
The last 25 years have brought an unprecedented level of scientific and technological advances, impacting virtually all dimensions of society, from communication and the digital revolution, to economics and food production to nanotechnology and medicine – and that’s just a start. The next few decades will rapidly expand this progress with exponential discovery and innovation, amidst more pressing global challenges than we’ve ever faced before. The opportunities to develop faster, better and cheaper products that improve modern living are limitless – Tesla electric cars, energy-saving fuels and machines, robotics – but they all share a common basic need for developing and studying materials in a more efficient manner. This will require a real-time acceleration of sharing, analytics and simulation through readily accessible databases. Essentially, an open-source wiki for materials scientists. In our in-depth article below, ScriptPhD.com explains why materials science is the most critical gateway towards 21st Century technology and how California startup company Citrine Informatics is providing revolutionary new information extraction software to create a crowdsourced, open access database available to any scientist.

There has been a public access revolution of sorts transforming science. A necessary one, at that. Science funding is in crisis. The peer-review process is under heavy scrutiny. And scientists are turning to transparency to help. Some notable billionaires are circumventing public funding and privatizing science. Molecular biologist Ethan Perlstein has used crowdfunding to raise hundreds of thousands of dollars from the public at large for a basic research lab. Last fall, as the Ebola crisis gripped the world’s attention, an expert researcher at The Scripps Research Institute (where I received a PhD) appealed to public crowd funding to raise $100,000 for vaccine research. With platforms like Experiment, RocketHub and KickStarter proliferating support for science, the public at large has begun to serve as an important incubator of innovation. More importantly, researchers are increasingly rethinking traditional academic publishing and recognizing the value of open data sharing through publications and databases. The Public Library of Science (PLoS) is the biggest non-profit advocate and publisher of open access research. Mainstream journals like Science have begun publishing free web-based alternatives that are immediately accessible. Calls for unified data sharing have grown louder and more widespread. Even the FDA has announced plans for crowdsourcing a genomics research platform to improve efficiency of diagnostic and clinical tests and their analysis. Far from hindering the scientific process and output, these efforts have accelerated alternative means of funding, data acquisition and exchange, collaboration and ultimately, discovery.

Think about virtually any practical aspect of life and it relies on materials. Transportation of any kind, Kevlar vests, sports equipment, communication devices, clothing, growing and making food… it’s impossible to think about modern society in even the most impoverished developing countries without them. Now think on a bigger scale. Superconductors. Carbon nanotubules. Graphene. The materials of the future that make even these breakthroughs obsolete. So crucial is materials science to all facets of economics, research and quality of life, that in 2011, the United States Government launched a Materials Genome Initiative. A partnership between the private sector industry, universities, and the government, its primary goal is to utilize a materials genome approach to cut the cost and time to market for basic materials products by 50%.

The only problem with materials research? Data. And lots of it. Aided largely by digital services and a proliferation of technology research – not to mention marketplace for the products that it makes possible – there is so much data produced today that the process of testing, developing, tweaking and inserting a material into a product takes about 20 years, according to the National Academy of Sciences. To combat this, materials scientists and engineers have growingly embraced a similar open access philosophy to that of life scientists. Leading science publisher Elsevier recently launched an infrastructure called “Open Data” to facilitate materials science data sharing across thirteen major publications. The Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory just created the world’s largest database of elastic properties, a virtual gold mine for scientists working on materials that require mechanical properties for things like cars and airplanes. NASA has even opened a Physical Science Informatics database of all of its space station materials research in the hopes that the crowdsourcing accelerates engineering research discovery, applicable both to space and Earth.
Citrine Informatics, a startup company in California, is hoping to unify these concepts of data sharing and mining through open access web-based software (boosted by crowdsourcing) to build a comprehensive, open database of materials and chemical data. Essentially, Citrine is rolling out a cloud platform (Citrination) that will act as a digital middle man between data acquisition and product development. And rather than storing it in vastly differing locations under differing access guidelines, Citrination’s algorithms gather all available data (from publications to databases to publicly shared data from private companies) in order to show properties under different conditions, including when they might fail. A simple, mainframe registry database allows users to upload data, build customized data sets and see all known properties of a particular material under all different physical conditions (see below). Rater than testing and retesting internal materials data internally, thus lengthening R&D pipelines, research labs can simply model based on available information and adjust experiments accordingly.
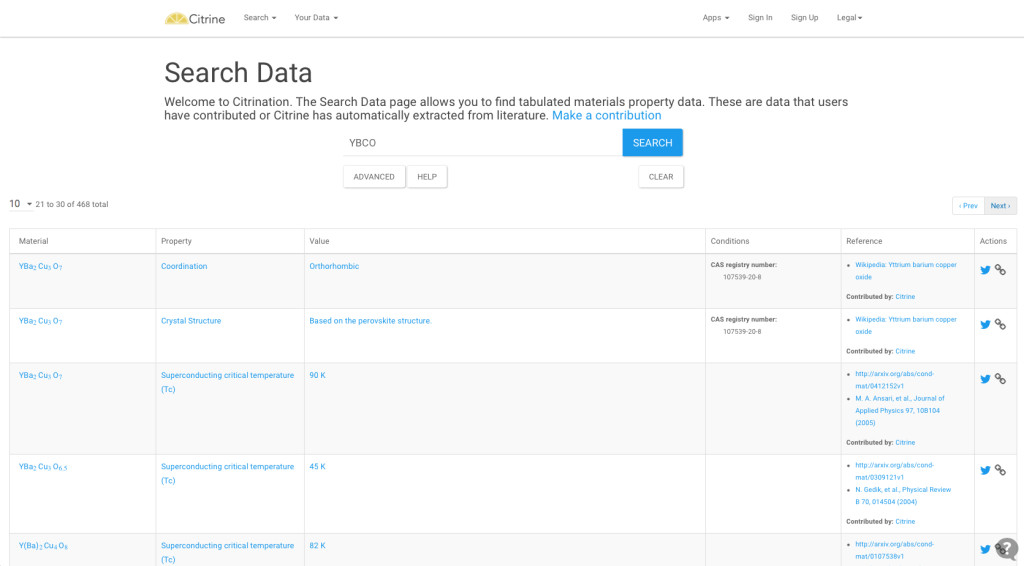
“What we do represents a big change in the status quo,” co-founder Bryce Meredig says. “A lot of the scientists in these industries don’t have a natural inclination to turn to software to solve these problems.” Until now. The software will be made free to not for profit research institutions and will sell to materials and chemical companies that want to avail themselves of the wealth of data. Citrine has used a large recent infusion of grant funding to raise their ambition beyond a database and towards applications like 3D printing, renewable energy technology (co-founder Greg Mulholland was recognized by Forbes as a 30 under 30 leader in energy) and the next generation of devices.
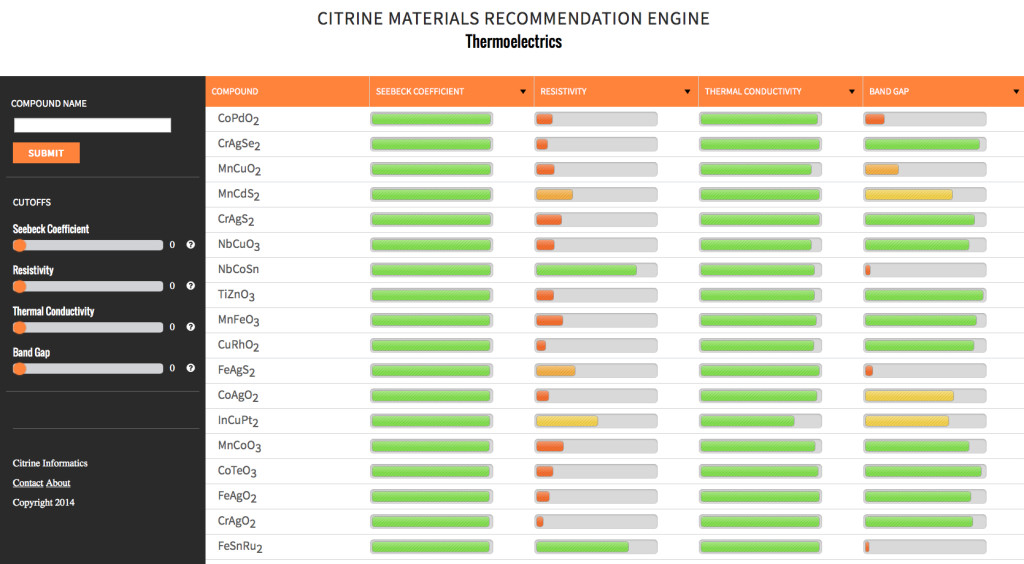
The practical benefits to society as a whole of extending open access and crowdsourcing to materials science are tremendous. On an individual level, virtually every computer and mobile device we put in our hands, every gadget and machine we buy in the future will depend on improved materials. On a more wide-scale level, materials will be at the forefront of solving the most complex, important challenges to our planet and its inhabitants, none more important than the energy crisis. Food production, water purification and distribution, transportation, infrastructure all will rely on creating sustainable energy. More ambitious endeavors such as space travel, medical treatments and advanced research collaborations will be even more reliant on new and improved materials. The faster that scientists, researchers and engineers are able to mine data from previous experiments, replicate it and design smarter studies based on computerized algorithms of how those materials behave, the faster they can produce breakthroughs in the laboratory and into the marketplace. The stakes are high. The scientific rewards are infinite. The time to open and use a free-access materials database is now.
This article was sponsored by Citrine Informatics.
*****************
ScriptPhD.com covers science and technology in entertainment, media and advertising. Hire our consulting company for creative content development. Follow us on Twitter and Facebook. Subscribe to our podcast on SoundCloud or iTunes.

Engineering has an unfortunate image problem. With a seemingly endless array of socioeconomic, technological and large-scale problems to address, and with STEM fields set to comprise the most lucrative 21st Century careers, studying engineering should be a no-brainer. Unfortunately, attracting a wide array of students — or even appreciating engineers as cool — remains difficult, most noticeably among women. When Google Research found out that the #2 reason girls avoid studying STEM fields is perception and stereotypes on screen, they decided to work with Hollywood to change that. Recently, they partnered with the National Academy of Sciences and USC’s prestigious Viterbi School of Engineering to proactively seek out ideas for creating a television program that would showcase a female engineering hero to inspire a new generation of female engineers. The project, entitled “The Next MacGyver,” came to fruition last week in Los Angeles at a star-studded event. ScriptPhD.com was extremely fortunate to receive an invite and have the opportunity to interact with the leaders, scientists and Hollywood representatives that collaborated to make it all possible. Read our full comprehensive coverage below.
“We are in the most exciting era of engineering,” proclaims Yannis C. Yortsos, the Dean of USC’s Engineering School. “I look at engineering technology as leveraging phenomena for useful purposes.” These purposes have been recently unified as the 14 Grand Challenges of Engineering — everything from securing cyberspace to reverse engineering the brain to solving our environmental catastrophes to ensuring global access to food and water. These are monumental problems and they will require a full scale work force to fully realize. It’s no coincidence that STEM jobs are set to grow by 17% by 2024, more than any other sector. Recognizing this opportunity, the US Department of Education (in conjunction with the Science and Technology Council) launched a five-year strategic plan to prioritize STEM education and outreach in all communities.

Despite this golden age, where the possibilities for STEM innovation seem as vast as the challenges facing our world, there is a disconnect in maximizing a full array of talent for the next generation of engineers. There is a noticeable paucity of women and minority students studying STEM fields, with women comprising just 18-20% of all STEM bachelor’s degrees, regardless of the fact that more students are STEM degrees than ever before. Madeline Di Nono, CEO of the Geena Davis Institute on Gender in Media and a judge at the Next MacGyver competition, boils a lot of the disinterest down to a consistent lack of female STEM portrayal in television and film. “It’s a 15:1 ratio of male to female characters for just STEM alone. And most of the science related positions are in life sciences. So we’re not showing females in computer science or mathematics, which is where all the jobs are going to be.” Media portrayals of women (and by proxy minorities) in science remains shallow, biased and appearance-focused (as profiled in-depth by Scientific American). Why does this matter? There is a direct correlation between positive media portrayal and STEM career participation.
It has been 30 years since the debut of television’s MacGyver, an action adventure series about clever agent Angus MacGyver, working to right the wrongs of the world through innovation. Rather than using a conventional weapon, MacGyver thwarts enemies with his vast array of scientific knowledge — sometimes possessing no more than a paper clip, a box of matches and a roll of duct tape. Creator Lee Zlotoff notes that in those 30 years, the show has run continuously around the world, perhaps fueled in part by a love of MacGyver’s endless ingenuity. Zlotoff noted the uncanny parallels between MacGyver’s thought process and the scientific method: “You look at what you have and you figure out, how do I turn what I have into what I need?” Three decades later, in the spirit of the show, the USC Viterbi School of Engineering partnered with the National Academy of Sciences and the MacGyver Foundation to search for a new MacGyver, a television show centered around a female protagonist engineer who must solve problems, create new opportunities and most importantly, save the day. It was an initiative that started back in 2008 at the National Academy of Sciences, aiming to rebrand engineering entirely, away from geeks and techno-gadget builders towards an emphasis on the much bigger impact that engineering technology has on the world – solving big, global societal problems. USC’s Yortsos says that this big picture resonates distinctly with female students who would otherwise be reluctant to choose engineering as a career. Out of thousands of submitted TV show ideas, twelve were chosen as finalists, each of whom was given five minutes to pitch to a distinguished panel of judges comprising of writers, producers, CEOs and successful show runners. Five winners will have an opportunity to pair with an established Hollywood mentor in writing a pilot and showcasing it for potential production for television.

If The Next MacGyver feels far-reaching in scope, it’s because it has aspirations that stretch beyond simply getting a clever TV show on air. No less than the White House lent its support to the initiative, with an encouraging video from Chief Technology Officer Megan Smith, reiterating the importance of STEM to the future of the 21st Century workforce. As Al Roming, the President of the National Academy of Engineering noted, the great 1950s and 1960s era of engineering growth was fueled by intense competition with the USSR. But we now need to be unified and driven by the 14 grand challenges of engineering and their offshoots. And part of that will include diversifying the engineering workforce and attracting new talent with fresh ideas. As I noted in a 2013 TEDx talk, television and film curry tremendous power and influence to fuel science passion. And the desire to marry engineering and television extends as far back as 1992, when Lockheed and Martin’s Norm Augustine proposed a high-profile show named LA Engineer. Since then, he has remained a passionate advocate for elevating engineers to the highest ranks of decision-making, governance and celebrity status. Andrew Viterbi, namesake of USC’s engineering school, echoed this imperative to elevate engineering to “celebrity status” in a 2012 Forbes editorial. “To me, the stakes seem sufficiently high,” said Adam Smith, Senior Manager of Communications and Marketing at USC’s Viterbi School of Engineering. “If you believe that we have real challenges in this country, whether it is cybersecurity, the drought here in California, making cheaper, more efficient solar energy, whatever it may be, if you believe that we can get by with half the talent in this country, that is great. But I believe, and the School believes, that we need a full creative potential to be tackling these big problems.”
So how does Hollywood feel about this movement and the realistic goal of increasing its array of STEM content? “From Script To Screen,” a panel discussion featuring leaders in the entertainment industry, gave equal parts cautionary advice and hopeful encouragement for aspiring writers and producers. Ann Merchant, the director of the Los Angeles-based Science And Entertainment Exchange, an offshoot of the National Academy of Sciences that connects filmmakers and writers with scientific expertise for accuracy, sees the biggest obstacle facing television depiction of scientists and engineers as a connectivity problem. Writers know so few scientists and engineers that they incorporate stereotypes in their writing or eschew the content altogether. Ann Blanchard, of the Creative Artists Agency, somewhat concurred, noting that writers are often so right-brain focused, that they naturally gravitate towards telling creative stories about creative people. But Danielle Feinberg, a computer engineer and lighting director for Oscar-winning Pixar animated films, sees these misconceptions about scientists and what they do as an illusion. When people find out that you can combine these careers with what you are naturally passionate about to solve real problems, it’s actually possible and exciting. Nevertheless, ABC Fmaily’s Marci Cooperstein, who oversaw and developed the crime drama Stitchers, centered around engineers and neuroscientists, remains optimistic and encouraged about keeping the doors open and encouraging these types of stories, because the demand for new and exciting content is very real. Among 42 scripted networks alone, with many more independent channels, she feels we should celebrate the diversity of science and medical programming that already exists, and build from it. Put together a room of writers and engineers, and they will find a way to tell cool stories.

At the end of the day, Hollywood is in the business of entertaining, telling stories that reflect the contemporary zeitgeist and filling a demand for the subjects that people are most passionate about. The challenge isn’t wanting it, but finding and showcasing it. The panel’s universal advice was to ultimately tell exciting new stories centered around science characters that feel new, flawed and interesting. Be innovative and think about why people are going to care about this character and storyline enough to come back each week for more and incorporate a central engine that will drive the show over several seasons. “Story does trump science,” Merchant pointed out. “But science does drive story.”
The twelve pitches represented a diverse array of procedural, adventure and sci-fi plots, with writers representing an array of traditional screenwriting and scientific training. The five winners, as chosen by the judges and mentors, were as follows:
Miranda Sajdak — Riveting
Sajdak is an accomplished film and TV writer/producer and founder of screenwriting service company ScriptChix. She proposed a World War II-era adventure drama centered around engineer Junie Duncan, who joins the military engineer corps after her fiancee is tragically killed on the front line. Her ingenuity and help in tackling engineering and technology development helps ultimately win the war.

Beth Keser, PhD — Rule 702
Dr. Keser, unique among the winners for being the only pure scientist, is a global leader in the semiconductor industry and leads a technology initiative at San Diego’s Qualcomm. She proposed a crime procedural centered around Mimi, a brilliant scientist with dual PhDs, who forgoes corporate life to be a traveling expert witness for the most complex criminal cases in the world, each of which needs to be investigated and uncovered.
Jayde Lovell — SECs (Science And Engineering Clubs)
Jayde, a rising STEM communication star, launched the YouTube pop science network “Did Someone Say Science?.” Her show proposal is a fun fish-out-of-water drama about 15-year-old Emily, a pretty, popular and privileged high school student. After accidentally burning down her high school gym, she forgoes expulsion only by joining the dreaded, geeky SECs club, and in turn, helping them to win an engineering competition while learning to be cool.
Craig Motlong — Q Branch
Craig is a USC-trained MFA screenwriter and now a creative director at a Seattle advertising agency. His spy action thriller centered around mad scientist Skyler Towne, an engineer leading a corps of researchers at the fringes of the CIA’s “Q Branch,” where they develop and test the gadgets that will help agents stay three steps ahead of the biggest criminals in the world.
Shanee Edwards — Ada and the Machine
Shanee, an award-winning screenwriter, is the film reviewer at SheKnows.com and the host/producer of the web series She Blinded Me With Science. As a fan of traditional scientific figures, Shanee proposed a fictionalized series around real-life 1800s mathematician Ada Lovelace, famous for her work on Charles Babbage’s early mechanical general-purpose computer, the Analytical Engine. In this drama, Ada works with Babbinge to help Scotland Yard fight opponents of the industrial revolution, exploring familiar themes of technology ethics relevant to our lives today.
Craig Motlong, one of five ultimate winners, and one of the few finalists with absolutely no science background, spent several months researching his concept with engineers and CIA experts to see how theoretical technology might be incorporated and utilized in a modern criminal lab. He told me he was equal parts grateful and overwhelmed. “It’s an amazing group of pitches, and seeing everyone pitch their ideas today made me fall in love with each one of them a little bit, so I know it’s gotta be hard to choose from them.”

Whether inspired by social change, pragmatic inquisitiveness or pure scientific ambition, this seminal event was ultimately both a cornerstone for strengthening a growing science/entertainment alliance and a deeply personal quest for all involved. “I don’t know if I was as wrapped up in these issues until I had kids,” said USC’s Smith. “I’ve got two little girls, and I tried thinking about what kind of shows [depicting female science protagonists] I should have them watch. There’s not a lot that I feel really good sharing with them, once you start scanning through the channels.” Motlong, the only male winner, is profoundly influenced by his experience of being surrounded by strong women, including a beloved USC screenwriting instructor. “My grandmother worked during the Depression and had to quit because her husband got a job. My mom had like a couple of options available to her in terms of career, my wife wanted to be a genetic engineer when she was little and can’t remember why she stopped,” he reflected. “So I feel like we are losing generations of talent here, and I’m on the side of the angels, I hope.” NAS’s Ann Merchant sees an overarching vision on an institutional level to help achieve the STEM goals set forth by this competition in influencing the next generation of scientist. “it’s why the National Academy of Sciences and Engineering as an institution has a program [The Science and Entertainment Exchange] based out of Los Angeles, because it is much more than this [single competition].”
Indeed, The Next MacGyver event, while glitzy and glamorous in a way befitting the entertainment industry, still seemed to have succeeded wildly beyond its sponsors’ collective expectations. It was ambitious, sweeping, the first of its kind and required the collaboration of many academic, industry and entertainment alliances. But it might have the power to influence and transform an entire pool of STEM participants, the way ER and CSI transformed renewed interest in emergency medicine and forensic science and justice, respectively. If not this group of pitched shows, then the next. If not this group of writers, then the ones who come after them. Searching for a new MacGyver transcends finding an engineering hero for a new age with new, complex problems. It’s about being a catalyst for meaningful academic change and creative inspiration. Or at the very least opening up Hollywood’s eyes and time slots. Zlotoff, whose MacGyver Foundation supported the event and continually seeks to promote innovation and peaceful change through education opportunities, recognized this in his powerful closing remarks. “The important thing about this competition is that we had this competition. The bell got rung. Women need to be a part of the solution to fixing the problems on this planet. [By recognizing that], we’ve succeeded. We’ve already won.”
The Next MacGyver event was held at the Paley Center For Media in Beverly Hills, CA on July 28, 2015. Follow all of the competition information on their site. Watch a full recap of the event on the Paley Center YouTube Channel.
*****************
ScriptPhD.com covers science and technology in entertainment, media and advertising. Hire our consulting company for creative content development. Follow us on Twitter and Facebook. Subscribe to our podcast on SoundCloud or iTunes.