor is exploring while learning the ropes on duty. There is, in the self-titled chapter, literally a naked lady standing on her head in the middle of a Boston psych ward. Dr. Small is the only doctor that can cure her baffling ailment, but in doing so, only begins to peel away at what is really troubling her. There is a bevvy of inexplicable fainting schoolgirls afflicting the Boston suburbs. Only through a fresh pair of eager eyes is the root cause attained, a cause that to this day sets the standard for mass hysteria treatment nationwide. And there is a mute hip painter from Venice beach, immobile for weeks until Small, fighting the rigid senior attendings, gets to the unlikely diagnosis. As the book, and Dr. Small’s career, flourishes, we meet a WebMD mom, a young man literally blinded by his family’s pressure, a man whose fiancé’s obsession with Disney characters resurfaces a painful childhood secret, and Dr. Small’s touching story of having to watch as the mentor he introduced at the book’s beginning hires him as a therapist so that he can diagnose his teacher’s dementia. Ultimately, all of the characters of The Naked Lady Who Stood on Her Head, and Dr. Small’s dedication and respect, have a common thread. They are real, they are diverse, and they are us. Psych patients are not one-dimensional figments of a screenwriter’s imagination. They are the brother who has childhood trauma, the friend with a dysfunctional or abusive family, the husband or wife with a rare genetic predisposition, and all of us are but one degree away from the abnormal behavior that these conditions can ignite. In his book, Dr. Small has pulled back the curtain of a notoriously secretive and mysterious field. It’s a riveting reveal, and absolutely worth an appointment. The Naked Lady Who Stood On Her Head has been optioned by 20th Century Fox, and may be coming to your televisions soon!
Podcast Interview
In addition to his latest novel, Gary Small is the author of the best-selling global phenomenon The Memory Bible: An Innovative Strategy For Keeping Your Brain Young and a regular contributor to The Huffington Post (several excellent recent articles can be found here and here). His seminal research on Alzheimer’s disease, aging and brain training has appeared in recent articles in NPR and Newsweek. A seminal brain imaging study recently completed in his laboratory garnered worldwide media attention for suggesting that Google searching can stimulate the brain and literally keep aging brains agile. Dr. Small regularly updates his research and musings on his personal blog.
ScriptPhD.com sat down for a one-on-one podcast with Dr. Small and discussed inspiration for the book, and how it conveys the inner thought process of a psychiatrist through their many interesting cases. In our podcast, we discuss how media and on-screen portrayal of psychiatrists contribute to people’s perceptions of the field, how the themes of empathy and humanity are indellibly woven into case studies, the challenges and fullfillment of psychiatry and the contribution of pop culture in modern psychoses.
~*ScriptPhD*~
*****************
ScriptPhD.com covers science and technology in entertainment, media and advertising. Hire our consulting company for creative content development. Subscribe to free email notifications of new posts on our home page.

Each of the brain’s 100 billion neurons has somewhere in the realm of 7,000 connections to other neurons, creating a tangled roadmap of about 700 trillion possible turns. But thinking of the brain as roads makes it sound very fixed—you know, pavement, and rebar, and steel girders and all. But the opposite is true: at work in our brains are never-sleeping teams of Fraggles and Doozers who rip apart the roads, build new ones, and are constantly at work retooling the brain’s intersections. This study of Fraggles and Doozers is the booming field of neuroplasticity: how the basic architecture of the brain changes over time. Scientist, neuro math geek, Science Channel personality and accomplished author Garth Sundem writes for ScriptPhD.com about the phenomenon of brain training and memory.
Certainly the brain is plastic—the gray matter you wake up with is not the stuff you take to sleep at night. But what changes the brain? How do the Fraggles know what to rip apart and how do the Doozers know what to build? Part of the answer lies in a simple idea: neurons that fire together, wire together. This is an integral part of the process we call learning. When you have a thought or perform a task, a car leaves point A in your brain and travels to point B. The first time you do something, the route from point A to B might be circuitous and the car might take wrong turns, but the more the car travels this same route, the more efficient the pathway becomes. Your brain learns to more efficiently pass this information through its neural net.
A simple example of this “firing together is wiring together” is seen in the infant hippocampus. The hippocampus packages memories for storage deeper in the brain: an experience goes in and a bundle comes out. I think of it like the pegboard at the Seattle Science Center: you drop a bouncy ball in the top and it ricochets down through the matrix of pegs until exiting a slot at the bottom. In the hippocampus, it’s a defined path: you drop an experience in slot number 5,678,284 and
it comes out exit number 1,274,986. How does the hippocampus possibly know which entrance leads to which exit? It wires itself by trial and error (oversimplification alert…but you get the point). Infants constantly fire test balls through the matrix and ones that reach a worthwhile endpoint reinforce worthwhile pathways. These neurons fire together, wire together, and eventually the hippocampus becomes efficient. It’s just that easy. (And because it’s so easy, researchers aren’t far away from creating an artificial hippocampus.)

Now let’s think about Sudoku. The first time you discover which missing numbers go in which empty boxes, you do so inefficiently. But over time, you get better at it. You learn tricks. You start to see patterns. You develop a workflow. And practice creates efficiency in your brain as neurons create the connections necessary for the quick processing of Sudoku. This is true of any puzzle: your plastic brain changes its basic architecture to allow you to complete subsequent puzzles more efficiently. Okay, that’s great and all, but studies are finding that the vast majority of brain-training attempts don’t generalize to overall intelligence. In other words, by doing Sudoku, you only get better at Sudoku. This might gain you street cred in certain circles, but it doesn’t necessarily make you smarter. Unfortunately, the same is true of puzzle regiments: you get better at the puzzles, but you don’t necessarily get smarter in a general way.
That said, one type of puzzle offers some hope: the crossword. In fact, researchers at Wake Forest University suggest that crossword puzzles strengthen the brain (even in later years) the same way that lifting weights can increase muscle strength. Still, it remains true that doing the crossword only reinforces the mechanism needed to do the crossword. But the crossword uses a very specific mechanism: it forces you to pull a range of facts from deep within your brain into your working memory. This is a nice thing to get better at. Think about it: there are few tasks that don’t require some sort of recall, be it of facts or experiences. And so training a nimble working memory through crosswords seems a more promising regiment than other single type of brain training exercise.
This is borne out by research. A Columbia University study published in 2008 found that training working memory increased overall fluid intelligence. So the answer to this article’s title question is yes, brain training is very real. (Only, there’s lot of schlock out there.) But hidden in this article lies the new key that many researchers hope will point the way to brain training of the future. Any ONE brain training regiment only makes you better at the one thing being trained. But NEW EXPERIENCES in general, promise a varied and continual rewiring of the brain for a fluid and ever-changing development of intelligence. In other words, if you stay in your comfort zone, the comfort zone decays around you. In order to build intelligence or even to keep what you have, you need to be building new rooms, outside your comfort zone. If you consume a new media source in the morning, experiment with a new route to work, eat a new food for lunch, talk to a new person, or…try a NEW puzzle, you’re forcing your brain to rewire itself to be able to deal with these new experiences—you’re growing new neurons and forcing your old ones to scramble to create new connections.
Here’s what that means for your brain-training regimen: doing a puzzle is little more than busywork; it’s the act of figuring out how to do it that makes you smarter. Sit down and read the directions. If you understand them immediately and know how you should go about solving a puzzle, put it down and look for something else…something new. It’s not just use it or lose it. It’s use it in a novel way or lose it. Try it. Your brain will thank you for it.
Garth Sundem works at the intersection of math, science, and humor with a growing list of bestselling books including the recently released Brain Candy: Science, Puzzles, Paradoxes, Logic and Illogic to Nourish Your Neurons, which he packed with tasty tidbits of fun, new experiences in hopes of making readers just a little bit smarter without boring them
into stupidity. He is a frequent on-screen contributor to The Science Channel and has written for magazines including Wired, Seed, Sand Esquire. You can visit him online or follow his Twitter feed.
*****************
ScriptPhD.com covers science and technology in entertainment, media and advertising. Hire our consulting company for creative content development.
Subscribe to free email notifications of new posts on our home page.
]]>
As Comic-Con winds down on the shortened Day 4, we conclude our coverage with two panels that exemplify what Comic-Con is all about. As promised, we dissect the “Comics Design” panel of the world’s top logo designers deconstructing their work, coupled with images of their work. We also bring you an interesting panel of ethnographers, consisting of undergraduate and graduate student, studying the culture and the varying forces that shape Comic-Con. Seriously, they’re studying nerds! Finally, we are delighted to shine our ScriptPhD.com spotlight on new sci-fi author Charles Yu, who presented his new novel at his first (of what we are sure are many) Comic-Con appearance. We sat down and chatted with Charles, and are pleased to publish the interview. And of course, our Day 4 Costume of the Day. Comic-Con 2010 (through the eyes of ScriptPhD.com) ends under the “continue reading” cut!
Comics Design

We are not ashamed to admit that here at ScriptPhD.com, we are secret design nerds. We love it, particularly since good design so often elevates the content of films, television, and books, but is a relatively mysterious process. One of THE most fascinating panels that we attended at Comic-Con 2010 was on the design secrets behind some of your favorite comics and book covers. A panel of the world’s leading designers revealed their methodologies (and sometimes failures) in the design process behind their hit pieces, lifting the shroud of secrecy that designers often envelop themselves in. An unparalleled purview into the mind of the designer, and the visual appeal that so often subliminally contributes to the success of a graphic novel, comic, or even regular book. We do, as it turns out, judge books by their covers.
As promised, we revisit this illuminating panel, and thank Christopher Butcher, co-founder of The Toronto Comic Arts Festival and co-owner of The Beguiling, Canada’s finest comics bookstore. Chris was kind enough to provide us with high-quality images of the Comics Design panel’s work, for which we at ScriptPhD.com are grateful. Chris had each of the graphic artists discuss their work with an example of design that worked, and design that didn’t (if available or so inclined). The artist was asked to deconstruct the logo or design and talk about the thought process behind it.
Mark Ciarello – (art + design director at DC Comics)

Mark chose to design the cover of this book with an overall emphasis on the individual artist. Hence the white space on the book, and a focus on the logo above the “solo” artist.
Adam Grano – (designer at Fantagraphics)

Adam took the title of this book quite literally, and let loose with his design to truly emphasize the title. He called it “method design.” He wanted the cover to look like a drunken dream.

For the Humbug collection, Grano tried hard not to impress too much of himself (and his tastes) in the design of the cover. He wanted to inject simplicity in a project that would stand the test of time, because it was a collector’s series.

Grano considered this design project his “failure.” It contrasts greatly with the simplicity and elegance of Humbug. He mentioned that everyone on the page is scripted and gridded, something that designers try to avoid in comics.
Chip Kidd – (designer at Random House)

Chip Kidd had the honor of working on the first posthumous Peanuts release after Charles M. Schultz’s death, and took to the project quite seriously. In the cover, he wanted to deconstruct a Peanuts strip. All of the human element is taken out of the strip, with the characters on the cover up to their necks in suburban anxiety.

Kidd likes this cover because he considers it an updated spin on Superman. It’s not a classic Superman panel, so he designed a logo that deviated from the classic “Superman” logo to match.

Kidd chose this as his design “failure”, but not the design itself. The cover represents one of seven volumes, in which the logo pictured disintegrates by the seventh issue, to match the crisis in the title. Kidd’s only regret here is that he was too subtle. He wishes he’d chosen to start the logo disintegration progression sooner, as there’s very little difference between the first few volumes.
Fawn Lau – (designer at VIZ)

Fawn was commissioned to redesign this book cover for an American audience. Keeping this in mind, and wanting the Japanese animation to be more legible for the American audience, she didn’t want too heavy-handed of a logo. In an utterly genius stroke of creativity, Lau went to an art store, bought $70 worth of art supplies, and played around with them until she constructed the “Picasso” logo. Clever, clever girl!
Mark Siegel – (First Second Books)

Mark Siegel was hired to create the cover of the new biography Feynman, an eponymous title about one of the most famous physicists of all time. Feynman was an amazing man who lived an amazing life, including a Nobel Prize in physics in 1965. His biographer, Ottaviani Myrick, a nuclear physicist and speed skating champion, is an equally accomplished individual. The design of the cover was therefore chosen to reflect their dynamic personalities. The colors were chosen to represent the atomic bomb and Los Alamos, New Mexico, where Feynman assisted in the development of The Manhattan Project. Incidentally, the quote on the cover – “If that’s the world’s smartest man, God help us!” – is from Feynman’s own mother.
Keith Wood – (Oni Press)

Wood remarked that this was the first time he was able to do design on a large scale, which really worked for this project. He chose a very basic color scheme, again to emphasize a collection standing the test of time, and designed all the covers simultaneously, including color schemes and graphics. He felt this gave the project a sense of connectedness.

Wood chose a pantone silver as the base of this design with a stenciled typeface meant to look very modern. The back of the cover and the front of the cover were initially going to be reversed when the artists first brought him the renderings. However, Wood felt that since the book’s content is about the idea of a girl’s traveling across the United States, it would be more compelling and evocative to use feet/baggage as the front of the book. He was also the only graphic artist to show a progression of 10-12 renderings, playing with colors, panels and typeface, that led to the final design. He believes in a very traditional approach to design, which includes hand sketches and multiple renderings.
The Culture of Popular Things: Ethnographic Examinations of Comic-Con 2010

Each year, for the past four years, Comic-Con ends on an academic note. Matthew J. Smith, a professor at Wittenberg University in Ohio, takes along a cadre of students, graduate and undergraduate, to study Comic-Con; the nerds, the geeks, the entertainment component, the comics component, to ultimately understand the culture of what goes on in this fascinating microcosm of consumerism and fandom. By culture, the students embrace the accepted definition by famous anthropologist Raymond J. DeMallie: “what is understood by members of a group.” The students ultimately wanted to ask why people come to Comic-Con in general. They are united by the general forces of being fans; this is what is understood in their group. After milling around the various locales that constituted the Con, the students deduced that two ultimate forces were simultaneously at play. The fan culture drives and energizes the Con as a whole, while strong marketing forces were on display in the exhibit halls and panels.
Maxwell Wassmann, a political economy student at Wayne State University, pointed out that “secretly, what we’re talking about is the culture of buying things.” He compared Comic-Con as a giant shopping mall, a microcosm of our economic system in one place. “If you’ve spent at least 10 minutes at Comic-Con,” he pointed out, “you probably bought something or had something tried to be sold to you. Everything is about marketing.” As a whole, Comic-Con is subliminally designed to reinforce the idea that this piece of pop culture, which ultimately advertises an even greater subset of pop culture, is worth your money. Wassmann pointed out an advertising meme present throughout the weekend that we took notice of as well—garment-challenged ladies advertising the new Green Hornet movie. The movie itself is not terribly sexy, but by using garment-challenged ladies to espouse the very picture of the movie, when you leave Comic-Con and see a poster for Green Hornet, you will subconsciously link it to the sexy images you were exposed to in San Diego, greatly increasing your chances of wanting to see the film. By contrast, Wassmann also pointed out that there is a concomitant old-town economy happening; small comics. In the fringes of the exhibition center and the artists’ space, a totally different microcosm of consumerism and content exchange.

Kane Anderson, a PhD student at UC Santa Barbara getting his doctorate in “Superheroology” (seriously, why didn’t I think of that back in graduate school??), came to San Diego to observe how costumes relate to the superhero experience. To fully absorb himself in the experience, and to gain the trust of Con attendees that he’d be interviewing, Anderson came in full costume (see above picture). Overall, he deduced that the costume-goers, who we will openly admit to enjoying and photographing during our stay in San Diego, act as goodwill ambassadors for the characters and superheroes they represent. They also add to the fantasy and adventure of Comic-Con goers, creating the “experience.” The negative side to this is that it evokes a certain “looky-loo” effect, where people are actively seeking out, and singling out, costume-wearers, even though they only constitute 5% of all attendees.
Tanya Zuk, a media masters student from the University of Arizona, and Jacob Sigafoos, an undergraduate communications major at Wittenberg University, both took on the mighty Hollywood forces invading the Con, primarily the distribution of independent content, an enormous portion of the programming at Comic-Con (and a growing presence on the web). Zuk spoke about original video content, more distinctive of new media, is distributed primarily online. It allows for more exchange between creators and their audience than traditional content (such as film and cable television), and builds a community fanbase through organic interaction. Sigafoos expanded on this by talking about how to properly market such material to gain viral popularity—none at all! Lack of marketing, at least traditional forms, is the most successful way to promote a product. Producing a high-quality product, handing it off to friends, and promoting through social media is still the best way to grow a devoted following.
And speaking of Hollywood, their presence at Comic-Con is undeniable. Emily Saidel, a Master’s student at NYU, and Sam Kinney, a business/marketing student at Wittenberg University, both took on the behemoth forces of major studios hawking their products in what originally started out as a quite independent gathering. Saidel tackled Hollywood’s presence at Comic-Con, people’s acceptance/rejection thereof, and how comics are accepted by traditional academic disciplines as didactic tools in and of themselves. The common thread is a clash between the culture and the community. Being a member of a group is a relatively simple idea, but because Comic-Con is so large, it incorporates multiple communities, leading to tensions between those feeling on the outside (i.e. fringe comics or anime fans) versus those feeling on the inside (i.e. the more common mainstream fans). Comics fans would like to be part of that mainstream group and do show interest in those adaptations and changes (we’re all movie buffs, after all), noted Kinney, but feel that Comic-Con is bigger than what it should be.
But how much tension is there between the different subgroups and forces? The most salient example from last year’s Con was the invasion of the uber-mainstream Twilight fans, who not only created a ruckus on the streets of San Diego, but also usurped all the seats of the largest pavilion, Hall H, to wait for their panel, locking out other fans from seeing their panels. (No one was stabbed.) In reality, the supposed clash of cultures is blown out of proportion, with most fans not really feeling the tension. To boot, Seidel pointed out that tension isn’t necessarily a bad thing, either. She gave a metaphor of a rubber band, which only fulfills its purpose with tension. The different forces of Comic-Con work in different ways, if sometimes imperfectly. And that’s a good thing.
Incidentally, if you are reading this and interested in participating in the week-long program in San Diego next year, visit the official website of the Comic-Con field study for more information. Some of the benefits include: attending the Comic-Con programs of your choice, learning the tools of ethnographic investigation, and presenting the findings as part of a presentation to the Comics Arts Conference. Dr. Matthew Smith, who leads the field study every year, is not just a veteran attendee of Comic-Con, but also the author of The Power of Comics.
COMIC-CON SPOTLIGHT ON: Charles Yu, author of How To Live Safely in a Science Fictional Universe.

Here at ScriptPhD.com, we love hobnobbing with the scientific and entertainment elite and talking to writers and filmmakers at the top of their craft as much as the next website. But what we love even more is seeking out new talent, the makers of the books, movies and ideas that you’ll be talking about tomorrow, and being proud to be the first to showcase their work. This year, in our preparation for Comic-Con 2010, we ran across such an individual in Charles Yu, whose first novel, How To Live Safely in a Science Fictional Universe premieres this fall, and who spoke about it at a panel over the weekend. We had an opportunity to have lunch with Charles in Los Angeles just prior Comic-Con, and spoke in-depth about his new book, along with the state of sci-fi in current literature. We’re pretty sure Charles Yu is a name science fiction fans are going to be hearing for some time to come. ScriptPhD.com is proud to shine our 2010 Comic-Con spotlight on Charles and his debut novel, which is available September 7, 2010.
How To Live Safely in a Science Fictional Universe is the story of a son searching for his father… through quantum-space time. The story takes place on Minor Universe 31, a vast story-space on the outskirts of fiction, where paradox fluctuates like the stock market, lonely sexbots beckon failed protagonists, and time travel is serious business. Every day, people get into time machines and try to do the one thing they should never do: try to change the past. That’s where the main character, Charles Yu, time travel technician, steps in. Accompanied by TAMMY (who we consider the new Hal), an operating system with low self-esteem, and a nonexistent but ontologically valid dog named Ed, Charles helps save people from themselves. When he’s not on the job, Charles visits his mother (stuck in a one-hour cycle, she makes dinner over and over and over) and searches for his father, who invented time travel and then vanished.
Questions for Charles Yu

ScriptPhD.com: Charles, the story has tremendous traditional sci-fi roots. Can you discuss where the inspiration for this came from?
Charles Yu: Well the sci-fi angle definitely comes from being a kid in the 80s, when there were blockbuster sci-fi things all over the place. I’ve always loved [that time], as a casual fan, but also wanted to write it. I didn’t even start doing that until after I’d graduated from law school. I did write, growing up, but I never wrote fiction—I didn’t think I’d be any good at it! I wrote poetry in college, minored in it, actually. Fiction and poetry are both incredibly hard, and poetry takes more discipline, but at least when I failed in my early writing, it was a 100 words of failure, instead of 5,000 words of it.
SPhD: What were some of your biggest inspirations growing up (television or books) that contributed to your later work?
CY: Definitely The Foundation Trilogy. I remember reading that in the 8th grade, and I remember spending every waking moment reading, because it was the greatest thing I’d ever read. First of all, I was in the 8th grade, so I hadn’t read that many things, but the idea that Asimov created this entire self-contained universe, it was the first time that I’d been exposed to that idea. And then to have this psychohistory on top, it was kind of trippy. Psychohistory is the idea that social sciences can be just as rigorously captured with equations as any physical science. I think that series of books is the main thing that got me into sci-fi.
SPhD: Any regrets about having named the main character after yourself?
CY: Yes. For a very specific reason. People in my life are going to think it’s biographical, which it’s very much not. And it’s very natural for people to do that. And in my first book of short stories, none of the main characters was named after anyone, and still I had family members that asked if that was about our family, or people that gave me great feedback but then said, “How could you do that to your family?” And it was fiction! I don’t think the book could have gotten written had I not left that placeholder in, because the one thing that drove any sort of emotional connection for the story for me was the idea of having less things to worry about. The other thing is that because the main character is named after you, as you’re writing the book, it acts as a fuel or vector to help drive the emotional completion.
SPhD: In the world of your novel, people live in a lachrymose, technologically-driven society. Any commentary therein whatsoever on the technological numbing of our own current culture?
CY: Yes. But I didn’t mean it as a condemnation, in a sense. I wouldn’t make an overt statement about technology and society, but I am more interested in the way that technology can sometimes not connect people, but enable people’s tendency to isolate themselves. Certainly, technology has amazing connective possibilities, but that would have been a much different story, obviously. The emotional plot-level core of this book is a box. And that sort of drove everything from there. The technology is almost an emotional technology that [Charles, the main character] has invented with his dad. It’s a larger reflection of his inability to move past certain limitations that he’s put on himself.
SPhD: What drives Charles, the main character of this book?
CY: What’s really driving Charles emotionally is looking for his dad. But more than that, is trying to move through time, to navigate the past without getting stuck in it.
SPhD: Both of his companions are non-human. Any significance to that?
CY: It probably speaks more to my limitations as a writer [laughs]. That was all part of the lonely guy type that Charles is being portrayed as. If he had a human with him, he’d be a much different person.
SPhD: The book abounds in scientific jargon and technological terminology, which is par for the course in science fiction, but was still very ambitious. Do you have high expectations of the audience that will read this book?
CY: Yeah. I was just reading an interview where the writer essentially said “You can never go wrong by expecting too much [of your audience].” You can definitely go wrong the other way, because that would come off as terrible, or assuming that you know more. But actually, my concerns were more in the other direction, because I knew I was playing fast and loose with concepts that I know I don’t have a great grasp of. I’m writing from the level of amateur who likes reading science books, and studied science in college—an entertainment layreader. My worry was whether I was BSing too much [of the science]. There are parts where it’s clearly fictional science, but there are other parts that I cite things that are real, and is anyone who reads this who actually knows something about science going to say “What the heck is this guy saying?”
SPhD: How To Live… is written in a very atavistic, retro 80s style of science fiction, and really reminded me of the best of Isaac Asimov. How do you feel about the current state of sci-fi literature as relates to your book?
CY: Two really big keys for me, and things I was thinking about while writing [this book], were one, there is kind of a kitchiness to sci-fi, and I think that’s kind of intentional. It has a kind of do-it-yourself aesthetic to it. In my book, you basically have a guy in the garage with his dad, and yes the dad is an engineer, but it’s in a garage without great equipment, so it’s not going to look sleek, you can imagine what it’s going to look like—it’s going to look like something you’d build with things you have lying around in the garage. On the other hand, it is supposed to be this fully realized time machine, and you’re not supposed to be able to imagine it. Even now, when I’m in the library in the science-fiction section, I’ll often look for anthologies that are from the 80s, or the greatest time travel stories from the 20th Century that cover a much greater range of time than what’s being published now. It’s almost like the advancement of real-world technology is edging closer to what used to be the realm of science fiction. The way that I would think about that is that it’s not exploting what the real possibility of science fiction is, which is to explore a current world or any other completely strange world, but not a world totally envisionable ten years from now. You end up speculating on what’s possible or what’s easily extrapollatable from here; that’s not necessarily going to make for super emotional stories.
Charles Yu is a writer and attorney living in Los Angeles, CA.
Last, but certainly not least, is our final Costume of the Day. We chose this young ninja not only because of the coolness of his costume, but because of his quick wit. As we were taking the snapshot he said, “I’m smiling, you just can’t see it.” And a check mate to you, young sir.

Incidentally, you can find much more photographic coverage of Comic-Con on our Facebook fan page. Become a fan, because this week, we will be announcing Comic-Con swag giveaways that only Facebook fans are eligible for.
~*ScriptPhD*~
*****************
ScriptPhD.com covers science and technology in entertainment, media and advertising. Hire our consulting company for creative content development.
Subscribe to free email notifications of new posts on our home page.
]]>
Day 3 was Star Wars Day at San Diego Comic-Con International and we have something shocking to report, ladies and gentlemen. We did not see a single light saber, not one! Since we almost incurred an unfortunate eye injury last year due to an overenthusiastic Jedi, this was most welcome relief. For ScriptPhD.com, today was all about science and technology. In a day that could not have been more tailor-made for our website, we enjoyed panels with the eminent sci-fi television writers of today discussing writing for genre TV (a must-read for any aspiring TV writers out there!), a visit from the greatest science fiction writer in the history of science fiction, Ray Bradbury, a preview of next season’s sci-fi show The Event, and a panel on how exactly shows like CSI “tech” out with gadgets galore. Oh, yes, did we mention we got to hang out privately with the MythBusters?? With the help of our intrepid reporter Bryy Miller, we bring you the most complete Comic-Con coverage on the web. Plus, our Costume of the Day, after the “continue reading” cut!
The Write Stuff: Creating Genre Television
LOST. CSI. V. Battlestar Galactica. It seems that sci-fi, tech, and geek-chic television is everywhere. Not only is it a staple of prime time (across basic and extended cable), it’s an increasingly popular genre for which good writers are constantly in demand. Since we are SCRIPTPhD.com, an opportunity to listen in as a panel of some of today’s hottest genre television writers gave away secrets of their craft and advice for aspiring writers was irresistible.


Since this panel consisted of so many writers, albeit a dream team thereof, there was only an allotted amount of time for three questions, each of which the panelists answered one by one down the line, and quite enthusiastically. The moderator, Jeff Goldsmith, who runs the industry rag Creative Screenwriting correctly pointed out that not only are they all working in TV, but if they weren’t on this panel, they’d be at Comic-Con anyway. He called them the “Algonquin geek table.” The first question was to ask each screenwriter what brilliant idea they had that would revolutionize a show they were working on at the time, but that couldn’t get past the network censors.
Mark Altman (Castle, Elvis Van Helsing) recalled creating a pilot called Elvis Van Helsing, but ABC went with The Middle Man instead. So he turned it into a graphic novel, and the rest was history. Charles Murray (V, Criminal Minds) actually recalled a terrific idea for an episode of Criminal Minds, where a serial killer would put a milk carton in someone’s fridge and the “Have You Seen This Person?” picture would be of the dead person. Clever, we thought! Steve Kriozere (NCIS, VIP) had the clever idea on VIP of casting Bruce Campbell to play Pamela Anderson’s uncle. The amazing and talented Jesse Alexander (Alias, LOST, Heroes) recalled a victory for geeks in the form of Heroes Season 1 in an episode entitled Days of Future Past where all the characters went into alternate future. He mentioned that it was so hard to approve and get on air, but the episode went on to win multiple awards. What didn’t make it? “Season 5.”
Steve Melching (Clone Wars, Transformers, The Batman) recalled writing for the animated series The Batman taking place in his first few years in Gotham City, and wanted (but failed) to approve a B story about a frat boy group dressing up in D-List costumes, committing fake crimes and then videotaping their subsequent ass kicking by Batman. We wonder why that didn’t get approved. Ashley E. Miller (Fringe, Terminator) wanted a Fringe follow up to the episode “Bishop Revival,” which had an immortal Nazi. He wanted a flashback episode to 1942, where we find out that Agent Phillip Broyles is 100 years old, and whacking Nazis. Jose Molina (Castle, Firefly) wanted a Firefly payoff episode with a 9-months-pregnant woman being evil, where the team kills her but they save the baby, and the episode would consist of three acts of “Three Men and a Baby.” Right. Sarah Watson (Middleman, Parenthood) recalled being hired to do a SyFy Channel movie of the week about an untapped volcano under Manhattan (seriously!), and she had grand plans for lava engulfing Statue of Liberty, taking over all of Manhattan island, but when the movie got produced the visual ended up being lava trickling out from under a garage. Robert Hewitt Wolfe (The Gates, Deep Space Nine) was writing for 4400 in its final season, and was obsessed with the idea of creating an aerosol promycin bomb over Seattle (hmmm, as a Seattleite, I booed this from the audience). The showrunners created a promycin bomb at the end. So the next time you think all TV writers are geniuses, just remember that for every great episode of your favorite show, there were many bad ideas tossed around in the writers’ room.
Next, Goldsmith asked the panel to recount (as diplomatically as possible) the stupidest network notes they’d ever encountered for a show script they worked on.
Mark Altman recalled working on a SyFy Channel movie where executives asked him to recap the whole plot at the beginning of the hour because of people tuning in from HBO. Charles Murray, while working on V, was told he couldn’t use the word lizard in an episode. How do you get past something like that, he was asked. “I left the show. That’s how you get past it.” Steve Kriozere revealed the #1 SyFy Channel rule of movies: don’t speak to the monster. Jesse Alexander, having worked on some of the greatest sci-fi hits ever, waxed more philosophical. Everyone has an opinion on these shows, but executives want the rules of the show’s world, they want everything spelled out clearly, a lot of exposition. They’re generally happier if the shows are procedurals, but sci-fi shows don’t have room for that—if all the secrets and exposition are revealed it drives people away from the content. Steve Melching pointed out that a lot of animated shows have hyper-sensors because they’re aimed at children. The dumbest note he ever received was that you can’t say “killer satellites.” Ashley E. Miller was reminded (we are shocked!) that you cannot have an 11 year old boy say douchenozzle on prime time TV. Jose Molina recalled an episode of Castle where a body is found in the teaser, the guys go through case, and find out that the victim was killed by a stiletto. Said the executives: “Does the killer have to kill with a shoe?” Sarah Watson revealed that the most annoying thing to writers on shows now is that they’re paid by sponsors, so writers have to put products into scenes strategically. Her worst example was an episode of a show with a surf competition…sponsored by Tampax. To make this work, they had to cover a poor actress’s entire surf bodysuit with Tampax logos. Robert Hewitt Wolfe was taken out to dinner by the main executives of a show he was working on and flat out asked to dumb down the series. Ahhh, the things you learn when the iron curtain goes down.
Finally, Goldsmith asked the panel to give advice to young TV writers (or aspiring writers) on how to best write for a budget, which is unfortunately what most young writers will face on television these days.
Without question, the panel answered unanimously that the secret in the writing is all. about. character. The best and cheapest special effects are two actors in a room with terrific conflict and terrific dialogue—that’s what’s compelling, that’s what’s intimate. Most physical action, they reminded us, is actually superfluous—only revert to it after all possible dialogue is tapped out. Ultimately, you must look at how what you cut (if you are forced to cut things) affects the character. If you put six people in a scene, make sure that all of them need to be in the scene, because it is extremely expensive to shoot. The writers lamented that networks sometimes have too much money, and a subsequent desire to compete with Transformers or Iron Man, which television can’t do. Writers must remember that character works for television, and you can have high-concept ideas for sci-fi. That’s why shows on cable, which are often budget-restricted, are so great. Sarah Watson reminded the audience that you can always make a show cheaper, and fantastic, with great writing and great dialogue. This is how Friday Night Lights, which shoots on a shoestring budget down in Texas, was able to survive for five seasons.
Mostly, in advice relevant to any writer reading this, they said not to repeat past mistakes.
The Event

This television show, premiering in the fall of 2010, might be the new LOST, or it might be the new FlashForward. I’m not sure yet. The Event, a show that is so steeped in mystery that even its title is nothing more than Something Happens, was a show—and will be a show—with as many problems as it has concepts. Fortunately, all of its flaws are structural.
The pilot is laid out as three separate stories (well, actually, four, but one is extremely short in comparison) over the course of three separate acts. We actually start the show in the middle of the story when our hero, Sean Walker (Jason Ritter), hijacks a plane in order to save it, and then flash back to eight days earlier, and then forward to seven days earlier, and then once more to the present. It gets even more confusing when President Eli Martinez (the incredibly suave Blair Underwood) gets his go at the story, and then his segment goes back an entire year. The other two stories comprise of the father of Sean’s girlfriend, whose house and family are assaulted by unknown forces, and Simon Lee (Ian Anthony Dale), the supposed second-in-command of a secret government base/prison that lies at the center of The Event. It’s a shame that Lee’s section is so short, as Dale is a fantastic actor even within the confines of such little material. But perhaps the best acting comes from ER/West Wing (and Northwestern University!) alumna, Laura Innes, who absolutely nails her cryptic sayings as Sofia, the leader of the base/prison/thing-to-be-revealed-later.
The show will need to cut out some of the flashes in order to survive past its initial thirteen episodes, but it is definitely a unique format that works for this type of story. The writing was high-quality and so was the dialogue; there were no qualms there. It also revealed quite a bit about the world that had been set up if you looked closely enough. Co-Producer Evan Katz made the promise that answers would actually come a lot faster than with other mystery longforms. This is welcome, especially since I am of the belief that mystery shows can maintain the mystery if they answer questions in the right or clever way. Sometimes, it is even essential to answer them if you want the show to progress to its next level of weirdness. Blair Underwood was then asked what it is like to be the first Cuban president, to which he replied that there would be no Salsa dancing.
Katz then ended the panel the only way it could have possibly ended:
“The Salsa is not The Event.”
Spotlight On: Ray Bradbury
He is brilliant. He is one of the foremost technology predictors since Leonardo DaVinci. He is irreverent, utterly aware of his importance, and quite simply, the greatest science fiction writer in the history of the genre. He none other than Ray Bradbury. Ray has been coming to Comic-Con since the very first year of its inception. A devoted comics and graphic novel buff, he loves interacting yearly with fans, and gracing them with his musings, knowledge and appreciation. We were honored and somewhat overwhelmed to be there in person for Ray’s 41st Comic-Con panel, on the heels of his 90th birthday. Because Bradbury’s words speak for themselves, we bring you the panel through his eyes.
Bradbury, not shy about quips and bold statements, starts out his panel with a bang: “I want to make an announcement. Sam Weller and I are working on a new book together: Let’s Let The Cat out of the Bag.” In actuality, Weller and Bradbury released a brand new book of interviews (out June 29th) entitled Listen to the Echoes: The Ray Bradbury Interviews. Weller has spent over a decade with Bradbury, getting to know him, studying his works, and acted as his guide during the panel (Mr. Bradbury has become a bit hard of hearing). Bradbury is currently working on a new book of 20 short stories entitled “Juggernaut” to be published next Christmas.

On how it feels to be Ray Bradbury and if he ever marvels at himself, after a long, thoughtful pause, a hearty laugh and: “It feels mighty damn good.”
Fahrenheit 451 was among the most prescient sci-fi works of all time, predicting technology such as earbuds, flat screen televisions, school violence, and the rise of graphic novels. How did Bradbury predict all this stuff?
“The secret of life is being in love. By being in love, you predict yourself. Whatever you want is what you get. You don’t think about things; just do them. Don’t predict them—just make them.”
Of the technologies Bradbury predicted, he also warned about many, including rise of mass media. What tech would he like to see next?
Again, a thoughtful pause. “I’d like certain technologies to disappear. The internet is a great, big, stupid goddamn bore.” Keep in mind that when Bradbury was approached by an internet magnate to publish his works as e-books for the internet, he responded with: “Prick up your ears and go to hell!” The internet magnate? None other than the CEO of Yahoo.
Another strong, recurring theme of Bradbury’s panel was his love (adoration, really) of space exploration, most notably colonization of Mars and the Moon. Why? “Because we’re going to live forever. We should go back and build a base on the Moon, put a civilization on Mars. 500 years from now, we’ll go out into the Universe, and when we do that, we have a chance to live forever.”
Weller tried to get Bradbury to discuss the new book, once again evoking his crotchety sense of humour: “You can’t afford it. So get out of here and forget it.” In an extremely revealing, intimate moment, Weller pointed out that many Mars stories and works are inspired by and cut from Bradbury’s Martian Chronicles, none more similar than the Twilight Zone. Bradbury then revealed something that many of his fans probably don’t know. “Rod Sterling came to my house many years ago. He didn’t know anything about writing sci-fi. So I took him down to my basement and gave him copies of books written by Roald Dahl, John Collier, a number of other great sci-fi authors, and myself. Rod Sterling forgot that he read all these books, and when he wrote his programs, he copied some of his ideas from me, and we got into a big argument.” The two never reconciled.
As we’ve mentioned, Bradbury came to Comic-Con in its first year, where he said only 300 people came to first meeting, quite different from today, where 1,000 people were gathered in his room alone. Why does he come so often? “Because I’ve been collecting comic strips all my life. I have 30 years’ of Prince Valiant Sunday illustrations put away, all of Buck Rogers. My background in becoming a writer was falling in love with comic strips.” How did they influence his prose and narrative? “Comic strips are full of imagination and glorious adventures. My all-time favorite is Mutts. A year from now, there will be a graphic novel of “The Martian Chronicles” and “Something Wicked This Way Comes.”” Bradbury is, in fact, the world’s greatest (and possibly oldest) fanboy. He is famous for writing fan letters to writers and other figures that he admires. He sent books to John Huston, the famous screenwriter and filmmaker. He sent a hand-written letter to Edgar Rice Burroughs begging him to come to a meeting of Bradbury’s science fiction society club.
Another thing fans may not know is that Bradbury is considered the patron saint of the American library system. He has been very active in rescuing libraries that are under fire because of budgetary crises. He recounted the story of his love affair with the library. “When I left high school, I had no money to go to college. I decided to not worry about going to college. I thought: “I will educate myself.” So I walked down the street, I walked into a library for 3 days a week for 10 years. Most of you in the audience can’t afford to go to college. But if you want to educate yourself, you can afford to go to the library. When I was 28 years old, I graduated from the library.”
The concept of time travel is explored in the short story “A Sound of Thunder.” If Bradbury could time travel, he was asked to what moment it would be? “Every. Single. Moment. Every single moment of my life has been incredible. I’ve savored it. It’s beautiful, because I’ve remained a boy. The man you see here tonight is a 12 year old boy, and he’s having fun!” How does he stay connected to his inner child? “Don’t worry about the future, or the past, you just explode every day. If you’re dynamic, you don’t have to worry about what age you are.”
Indeed, childhood is a theme of many of his short stories. Why is this so important to Bradbury? “Because I grew up loving carnivals and circuses. That’s why I wrote those stories.”
When asked if he had any regrets in life, Bradbury evoked the biggest laugh of the day: “I regret that I didn’t have more time with Bo Derek.” What’s the Bo Derek story? She came up to him in Paris train station, and exclaimed “Mr. Bradbury, I love you!” To which he responded, “Who are you?” She replied, “My name is Bo Derek. Mr. Bradbury, will you travel on the train with me?” With a stoic face he recalled replying: “Yep, I will!” The rest was censored.
Other than Be Derek, what was his greatest love? Bradbury turned philosophical. “I am the world’s greatest lover. I love to write short stories. I write them. I love to write novels. I write them. I love to write poetry. I write it. I love to paint pictures. I paint them. I loved directing a film. So I directed it. Those are my greatest lovers. I have loved all these things I have told you about.”
What authors inspired Bradbury growing up? “Edgar Rice Burrows. And Edgar Allan Poe—scared the hell out of me.”
Another fact about Bradbury that many people may not know is his rather illuminating and successful career as a designer and architect. He was asked how he got involved with designing the San Diego city center Horton Plaza. ”I designed a lot of other places all over LA. 50 years ago, the people who were building the New World’s Fair asked me to redesign the United States Pavilion. I helped build Epcot down in Florida. Because of those works, the people of San Diego came and asked for input in building The Horton Plaza at the center of San Diego.”
Aldous Huxley famously said of Bradbury, “You know what you are sir? You are a poet.” When asked who the poets are that have influenced his writing, Bradbury immediately responded: “Shakespeare and Alexander Pope.”
What are the things that keep Bradbury motivated now? “I have more work to do.”
On how his writing has changed over time: “It’s gotten more brilliant.”
As such a fan of Mars, Bradbury was asked how he feels about the ongoing Martian probes, and the real science evidence they have brought back to Earth. “I’m glad we are doing that [research], but we should be doing more. We should be going there in person. Not with a lander, but with a real rocket ship and landing on Mars.” In a rather endearing moment, Weller revealed that Bradbury has never driven an automobile. But he was invited to the Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, where scientists asked him if he’d like to drive the Mars Rover over Mars. So he hasn’t driven on the 405 freeway, but he has driven across Mars! The scientists even gave him a Martian drivers license.
Any futuristic technologies for cities that Bradbury would like to see? “Monorails all over LA and California. Get rid of the goddamn freeways!” As a Los Angeles resident, hear, hear, Mr. Bradbury!
What was the intended audience of Fahrenheit 451 and how does he feel about its rise to prominence as a true modern American classic? “I am not a science fiction writer. All my books are fantasy. But the one book that is pure science fiction is Fahrenheit 451. So I’m glad that I wrote it. I’m glad that you all feel that way about it too.”
Does Bradbury have a favorite work? “All of my books are my favorites. All of my books are my children. I love all my children.”
How does Bradbury feel about digital books? With a cranky grunt: “I’ve already told you that. I don’t like them. I think of iPads and Kindles as books with a computer screen. Real books smell, real books have memories.” We here at ScriptPhD.com would like to give that statement a heartfelt “AMEN!”
Finally, Bradbury, on turning 90 in a few weeks. How does it feel? “It’s been 90 goddamned incredible years!” To which the audience responded by singing him “Happy Birthday.” A surreal, incredible and special moment.
Teching Out on TV
This panel started out with an inundating montage of clips from tech-chic procedurals CSI and NCIS that involved technology of all sorts. It was part awesome and part utterly corny, as words to the song that was spliced in occasionally would find themselves on to the screen. I was afraid that this foreshadowed the panel being just a huge PR stroke for both shows, but I was later proven wrong. Despite the moderator speaking in a loud, fast, incoherent style of mumbling, the rest of the speakers (Anthony Zuicker, creator of CSI; Pauley Perette, CSI; Barrett Foa, NCIS: Los Angeles; Kirsten Vangsness, Criminal Minds; and Rich Catalani, producer of CSI) were very articulate about all aspects of technology on their shows. They strove to make it less a panel about technology on CSI and NCIS and more about technology and how it relates to CSI and NCIS.
The presentation started out with questions about how everyone got involved in their work, and more specifically, how they got involved in technology, or if they even were. Perette studied forensics in college, talking about how, back in her early years, nobody knew a thing about it. She related a story that the first time that her computer was hacked into, she tried to tell the police, but ended up having to explain to them what an IP Address was. Then, after shows such as CSI and Law & Order made technology and forensics mainstream, everyone was a part of a club that they felt they cultivated. “We all became semi-experts,” she said. “It’s been an incredible decade of change. What we’re showing on our show is the grand upmovement”. Vangsness was a tad in the opposite direction: she took teaching jobs in order to support herself, and one of those jobs was teaching PowerPoint to third graders. She now has images of third graders hacking into government installations to post spam of kittens.
Foa stopped the discussion at one point to explain to the audience that his show, unlike the original CSI, does not stare at a green screen when looking at his computer tomfoolery. It is all real. Which complicated matters greatly when Perette’s character met Foa’s in a crossover between their two shows. She had to literally teach him on set how to react to a green screen as oppose to a real image. Foa also related how the super-tech that we often think of as fictional and made up is actually real. The CSI writers have access to China Lake, a military outpost where they test experimental technology. Scary, huh?
But sometimes technology cannot save you, and honest-to-God legwork must be put into use. For one CSI episode involving a stampede of ants, they actually had to hire an Ant Wrangler and clean up all the creepy crawlies using a vacuum. CGI was expected to just look too ridiculous. Then, in a devilish sort of irony, the projector broke, so the panel was cut short and went straight to questions. Perette was met with a young woman who was going to major in Cellular Biology in college because of Perette’s performance on CSI.
Thus, the cycle continues.
MythBusters: Panel + Press Room Coverage
How popular are Discovery Channel’s MythBusters? Very. Each year, the group of geeky demolition rock stars, who prove and disprove popular science myths through the scientific method, represent one of the fan favorite panels at Comic-Con. This year was no different. Press pass notwithstanding, we barely squeezed into a sardine-tight hall full of science fans awaiting their heroes’ arrival. Take a look at the picture below:

As if the presence of television’s most explosive group wasn’t enough, the audience was tantalized two-fold before the panel. First, a montage video introducing the Busters had us cracking up with its over-the-top… what else?… explosions!

Then, a special guest, Geoff The Robot from The Late Show with Craig Ferguson, stepped out to proclaim his nerdy love of all things MythBusters.

Finally, to ear-deafening applause, Chris Hardwick of one of our favorite blogs The Nerdist (follow him on Twitter) introduced the MythBusters, who announced that they’ve signed up for 7 more years of glorious science. This is a very special Comic-Con for them. It’s the first time all five have come as a group, and it is gorgeous geek diva Kari Byron’s first Con.

The first thing the MythBusters wanted their fans to know is just how very real they are. Although they feel like royalty at the Con, when they go back home to San Francisco, MythBusters is far from glamorous. Inside their workshop, which is a workshop and not a studio, they are doing all of the stunts and building themselves. They get dirty, they get bruised, and they do all of the experimenting. Says Adam Savage: “If you see it, we built it.” Although Savage has started getting more involved behind-the-scenes, he explained that the team is so knowledgeable about how to build things, that it’s faster and more efficient for them to do the building than to leave it to someone else. Tory Bellici mused that it would be nice to have stunt doubles sometimes, to which Kari Byron quipped: “They’re not stunts when you fall off.” Did we mention that we love Kari? Jamie Hyneman, who initially signed up for MythBusters because of the allure of getting to try new things, is still having a hard time acknowledging being on TV. When asked what famous people he’d met because of MythBusters, he couldn’t recall one. “President Obama?” nudged Byron. “Oh. Yeah,” replied Hyneman hysterically. Not so for Grant Imahara, possibly the most famous robotics guy in the world. “Craig Ferguson called me the Keith Richards of robotics,” said Grant. “I’m not sure how to take that.”
The audience was treated to a highlight reel of the upcoming season, which promises to have the best, and most extreme, experiments yet. The team revealed some of the secrets. Adam Savage revealed that a scene of a Porsche flipping backwards violently was done to bust an old 1980s myth that classic sports cars are more aerodynamic going backwards than forwards. In an utterly bad-ass bit of reconstruction, the body of a Porsche chassis was cut off, flipped backwards on the car, then raced at 100 miles per hour. Any more questions, kids? A scene showing Kari puking violently (she joked that it was in her contract to have to throw up every year) was explained as an episode testing whether people really do get cold feet when they have to do something scary. For the team, scary meant picking, then eating, two of the most disgusting selections from a table of delicacies consisting of spiders, cockroaches, chicken feet and more. And where does the team get their constant supply of ideas? “Surfing the internet really works!” joked Grant Imahara.
As to whether the team is cognizant of how much they advance science and critical thinking, and actively try to build experiments around didactic aims, the answer is… NO! Jamie remarked that as a whole, the MythBusters are a remarkably curious group. They are curious about stuff, they try to figure it out, and do so in a methodical and logical way. But they never set out to do science. Which, honestly, in the opinion of this website, is why their science is so great.
At this point, the team shared fun and hilarious inside stories from their Comic-Con experience and tidbits from back home in San Francisco. Adam recalls being shocked at two geeks that came up to him at an autograph table with their baby, wearing a onesie that said “Proof that nerds have sex.” Despite his uncomfortable laughter, the duo then asked him to sign their baby! Another fan went up to Jamie and remarked: “I’ve been watching your shows since I was a little girl and now I’m a PhD!” We’re pretty sure Jamie was kidding, but Adam still poked fun back at him. “You’re old!”
Just in time for next week’s Discovery Channel Shark Week, Adam recalled a fan coming up to him a few months back with what the fan was convinced was a brilliant suggestion: “Dude, you know what you should totally do? You should totally prove that, like, punching sharks will make them go away! Seriously, dude, it would be awesome! You’d just punch them.” A brief pause from Adam. “8 months later, there we were, knee deep in sharks, punching them in the face…”
Kari revealed that she filmed the show up to her 10th month of pregnancy. She pointed out that it’s a myth that pregnancy only lasts 9 months. (BUSTED!) She was worried that her baby would never come out. Replied Grant: “With all those explosions and gunshots outside, I wouldn’t come out either!”
Finally, to a fan that asked whether the team is ever scared of an experiment as too dangerous, Jamie reminded him that danger is a relative term. Nothing the MythBusters do is any less dangerous than driving down a freeway at 70 miles an hour. The trick is to good engineering and survive by doing a good job.
The new season of MythBusters premieres in the fall. Find coverage of their Comic-Con panel and clips from the new season on the MythBusters website.

We got to spend even more time hanging out with the MythBusters (and Geoff) backstage in the press area to get even more scoop about the show. We all wondered about the research process that the team undergoes. First and foremost, Adam proclaimed that they “don’t ever get things tested because they’re too dangerous.” There’s nothing the team is afraid of, and no length of time is too long to wait for a payoff. The research can take anywhere from 2 weeks to 2 years. The team searched 19 months for a lead layer thin enough to do an experiment properly. By contrast, the poppy seed drug testing experiment took two hours. They ate poppy seed muffins at 9 AM, and tested positive for heroin at 11 AM (well into the next day).
When asked about their terrific rapport, the team reiterated that they very much enjoy each other’s company and socialize quite well. All of the process, from picking to carrying out experiments, is totally collaborative. Secondly, the team shares a bond because they know each other quite well. “It’s not like we’re a science show boy band,” joked Adam. Most of them have known each other and worked together well before MythBusters began. Unlike other shows, MythBusters goes on for most of the year (46-47 weeks) because the building portions of the segments are so time-consuming. The most important thing to Jamie is a strong sense of respect that trickles down all the way to the show’s loyal crew of 23 people.
For the future of the show, Jamie revealed an interest in looking at the dichotomy of destructive things that do good work as well, steam being high on his list. The team never gets inspiration from movie trailers or clips if there’s no story there and they’re not worthy of a myth.
Adam revealed the interesting fact that somebody actually bought the Corvette which had been fouled by a decomposing pig to prove that a decomposing body can destroy the inside of the car. Adam now associates the smell of cleaner with that episode, which makes him sick to this day. Was that the team’s least favorite experiment, wondered ScriptPhD.com? Grant picked the ear wax candle experiment, jokingly calling it the “seasickness experiment.” Tory picked the chili pepper cure experiment. (“Burns on the way in, burns on the way out!”), while Kari picked the water torture episode. The most destructive experiment to this day, much to the chagrin of OSHA and safety regulation organizations of San Francisco, was the Civil War rocket, tested with a wax core. The team thought they had a proper bunker in the shop, but unfortunately ended up setting fire to their ceiling!
On any potential Discovery Channel crossover shows, Adam revealed that he’d like to go out into the wild with Bear Grylls (and so would I!) while Kari revealed that she would not like to do a dirty job.
And for the highlight of my personal day…

Last, but not least, is our official Day 3 Costume of the Day. We chose this warrior for a simple reason. He braved the chilly convention center without a shirt, yet with a completely covered head. Now if that isn’t upside-down thinking, we don’t know what is!

Incidentally, you can find much more photographic coverage of Comic-Con on our Facebook fan page. Become a fan, because this week, we will be announcing Comic-Con swag giveaways that only Facebook fans are eligible for.
~*ScriptPhD*~
*****************
ScriptPhD.com covers science and technology in entertainment, media and advertising. Hire our consulting company for creative content development.
Subscribe to free email notifications of new posts on our home page.
]]>
Day 2 of Comic-Con is over and now, the Convention is really underway! Today’s ScriptPhD.com coverage has a heavy focus on television, and sci-fi television to be specific. Really, is there any other kind? We spent time in the press room with the stars and producers of SyFy Channel hits Caprica and Stargate Universe, our favorite geeky physics show Big Bang Theory and the exciting (first-time ever!) Comic-Con Discovery Channel unveiling of their new scripted series Reign of the Dinosaurs. As always we try to pay hommage to the roots of Comic-Con with coverage of the design tricks behind comics and graphic novels. Additionally, we provide pictorial documentation of the costumes and happenings of the Con, and our Day 2 Costume of the Day. Complete coverage under the “continue reading” cut.
From the Press Room: Stargate Universe
We were delighted to start our day with the cast of one of our favorite sci-fi shows on the air, Stargate Universe, to get a little peek into the cast’s geeky sides and what they think of their characters and show.

For star David Blue, playing the ship’s resident math geek Eli Wallace, this year is a completely different experience. Last year, there was so much uncertainty about the show’s acceptance and success, while this year, the cast walks into Comic-Con confident of where they are headed. He spoke of liking the idea of Eli as a hero, the show’s surrogate for the audience. Though he admits to being a geek, he was very hesitant to play the role when he heard about it, because of his previous computer nerd role on Moonlight for fear of typecasting. But Eli is not a stereotypical nerd, and experiences a lot more emotional and character growth over the course of Season 2. “I am proud to be a geek/nerd,” Blue says. “Everything from computer programming to comic books to video games.”
We were so thrilled to hear that David was a certified Grade A USDA organic geek, that we got him to proclaim so on camera for you guys:

Ming-Na, whose character Camile Wray is far more controversial and decisive on the show, was asked right off the bat what she’d do differently in real life as opposed to her character. “Well, I wouldn’t be a lesbian,” the married actress quipped. Turning more serious, she said that she wouldn’t be as level-headed and calm as her character, who is often asked to make difficult, morally ambiguous decisions based on emotional issues. The fan’s response to Camile is largely a love-hate relationship. She’s gotten great response from the gay community, something that Na appreciates, but Camile’s escape from cliches or stereotypes is something that has resonated. The morally wrenching decisions are a staple of the show (and sci-fi television in general), and will only continue into Season 2. “You may not like her decisions,” says Na, “But I like her.”
From the Press Room: Caprica

One of the most pivotal roles in the history of sci-fi television (the first Cylon) went to a girl that didn’t even really know the significance of the part. “I didn’t know what Battlestar was before I got the role,” admits Torresani, who was not a real sci-fi geek growing up. “I actually turned it down because I didn’t want to do [Caprica]. I wanted to do [Gossip Girl-type fluff]. It’s exciting now to [realize how important the role is], but it wasn’t nerve-wracking at the beginning. When I read the pilot, she was a spoiled brat, and then she gets in a robot. We didn’t know that I was going to be a Cylon. We just thought they’d use my voice and the robot’s body.” Filming the scenes as the Cylon, Torresani revealed, involves acting next to a giant green 7′ tall stick that everyone communicates with as the Cylon. She finds that the hardest part for her as an actress are scenes as the Cylon where she can’t communicate vocally, such as being lit on fire and not being able to utter a single word. “It’s really challenging. That’s something I never thought I’d have to do.”

We started our time with executive producer David Eick with a humdinger—the question we know fans would want to ask. What has been the producers’ reaction to mixed reviews and fan division of the show, most notably from the Battlestar Galactica fanbase? “We knew to expect a much greater mix [of opinions] because we knew going in that we were not going to craft it or market it as a spin-off of Battlestar,” replied Eick. Rather than containing cheeky references to BSG or inside jokes only the audience knows, Caprica is very much its own beast. He hopes fervently that as the show finds itself and its own focus, that the audience, too, would find its own way in the show. He reminded us that the early days of Battlestar were equally contentious in terms of critical and fan opinions. “The very first Comic-Con we came to for Battlestar was like George W. Bush showing up at an ACLU rally.”
In many ways, he feels more challenged by Caprica, which lacks the ticking time-clock feel of BSG. It’s a more sophisticated style of storytelling, which is based in defining the characters and the world around then, Rome before the fall. The mythology of that world is deepened as the show progresses, and how it’s harnessed by Zoey to express herself. Eick spoke of how much more graceful and elegant Caprica is visually and content-wise, with Blade Runner being a huge influence on the producers and writers. By contrast, BSG had much more of a Black Hawk Down, action feel to it.
By the way, Ron and David have a longstanding tradition of taking a drink of tequila together before either a major show launch or major seminar/Convention. In fact, David brought the bottle and we all had a little fun. Kidding. But seriously, folks, next time you think the storylines on Caprica are getting a liiiiiiiittle wacky, just remember this picture:


Ronald D. Moore, who made a rare media appearance at Comic-Con this year, largely echoed Eick’s comments. Caprica, he maintained is a serial, and (purposefully) as different from Battlestar Galactica as possible. In an even rarer move, Moore openly self-criticized himself for some of the early hiccups of the show. He admitted that it was hard to follow, that the story was indeed confusing, but that the show gained confidence as it went on. He predicted as strong of a build-up for Caprica as the eventual success of Battlestar Galactica. Another fun tidbit that Moore revealed was that the group marriage concept was tossed around for Battlestar Galactica, but just never found the story or the characters to make it happen.
We asked Ron about his thoughts on the current state of sci-fi and what he enjoys. “I’m probably not up to speed on a lot of other science fiction,” Moore said. “I almost avoid it now because I spend so much of my time in a science fiction world that I tend not to go there. It becomes almost like more work to watch other science fiction shows. In my brain, I’m inevitably thinking ‘How does that compare to us? And that’s their structure. How many characters do they have? I wonder what their CGI budget was.’ I haven’t watched a lot of other science fiction television for that reason.” Nevertheless, he maintains that it’s a thriving genre that will always be with us, despite the rise and fall of popularity. The one holy grail Moore hopes for is a broadcast network (read mainstream) sci-fi hit. He isn’t sure what the reason is that this popularity has remained so elusive, LOST notwithstanding. “Maybe it’s just us,” he mused. “Maybe it’s just us [the collective sci-fi geekdom], and there’s not this gigantic mass market for it in television in the way that there is a gigantic mass market for movies. Maybe that will never happen.”
We here at ScriptPhD.com hope otherwise.
From the Press Room: Big Bang Theory
If Ronald D. Moore is concerned about the viability of a basic network science fiction hit, at least he can take solace in Big Bang Theory, arguably the smartest, most successful, streamlined show about science and scientists in the history of television. We had such a fun time hanging out with the actors last year, that this year, with access to the full production team, we decided to get as much scoop from the show as possible.


One thing fans would be surprised to learn, and the first question we asked right off the bat, is just how geeky the team behind Big Bang Theory is. Producer/writer Lee Aaronson, a self-certified comics and graphic novel geek, used to own his own comic book store. This is where a lot of the inspiration for Sheldon (and the rest of the team’s) love of geek culture comes from. They also have a close relationship to UCLA physics professor and the show’s science advisor David Salzberg. Often, they will write a line like “Hey guys, I was just working on [insert science here]” and let him fill in the blanks. We were wondering about that, too!
Geeky enough? Not even close. Showrunner and co-creator Bill Prady is a former computer programmer. He’s far more excited about Apple founder Steve Wozniak guest starring on the show than any fame or fortune that has incurred because of it. He and
co-creator Chuck Lorre maintained that the geek culture was their most important singular focus in writing the show. As one might glean from walking the halls of Comic-Con, they maintained that all geeks/nerds/scientists are not the same. There is a lot of heterogeneity amongst them, and differing, personal passions—be they Star Trek or the mathematical concepts behind string theory. And where do they get all their geeky throwaway lines? “Oh, those are all available on the internet!” And THAT is why we love Big Bang Theory.


The actors themselves get right in the thick of the fun. Kaley Cuoco, playing perhaps the non-geekiest of the bunch in Penny, has nevertheless embraced geekdom. Her latest love? Her iPad! She and Johnny Galecki would both like to see a romance blossom between Penny and Sheldon (“Peldon,” joked Cuoco), but acknowledge that the road from platonic friendship to romantic involvement is filled with bumps and individual growth. Jim Parsons, who I shamelessly adore, started his time with us by telling me to shove it. He was, of course, talking about my tape recorder, but when I joked that I couldn’t believe Sheldon told me to shove it, his reply was: “And he’d tell you to shove it again and again!” Before telling Simon Helberg to bite him. Nice to know he stays in character so well!
We couldn’t leave a Big Bang Theory press room without getting our favorite superior elitist nerd to do something only for ScriptPhD.com fans. So here you have it, kids. From Jim Parsons, to you… a personal “Bazinga!”
Comics Design

One of THE most fascinating panels that we attended at Comic-Con so far was on the design secrets behind some of your favorite comics and book covers. A panel of some of the world’s leading designers revealed their methodologies (and sometimes failures) in the design process behind their hit pieces. An unparalleled purview into the mind of the designer, and the visual appeal that so often subliminally contributes to the success of a graphic novel, comic, or even regular book. We do, as it turns out, judge books by their covers.
We will be revealing each designer’s comments on their thought and art process, but are waiting for images from the panel to be emailed to us. So consider this a placeholder until we can finish this writeup and include it in Saturday or Sunday’s coverage. Stay tuned . . .
Graphic Novels: The Personal Touch
(From our correspondent Bryy Miller)

Some panels have mysterious names, some not so much. This one belongs in the latter category. There was no hidden meaning behind the phrase “personal touch.” This was all about the writers (Gabrielle Bell of Cecil & Jordan in New York, Howard Cruse of Stuck Rubber Baby, Vanessa Davis of Make Me A Woman, Larry Marder of Beanworld, Jilliam Tamaki of Skim, C. Tyler of You’ll Never Know, and moderator Shaenon Garrity of Skin Horse). More importantly and interestingly, it was about who they were. Some didn’t know who they were, others did, but they all knew one thing: that something inside of them needed to write.
Tamaki started off the discussion by stating perhaps the simplest answer of why she writes what she does, “I think that’s the only kind of book I wanna make.” Davis continued by adding that “anytime… it’s going to have a personal touch. Comics can soak up the people’s idiosyncrasies and sensibilities.” Marder, perhaps the odd man in the group, stated that even though his autobiography is a FANTASY, it still is an autobiography in the sense that it tells stories about his own feelings. Before anyone else could chime in, C. Tyler (arguably the oldest member of the panel) shot to life with an amazing amount of energy and playfulness. “I’ve taken autobiographies for granted.” she started “I know we’re at Comic-Con, but I hate superhero comics. When I read the first autobiographical comic, I was floored… it was disturbing and in a comic.” She went on to describe how she is fascinated with the idea of putting yourself out there, grabbing pieces of scraps from the table and showing us as if they were her life story – or even her creative process – in visual form. She would get extremely animated, and it really helped to humanize the element of the mysterious writer’s block and constant internal struggle to find how to portray your story. She ended her opening remarks with this, “the personal touch for me is I do it all by hand.”
Bell was the most reluctant to speak, but also, besides Tyler, the most visual. Not in the sense that she was very gesticulative or alive, but that she obviously was thinking very hard but having trouble in how to phrase her thoughts. “I try to cut my personal touch out,” she started, displaying the classic writer’s twitch of not looking directly at her audience “[I try to] make it universal. Professional.”
This instigated a very visceral response from Tyler, who on the spot tried to get into an earnest conversation with her fellow comic artist about what it means to be professional. Sadly, it didn’t last that long as Bell migrated back into thought. Cruse then brought up the point that, if your content is good, then mistakes in your craft are easily overlooked by a reader. The discussion (because calling it a panel at the end would just feel weird) had reached its time limit. Cruse gave some parting advice to young writers, “It will literally paralyze you to think of how many people have an idea similar to yours.” Marder stated that you have to fail in public. Garrity reminded everyone to heed that advice, as “Carol, Larry, and Howard have been in the comics since the seventies.”
Tyler let out a self-taunting gag.
Reign of the Dinosaurs

the Dinosaurs creative team (from left to right): Pete Von Sholly, Mishi McCaig,Tom DeRosier, David Krentz, Ricardo Delgado and Iain McCaig. (Executive producer Erik Nelson speaks on the jumbotron.)
In November of 2008, the hoi polloi at Discovery Channel approached producer Erik Nelson (Grizzly Man) with a simple request: “the ultimate kick-ass dinosaur show.” They poured enormous resources, creative and fiduciary, to create a television series that will truly break ground, both for Discovery Channel and its own medium. Scripted, yet unnarrated, scientifically stunning, yet bereft of the omniscient “talking head” paleontologist, Reign of the Dinosaurs is the ultimate exercise in “show don’t tell.” Premiering in the Spring of 2011, Reign will consist of 36 self-contained episodes erected from the art up. The stories will be chronological, detailing the rise, reign, and ultimate extinction (with a twist!) of the dinosaur species. But unlike the plethora of educational shows that cover the same topic, these will be rooted in storytelling, in treating the dinosaurs not as dinosaurs, but characters with whom we share an emotional connection. Trust me, having seen the first few world-premiere clips, you will care for these creatures, and the show will both exhilarate you and break your heart.
The true key to the success of Reign of the Dinosaurs was a dedication to amassing cream of the crop talent, formerly of Disney and Pixar, which allowed them to channel superlative animation and design talents towards an ambitious format. Along with Nelson, the team (and Comic-Con panel) consisted of renowned artists Ricardo Delgado (Dark Horse’s Age of Reptiles), Tom DeRosier (Lilo and Stitch, Mulan), self-proclaimed dinosaur nerd David Krentz (Disney’s Dinosaur, John Carter of Mars), Iain McCaig (Star Wars 1, 2, and 3), Mishi McCaig (Iron Man), Pete Von Sholly (The Mask, Darkman). Along with showing the audience their two (so-far) completed “cold open” teasers that will open episodes of the show, several of the animators simulated storyboard pitches (see picture below), just like the ones they would exchange in a writers’ room for several forthcoming episodes.

Several things impressed me upon the early viewing of Reign of the Dinosaurs, aside from the stunning art direction and well thought-out design. First of all, this show is really cheeky and funny. When the writers say that they’ll give the creatures personalities, they mean it, and it’s all done through expository action rather than showy narration. An early cold open has a dinosaur, trying to soothe her babies to sleep in the wee hours of the dawn, annoyed at the incessant chirping of a smaller dinosaur deep in the forest. Finally, she marches over and does what a dinosaur would do: bites the head off of her more annoying, diminutive co-habiting pest. Literally. Secondly, the stories pack an emotional wallop. A cinema-quality sequence shown at the end, taking place post-impact of the asteroid that ultimately killed off the dinosaurs, has the post-apocalyptic feel of Cormack McCarthy’s The Road (which the illustrator said influenced him) and visual appeal of Blade Runner. The ending, a hopeful coda on the extinction of the dinosaurs as an evolutionary stepping stone for our modern birds, had me sobbing. And then giving the panel a standing ovation.
Spring of 2011 is far away in television terms, but close enough for me to say this. Be excited, folks. Be very, very excited.
From the Press Room: Reign of the Dinosaurs

Not only did we get treated to a front-row preview of Reign of the Dinosaurs, ScriptPhD.com was extraordinarily fortunate to join the Discovery creative team for an intimate roundtable discussion panel after their panel. We were able to get enormous insight into the team’s collaborative process, storytelling aims, and dedication to balancing scientific accuracy with emotional connection, all while reinventing an entire medium. Ambitious? Just slightly.
One of the first things that impressed me upon talking to the Reign of the Dinosaurs team after their panel was their sheer dedication to, almost obsession with, “getting the science right.” Mishi McCaig and Iain McCaig spoke at length about the team’s dedication to nearing the line between science and entertainment. Hugely important to the project was the involvement of renowned University of Maryland paleontologist Thomas Holz, Jr., who cross-checks and gets pitched all the storyboard ideas. The behavior depicted in the show is speculative, but based on facts. This includes the animal’s muscle movements, how they would hunt prey, how they would interact—all aided by the paleontology knowledge of illustrator Dave Krentz. Ultimately, the team wants interest in the show to launch a more widespread educational initiative, which will include a Discovery multi-media website, and other supplementary materials to the show itself. Even when stories delve into the outrageous or fun, they’re rooted in research. A clip depicting high dinosaurs hallucinating was rooted in the marula tree, whose hallucinogenic fruit animals will eat and get high off of.
Producer Erik Nelson and illustrators Tom DeRosier and Ricardo Delgado spoke at length about the collaborative process of making the show, which they described like a TV writing room, only with animators. “Everyone’s sensibilities came together in a ‘hive mind’,” said Nelson. This visionary approach was important to the team, which is essentially trying to reinvent a TV genre. The last non-narrated, no-dialogue animated show was Walt Disney’s “Silly Symphonies” back in 1938. Needless to say, we’ve come a long way since then. The team was amazed at how constructing the dinosaurs’ stories moved them, comparing their effort to “March of the Penguins,” another simple vehicle showcasing animals that was rooted in an emotional audience response. This empathy for the dinosaurs peaks with the show’s conclusion, in which the dinosaurs die out (spoiler alert!), but which is still painted in an upbeat, survivalist way, as most geologists and paleontologists agree that modern birds are the direct evolutionary ancestors of dinosaurs.
“We’re not trying to hook you as a dinosaur person,” concluded Delgado. “We’re trying to hook you as a human being.”
Two last fun tidbits from today. Last year, on Day 3 of Comic-Con, we got geeky in the press room with our friend Barry of The Ugly Couch Show. When we saw each other again this year, we thought we’d start an annual tradition. So here it is, ladies and gentlemen. Two very tired, cranky, overworked press corps members getting silly in the press room:

And last, but definitely not least, is a very worthy Day 2 Costume of the Day. These ladies hit it out of the park. Bonus points if you can tell us which comics they’re representing:

Come back tomorrow for more geeky sci-fi fun! And don’t forget to become a fan of our Facebook fan page for extra Comic-Con photos and a chance to win amazing surprise swag when we get back from San Diego.
~*ScriptPhD*~
*****************
ScriptPhD.com covers science and technology in entertainment, media and advertising. Hire our consulting company for creative content development.
Subscribe to free email notifications of new posts on our home page.
]]>