
Space exploration is enjoying its greatest popularity revival since the Cold War, both in entertainment and the realm of human imagination. Thanks in large part to blockbusters like Gravity, The Martian and Interstellar, not to mention privatized innovation from companies like SpaceX, and fascination with inter-galactic colonization has never been more trenchant. Despite the brimming enthusiasm, there hasn’t been a film or TV series that has tackled the subject matter in a nuanced way. Until now. The Expanse, ambitiously and faithfully adapted by SyFy Channel from the best-selling sci-fi book series, is the best space epic series since Battlestar Galactica. It embraces similar complex, grandiose and ethically woven storylines of human survival and morality amidst inevitable technological advancement. Below, a full ScriptPhD review and in-depth podcast with The Expanse showrunner Naren Shankar.
200 years in future, humans have successfully colonized space, but not without discord. The Earth, overpopulated and severely crunched for resources, has expanded to the asteroid belt and a powerful, wealthy and now-autonomous Mars. Though the colonies of the asteroid belt are controlled by Earth (largely to pillage materials and water), its denizens are second-class citizens, exploited by wealthy corporations for deadly labor. Inter-colony friction, class warfare, resource allocation and uprising frame the backdrop for a political standoff between Mars and Earth that could destroy humanity.
Deeper questions of righteous terrorism, political conspiracy and human rights are embodied in a triumvirate of smart, interweaving plots that will eventually coalesce to unravel the fundamental mystery. Josephus Miller (Thomas Jane) is a great detective, but a lowly belter and miserable alcoholic, mostly paid to settle minor Belt security and corporate matters. But when he’s hired to botch an investigation into the disappearance of a wealthy Earth magnate’s family, Miller starts to uncover dangerous connections between political unrest and the missing heiress. Jim Holden (Steven Strait) is a reluctant hero – a “Belter” ship captain thrown into a tragic quest for justice – who unwittingly leads his mates directly into the conflict between Mars and Earth and, as he delves deeper, unravels a potentially calamitous galactic threat. Finely balancing this tightwire is Chrisjen Avasarala (Shohreh Aghdashloo), the Deputy Undersecretary of the United Nations, who must balance the moral quandaries of peacekeeping with a steely determination to avoid war at all costs.

Colonization is a very trendy topic right now in space and astrophysics circles, particularly on Mars, having discovered liquid water, which fosters favorable conditions for the evolution and sustainability of life. Could it ever actually happen? There would certainly be considerable engineering and habitability obstacles.
For now, modest manned exploration of Mars and Europa by human astronauts is a tentative first step for NASA.
The Expanse assumes all these challenges and explorations have ben overcome, and picks up at a time when humans biggest problem isn’t conquering space – it’s conquering each other. The show is sleek and very technologically adept, in direct visual contrast to the more dilapidated environment of Battlestar Galactica. Fans of geek chic technology can ogle at complex docking stations as ships move around the belt to and from Earth and Mars, see through tablets, pills that induce omniscience during interrogations and ubiquitous voice-controlled artificial intelligence. However, though a new way of life has been established, remnants of our current quotidian existence and human essence are still instantly recognizable. This isn’t the techno-invasive dystopia of Blade Runner or Minority Report.

Like, Battlestar Galactica, (a show The Expanse will invariably be compared to) there is a crisp, smart overarching commentary on human existentialism under tense circumstances. Survival and life in space. Adapting to the changing gravitational forces and physical conditions of travel between planets and the asteroid belt colonies. Most importantly, navigating the incendiary dynamics of a species on the brink of all-out galactic warfare. As show runner Naren Shankar mentions in our podcast below, all great sci-fi is historically rooted in allegory – the exploration of disruptive technological innovation (and the fear thereof) as a symbol of combating inequality and/or political injustice. At a time of great social upheaval in our world, a fight for dwindling global resources and against proliferating environmental devastation, many of the themes explored in The Expanse books and series are eerily salient. Perhaps they also act as a reminder that even if a technological revolution facilitates an eventual expansion into outer space, our tapestry of inclinations (good and bad) is sure to follow.
Naren Shankar, the executive producer and show runner of The Expanse, helped develop the adaptation of the sci-fi series buoyed by decades of merging the creative compasses of science and entertainment. A PhD-educated physicist and engineer, Shankar was a writer/producer on Star Trek: The Next Generation, Almost Human and Grimm, as well as a co-showrunner of the groundbreaking forensics procedural CSI. Dr. Shankar exclusively joined the ScriptPhD.com podcast to discuss his transition from PhD scientist to working Hollywood writer, the lasting iconic impact of Star Trek and CSI and how The Expanse evokes the best allegory and elements of the sci-fi genre to tell an existential narrative. Listen below:
*****************
ScriptPhD.com covers science and technology in entertainment, media and advertising. Hire our consulting company for creative content development. Follow us on Twitter and Facebook. Subscribe to our podcast on SoundCloud or iTunes.

Dr. Kevin Grazier has made a career of studying intergalactic planetary formation, and, over the last few years, helping Hollywood writers integrate physics smartly into storylines for popular TV shows like Battlestar Galactica, Eureka, Defiance and the blockbuster film Gravity. His latest book, Hollyweird Science: From Quantum Quirks to the Multiverse traverses delightfully through the science-entertainment duality as it first breaks down the portrayal of science in movies and television, grounding the audience in screenplay lexicon, then elucidates a panoply of physics and astronomy principles through the lens of storylines, superpowers and sci-fi magic. With the help of notable science journalist Stephen Cass, Hollyweird Science is accessible to the layperson sci-fi fan wishing to learn more about science, a professional scientist wanting to apply their knowledge to higher-order examples from TV and film or Hollywood writers and producers of future science-based materials. From case studies, to in-depth interviews to breaking down the Universe and its phenomena one superhero and far-away galaxy at a time, this first volume of an eventual trilogy is the essential foundation towards understanding how science is integrated into a story and ensuring that future TV shows and movies do so more accurately than ever before. Full ScriptPhD review and podcast with author and science advisor Dr. Grazier below.
Most people who watch movies and TV shows never went to film school. They are not familiar with the intricacies of three-act structure, tropes, conceits and MacGuffins that are the skeletal framework of a standard storytelling toolkit. Yet no genre is more rooted in and dependent on setup and buying into a payoff than sci-fi and films conceptualized in scientific logic. Many, if not most, critiques of science in entertainment don’t fully acknowledge that integrating abstruse science/technology with the complex constraints of time, length, character development and screenplay format is incredibly demanding. Hollyweird Science does point out some egregious examples of “information pollution” and the “Hollywood Curriculum Cycle” – the perpetuation bad, if not fictitious, science. But after grounding the reader in a primer of the fundamental building blocks of movie-making and TV structure, not only is there a more positive, forgiving tone in breaking down the history of the sci-fi canon (some of which predicted many of the technological gadgets we enjoy today), but even a celebration of just how much and how often Hollywood gets the science right.

Conversely, the vast majority of Hollywood writers, producers and directors don’t regularly come across PhD scientists in real life, and have to form impressions of doctors, scientists and engineers based on… other portrayals in entertainment. Scientists, after all, represent only 0.2 percent of the U.S. population as a whole, and less than 700,000 of all jobs belong to doctors and surgeons. And while these professions are amply represented on screen in number, that’s not necessarily been the case in accuracy. The insular self-reliance of screenwriters on their own biases has led to stereotyping and pigeonholing of scientists into a series of familiar archetypes (nerds, aloof omniscient sidekicks), as Grazier and Cass take us through a thorough, labyrinthine archive of TV and movie scientists. But as scientists have become more involved in advising productions, and have become more prominent and visible in today’s innovation-driven society, their on screen counterparts have likewise become a more accurate reflection of these demographics – mainstream hits like The Big Bang Theory, CSI (and its many procedural spinoffs), Breaking Bad and films like Gravity, The Martian, Interstellar and The Imitation Game are just a recent sampling.

If you’re going to teach a diverse group of readers about the principles of physics, astronomy, quantum mechanics and energy forms, it’s best to start with the basics. Even if you’ve never picked up a physics textbook, Hollyweird Science provides a fundamental overview of matter, mass, elements, energy, planet and star formation, time, radiation and the quantum mechanics of universe behavior. More important than what these principles are, Grazier discerns what they are not, with running examples from iconic television series, movies and sci-fi characters. What exactly is the difference between weight and mass and force, per the opening scene of the film Gravity? How are different forms of energy classified? Are the radioactive giants of Godzilla and King Kong realistic? What exactly happens when Scotty is beamed up? Buoying the analytical content are a myriad of interviews with writers and producers, expounding honestly about working with scientists, incorporating science into storytelling and where conflicts arose in the creative process.

People who want to delve into more complex science can do so through “science boxes” embedded throughout the book – sophisticated mathematical and physics analyses of entertainment staples, trivial and significant. Among my favorites: why Alice in Wonderland is a great example of allometric scaling, the thermal radiation of cinematography lighting, hypothesizing Einsteinian relativity for the Back To The Future DeLorean, and just how hot is The Human Torch in the Fantastic Four? (Pretty dang hot.)
The next time readers see an asteroid making a deep impact, characters zipping through interplanetary travel, or an evil plot to harbor a new form of destructive energy, they’ll have a scientific foundation to ask simple, but important, questions. Is this reasonable science, rooted in the principles of physics? Even if embellished for the sake of advancing a story, could it theoretically happen? And for Hollywood writers, how can science advance a plot or help a character solve their connundrum? In our podcast below, Dr. Grazier explains why physics and astronomy were such an important bedrock of the first book – and of science-based entertainment – and previews what other areas of science, technology and medicine future sequels will analyze.
In the long run, Hollyweird Science will serve as far more than just a groundbreaking book, regardless of its rather seamless nexus between fun pop culture break-down and serious scientific didactic tool. It’s a part of a conceptual bridge towards an inevitable intellecutal alignment between Hollywood, science and technology. Over the last 10-15 years, portayal of scientists and ubiquity of science content has increased exponentially on screen – so much so, that what was a fringe niche even 20 years ago is now mainstream and has powerful influence in public perception and support for science. Science and technology will proliferate in importance to society, not just in the form of personal gadgets, but as problem-solving tools for global issues like climate change, water access and advancing health quality. Moreover, at a time when Americans’ grasp of basic science is flimsy, at best, any material that can repurpose the universal love of movies and television to impart knowledge and generate excitement is significant. We are at the precipice of forging a permanent link between Hollywood, science and pop culture. The Hollyweird series is the perfect start.

In an exclusive podcast conversation with ScriptPhD.com, Dr. Grazier discussed the overarching themes and concepts that influenced both “Hollyweird Science” and his ongoing consulting in the entertainment industry. These include:
•How the current Golden Age of sci-fi arose and why there’s more science and technology content in entertainment than ever
•Why scientists and screenwriters are remarkably similar
•Why physics and astronomy are the building blocks of the majority of science fiction
•How the “Hollyweird Science” trilogy can be used as a didactic tool for scientists and entertainment figures
•His favorite moments working both in science and entertainment
*****************
ScriptPhD.com covers science and technology in entertainment, media and advertising. Hire our consulting company for creative content development. Follow us on Twitter and Facebook. Subscribe to our podcast on SoundCloud or iTunes.

The Martian, is a film adaptation of the inventive, groundbreaking hard sci-fi adventure tale. Like Robinson Crusoe on Mars, it’s a triumph of engineering and basic science, a love letter to innovation and the greatest feats humans are capable of through collaboration. Directed by sci-fi legend Ridley Scott, and following in the footsteps of space epics Gravity and Interstellar, The Martian offers a stunning virtual imagination of Mars, glimpses of NASA’s new frontier – astronauts on Mars – and the stakes of a mission that will soon become a reality. Below, ScriptPhD.com reviews The Martian (an Editor’s Selection) and, with the help of a planetary researcher at The California Science Center, we break down some basics about Mars missions and the planetary science depicted in the film (interactive video).
That the film version of The Martian even exists is a testament to the unlikely success story of Andy Weir’s novel. A self-described science geek and gainfully employed computer programmer, he started writing a novel on the side, self-publishing chapter by chapter on an independent website. Word spread naturally, readers flocked, eventually, a completed book found a publisher and inevitably Hollywood came calling. Sounds about as realistic as… an astronaut being abandoned on a planet and having to make his own way back to Earth. But this is the exact fast-paced, thrilling plot behind one of the biggest hard sci-fi adventures of all time. Amidst an unexpected Martian sand storm, the crew of Ares 3 (the third fictionalized manned mission to Mars) becomes separated and erroneously thinks one of their members, Mark Watney, has died. They scramble to evacuate the red planet, leaving him very much alive with minimal food, water and tools to fend for himself and no communication to speak of.

With chemistry, botany, physics, engineering, home garage junk science and some self-deprecating humor, Watney must protect himself in the harsh Martian setting, figure out a way to let NASA know he’s alive, craft an escape plan, all while managing to overcome one after another devastating setback. At its heart, The Martian is a pure self-reliant survival tale, a staple of popular fiction. Despite its space setting and unapologetically elaborate scientific plot, it’s a story about a really smart guy who is – in the words of one of the many 70s disco songs throughout – stayin’ alive.
The movie adaptation remains mostly faithful to the central plot, necessarily trimming a few of Mark Watney’s perilous side adventures and unnecessarily supplanting Weir’s sardonic dialogue and one liners. The film sometimes lacks the ubiquitous sense of immediate urgency and desperation present throughout the book, but it makes up for it with more polished transitions and the ability to “think big” that is unique to cinema and critical to a science fiction. Most importantly, Matt Damon (as Watney) ably juggles vulnerability, scientific confidence and geek-chic sarcasm of an iconic sci-fi character.
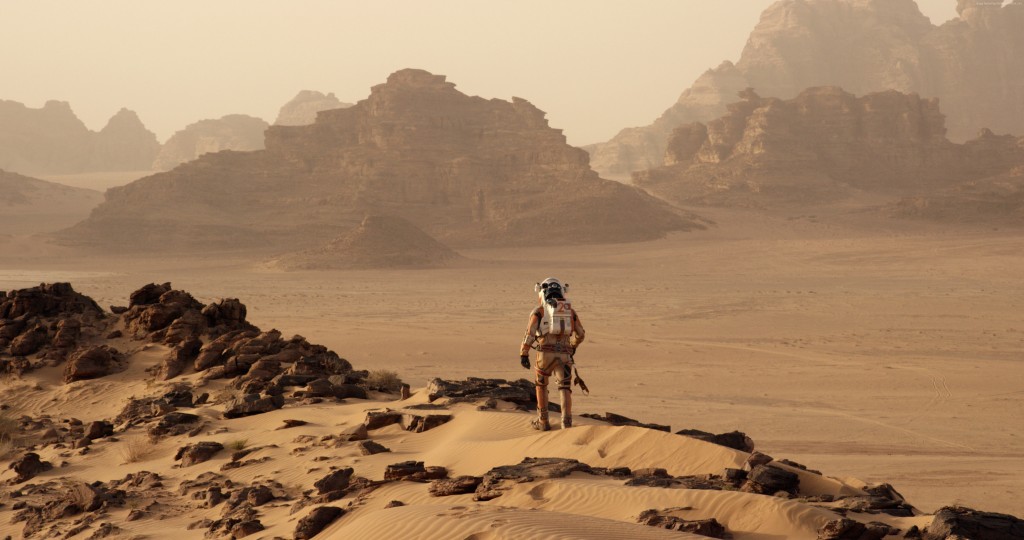

One of the strengths of Weir’s book is the reader’s ability to visualize every detail of the Mars landscape and its phenomena through intricate first-person storytelling. The most important transition from such a detailed book to film is translating that visual realm, from the rolling red Martian plains and hills to the contrast of the confined space shuttle his crew is in to the chaotic flurry of NASA and the Jet Propulsion Laboratory. The vastness of the Martian terrain, incurring both abject loneliness and giddy awe in Watney (with whom we spend the majority of the film) is brilliantly rendered by Scott’s wide angles and grand, sweeping shots. It renders more power to a scene in which the astronaut, unsure if he’ll make it out alive, asks that his parents be told how happy he still is as a scientist, despite everything. “Tell them I love what I do. It’s important. It’s bigger than me.” In that moment, we truly believe him.
For a narrative in which the main character is forced to “science the s—t” out of his predicament, not knowing that back on Earth NASA is doing the very same, one would expect an endless supply of science and technology magic. In that regard, neither the book nor the movie disappoints. But what is truly surprising is the degree of plausibility and accuracy woven throughout the space survival tale. While all recent space films, including Gravity and Interstellar, have been meticulously well researched and inventive, The Martian compounds imagination with incredible scientific reality. For one thing, much of the technology already used by NASA is incorporated into the story. For another, author Andy Weir and director Ridley Scott reaffirmed how hard they worked to get the science right. “Originally The Martian was a serial that I had posted on my website chapter-by-chapter,” said author Weir. “If there were errors in the physics or chemistry problems or whatever, [my readers] would email me. It was great. I got sort of crowd-sourced fact checking. And while some of the science is still not quite air-tight, not only does The Martian take its science very seriously, it managed to thoroughly impress the toughest customer of all – NASA itself!
(For a full Mars primer and breakdown of the planetary science seen in the film, see ScriptPhD.com’s excusive video below.)

With all of the people furiously working to keep Watney alive – the NASA ground crew, Jet Propulsion Laboratory engineers, the Ares 3 crew, and even Watney himself – the real hero and main star of The Martian is science itself. Science facilitates Watney’s survival of the initial Martian storm, allows him to generate food and water to stay alive, traverse the unforgiving landscape and engineer a series of clever technological adaptations to establish communication and series of hopeful escape plans. Most importantly, it allows for an unlikely international alliance to save Watney. “It just goes to show,” [NASA Director] Teddy [Sander] said. “Love of science is universal across all cultures.” This important line from the book is reiterated in the film.
NASA has stated that it aspires to execute a manned mission to Mars by about 2030, a project no doubt buoyed by the exciting revelation that the Curiosity rover has found evidence of flowing water nearby. Expensive, dangerous missions, however, rely on public support for momentum – particularly because NASA research is publicly funded. And movies are often an important cultural gateway to engender and grow such support. NASA advisors of sci-fi film The Europa Report hoped it would inspire a real mission someday. One of ScriptPhD’s favorites from the last few years, Moon, and ambitious sci-fi hit Interstellar have the potential to re-ignite a new space race.
In an exclusive podcast with ScriptPhD.com a few years ago, noted astronomer and science communicator Brian Cox fervently advocated that NASA embrace its greatest challenge to date – manned exploration of Mars: because it’s hard, because we are meant to push the boundaries of the far edges of our galactic frontiers, because space exploration is the greatest universal manifestation of our ability to innovate and engineer. To the extent that The Martian manages to inspire and ignite this idea wih the mainstream public, it will stake claim as more than just a sci-fi benchmark. It will be seen as a catalyst for exploration history. After all, NASA did just announce plans to finally explore life on Jupiter’s moon Europa as depicted in Stanley Kubrik’s classic 2001: A Space Odyssey.
Interested in learning more about all the planetary science that goes into executing a Mars mission? The likelihood of Watney’s survival and some of the technical and scientific feats he pulls off on the red planet? I was privileged to head out to the California Science Center, location of the first ever Viking Mars rover prototype, to break down the science of Mars missions with Devin Waller, a planetary scientist and former Mars researcher.
*****************
ScriptPhD.com covers science and technology in entertainment, media and advertising. Hire our consulting company for creative content development. Follow us on Twitter and Facebook. Subscribe to our podcast on SoundCloud or iTunes.

Engineering has an unfortunate image problem. With a seemingly endless array of socioeconomic, technological and large-scale problems to address, and with STEM fields set to comprise the most lucrative 21st Century careers, studying engineering should be a no-brainer. Unfortunately, attracting a wide array of students — or even appreciating engineers as cool — remains difficult, most noticeably among women. When Google Research found out that the #2 reason girls avoid studying STEM fields is perception and stereotypes on screen, they decided to work with Hollywood to change that. Recently, they partnered with the National Academy of Sciences and USC’s prestigious Viterbi School of Engineering to proactively seek out ideas for creating a television program that would showcase a female engineering hero to inspire a new generation of female engineers. The project, entitled “The Next MacGyver,” came to fruition last week in Los Angeles at a star-studded event. ScriptPhD.com was extremely fortunate to receive an invite and have the opportunity to interact with the leaders, scientists and Hollywood representatives that collaborated to make it all possible. Read our full comprehensive coverage below.
“We are in the most exciting era of engineering,” proclaims Yannis C. Yortsos, the Dean of USC’s Engineering School. “I look at engineering technology as leveraging phenomena for useful purposes.” These purposes have been recently unified as the 14 Grand Challenges of Engineering — everything from securing cyberspace to reverse engineering the brain to solving our environmental catastrophes to ensuring global access to food and water. These are monumental problems and they will require a full scale work force to fully realize. It’s no coincidence that STEM jobs are set to grow by 17% by 2024, more than any other sector. Recognizing this opportunity, the US Department of Education (in conjunction with the Science and Technology Council) launched a five-year strategic plan to prioritize STEM education and outreach in all communities.

Despite this golden age, where the possibilities for STEM innovation seem as vast as the challenges facing our world, there is a disconnect in maximizing a full array of talent for the next generation of engineers. There is a noticeable paucity of women and minority students studying STEM fields, with women comprising just 18-20% of all STEM bachelor’s degrees, regardless of the fact that more students are STEM degrees than ever before. Madeline Di Nono, CEO of the Geena Davis Institute on Gender in Media and a judge at the Next MacGyver competition, boils a lot of the disinterest down to a consistent lack of female STEM portrayal in television and film. “It’s a 15:1 ratio of male to female characters for just STEM alone. And most of the science related positions are in life sciences. So we’re not showing females in computer science or mathematics, which is where all the jobs are going to be.” Media portrayals of women (and by proxy minorities) in science remains shallow, biased and appearance-focused (as profiled in-depth by Scientific American). Why does this matter? There is a direct correlation between positive media portrayal and STEM career participation.
It has been 30 years since the debut of television’s MacGyver, an action adventure series about clever agent Angus MacGyver, working to right the wrongs of the world through innovation. Rather than using a conventional weapon, MacGyver thwarts enemies with his vast array of scientific knowledge — sometimes possessing no more than a paper clip, a box of matches and a roll of duct tape. Creator Lee Zlotoff notes that in those 30 years, the show has run continuously around the world, perhaps fueled in part by a love of MacGyver’s endless ingenuity. Zlotoff noted the uncanny parallels between MacGyver’s thought process and the scientific method: “You look at what you have and you figure out, how do I turn what I have into what I need?” Three decades later, in the spirit of the show, the USC Viterbi School of Engineering partnered with the National Academy of Sciences and the MacGyver Foundation to search for a new MacGyver, a television show centered around a female protagonist engineer who must solve problems, create new opportunities and most importantly, save the day. It was an initiative that started back in 2008 at the National Academy of Sciences, aiming to rebrand engineering entirely, away from geeks and techno-gadget builders towards an emphasis on the much bigger impact that engineering technology has on the world – solving big, global societal problems. USC’s Yortsos says that this big picture resonates distinctly with female students who would otherwise be reluctant to choose engineering as a career. Out of thousands of submitted TV show ideas, twelve were chosen as finalists, each of whom was given five minutes to pitch to a distinguished panel of judges comprising of writers, producers, CEOs and successful show runners. Five winners will have an opportunity to pair with an established Hollywood mentor in writing a pilot and showcasing it for potential production for television.

If The Next MacGyver feels far-reaching in scope, it’s because it has aspirations that stretch beyond simply getting a clever TV show on air. No less than the White House lent its support to the initiative, with an encouraging video from Chief Technology Officer Megan Smith, reiterating the importance of STEM to the future of the 21st Century workforce. As Al Roming, the President of the National Academy of Engineering noted, the great 1950s and 1960s era of engineering growth was fueled by intense competition with the USSR. But we now need to be unified and driven by the 14 grand challenges of engineering and their offshoots. And part of that will include diversifying the engineering workforce and attracting new talent with fresh ideas. As I noted in a 2013 TEDx talk, television and film curry tremendous power and influence to fuel science passion. And the desire to marry engineering and television extends as far back as 1992, when Lockheed and Martin’s Norm Augustine proposed a high-profile show named LA Engineer. Since then, he has remained a passionate advocate for elevating engineers to the highest ranks of decision-making, governance and celebrity status. Andrew Viterbi, namesake of USC’s engineering school, echoed this imperative to elevate engineering to “celebrity status” in a 2012 Forbes editorial. “To me, the stakes seem sufficiently high,” said Adam Smith, Senior Manager of Communications and Marketing at USC’s Viterbi School of Engineering. “If you believe that we have real challenges in this country, whether it is cybersecurity, the drought here in California, making cheaper, more efficient solar energy, whatever it may be, if you believe that we can get by with half the talent in this country, that is great. But I believe, and the School believes, that we need a full creative potential to be tackling these big problems.”
So how does Hollywood feel about this movement and the realistic goal of increasing its array of STEM content? “From Script To Screen,” a panel discussion featuring leaders in the entertainment industry, gave equal parts cautionary advice and hopeful encouragement for aspiring writers and producers. Ann Merchant, the director of the Los Angeles-based Science And Entertainment Exchange, an offshoot of the National Academy of Sciences that connects filmmakers and writers with scientific expertise for accuracy, sees the biggest obstacle facing television depiction of scientists and engineers as a connectivity problem. Writers know so few scientists and engineers that they incorporate stereotypes in their writing or eschew the content altogether. Ann Blanchard, of the Creative Artists Agency, somewhat concurred, noting that writers are often so right-brain focused, that they naturally gravitate towards telling creative stories about creative people. But Danielle Feinberg, a computer engineer and lighting director for Oscar-winning Pixar animated films, sees these misconceptions about scientists and what they do as an illusion. When people find out that you can combine these careers with what you are naturally passionate about to solve real problems, it’s actually possible and exciting. Nevertheless, ABC Fmaily’s Marci Cooperstein, who oversaw and developed the crime drama Stitchers, centered around engineers and neuroscientists, remains optimistic and encouraged about keeping the doors open and encouraging these types of stories, because the demand for new and exciting content is very real. Among 42 scripted networks alone, with many more independent channels, she feels we should celebrate the diversity of science and medical programming that already exists, and build from it. Put together a room of writers and engineers, and they will find a way to tell cool stories.

At the end of the day, Hollywood is in the business of entertaining, telling stories that reflect the contemporary zeitgeist and filling a demand for the subjects that people are most passionate about. The challenge isn’t wanting it, but finding and showcasing it. The panel’s universal advice was to ultimately tell exciting new stories centered around science characters that feel new, flawed and interesting. Be innovative and think about why people are going to care about this character and storyline enough to come back each week for more and incorporate a central engine that will drive the show over several seasons. “Story does trump science,” Merchant pointed out. “But science does drive story.”
The twelve pitches represented a diverse array of procedural, adventure and sci-fi plots, with writers representing an array of traditional screenwriting and scientific training. The five winners, as chosen by the judges and mentors, were as follows:
Miranda Sajdak — Riveting
Sajdak is an accomplished film and TV writer/producer and founder of screenwriting service company ScriptChix. She proposed a World War II-era adventure drama centered around engineer Junie Duncan, who joins the military engineer corps after her fiancee is tragically killed on the front line. Her ingenuity and help in tackling engineering and technology development helps ultimately win the war.

Beth Keser, PhD — Rule 702
Dr. Keser, unique among the winners for being the only pure scientist, is a global leader in the semiconductor industry and leads a technology initiative at San Diego’s Qualcomm. She proposed a crime procedural centered around Mimi, a brilliant scientist with dual PhDs, who forgoes corporate life to be a traveling expert witness for the most complex criminal cases in the world, each of which needs to be investigated and uncovered.
Jayde Lovell — SECs (Science And Engineering Clubs)
Jayde, a rising STEM communication star, launched the YouTube pop science network “Did Someone Say Science?.” Her show proposal is a fun fish-out-of-water drama about 15-year-old Emily, a pretty, popular and privileged high school student. After accidentally burning down her high school gym, she forgoes expulsion only by joining the dreaded, geeky SECs club, and in turn, helping them to win an engineering competition while learning to be cool.
Craig Motlong — Q Branch
Craig is a USC-trained MFA screenwriter and now a creative director at a Seattle advertising agency. His spy action thriller centered around mad scientist Skyler Towne, an engineer leading a corps of researchers at the fringes of the CIA’s “Q Branch,” where they develop and test the gadgets that will help agents stay three steps ahead of the biggest criminals in the world.
Shanee Edwards — Ada and the Machine
Shanee, an award-winning screenwriter, is the film reviewer at SheKnows.com and the host/producer of the web series She Blinded Me With Science. As a fan of traditional scientific figures, Shanee proposed a fictionalized series around real-life 1800s mathematician Ada Lovelace, famous for her work on Charles Babbage’s early mechanical general-purpose computer, the Analytical Engine. In this drama, Ada works with Babbinge to help Scotland Yard fight opponents of the industrial revolution, exploring familiar themes of technology ethics relevant to our lives today.
Craig Motlong, one of five ultimate winners, and one of the few finalists with absolutely no science background, spent several months researching his concept with engineers and CIA experts to see how theoretical technology might be incorporated and utilized in a modern criminal lab. He told me he was equal parts grateful and overwhelmed. “It’s an amazing group of pitches, and seeing everyone pitch their ideas today made me fall in love with each one of them a little bit, so I know it’s gotta be hard to choose from them.”

Whether inspired by social change, pragmatic inquisitiveness or pure scientific ambition, this seminal event was ultimately both a cornerstone for strengthening a growing science/entertainment alliance and a deeply personal quest for all involved. “I don’t know if I was as wrapped up in these issues until I had kids,” said USC’s Smith. “I’ve got two little girls, and I tried thinking about what kind of shows [depicting female science protagonists] I should have them watch. There’s not a lot that I feel really good sharing with them, once you start scanning through the channels.” Motlong, the only male winner, is profoundly influenced by his experience of being surrounded by strong women, including a beloved USC screenwriting instructor. “My grandmother worked during the Depression and had to quit because her husband got a job. My mom had like a couple of options available to her in terms of career, my wife wanted to be a genetic engineer when she was little and can’t remember why she stopped,” he reflected. “So I feel like we are losing generations of talent here, and I’m on the side of the angels, I hope.” NAS’s Ann Merchant sees an overarching vision on an institutional level to help achieve the STEM goals set forth by this competition in influencing the next generation of scientist. “it’s why the National Academy of Sciences and Engineering as an institution has a program [The Science and Entertainment Exchange] based out of Los Angeles, because it is much more than this [single competition].”
Indeed, The Next MacGyver event, while glitzy and glamorous in a way befitting the entertainment industry, still seemed to have succeeded wildly beyond its sponsors’ collective expectations. It was ambitious, sweeping, the first of its kind and required the collaboration of many academic, industry and entertainment alliances. But it might have the power to influence and transform an entire pool of STEM participants, the way ER and CSI transformed renewed interest in emergency medicine and forensic science and justice, respectively. If not this group of pitched shows, then the next. If not this group of writers, then the ones who come after them. Searching for a new MacGyver transcends finding an engineering hero for a new age with new, complex problems. It’s about being a catalyst for meaningful academic change and creative inspiration. Or at the very least opening up Hollywood’s eyes and time slots. Zlotoff, whose MacGyver Foundation supported the event and continually seeks to promote innovation and peaceful change through education opportunities, recognized this in his powerful closing remarks. “The important thing about this competition is that we had this competition. The bell got rung. Women need to be a part of the solution to fixing the problems on this planet. [By recognizing that], we’ve succeeded. We’ve already won.”
The Next MacGyver event was held at the Paley Center For Media in Beverly Hills, CA on July 28, 2015. Follow all of the competition information on their site. Watch a full recap of the event on the Paley Center YouTube Channel.
*****************
ScriptPhD.com covers science and technology in entertainment, media and advertising. Hire our consulting company for creative content development. Follow us on Twitter and Facebook. Subscribe to our podcast on SoundCloud or iTunes.

Ray Bradbury, one of the most influential and prolific science fiction writers of all time, has had a lasting impact on a broad array of entertainment culture. In his canon of books, Bradbury often emphasized exploring human psychology to create tension in his stories, which left the more fantastical elements lurking just below the surface. Many of his works have been adapted for movies, comic books, television, and the stage, and the themes he explores continue to resonate with audiences today. The notable 1966 classic film Fahrenheit 451 perfectly captured the definition of a futuristic dystopia, for example, while the eponymous television series he penned, The Ray Bradbury Theatre, is an anthology of science fiction stories and teleplays whose themes greatly represented Bradbury’s signature style. ScriptPhD.com was privileged to cover one of Ray Bradbury’s last appearances at San Diego Comic-Con, just prior to his death, where he discussed everything from his disdain for the Internet to his prescient premonitions of many technological advances to his steadfast support for the necessity of space exploration. In the special guest post below, we explore how the latest Bradbury adapataion, the new television show The Whispers, continues his enduring legacy of psychological and sci-fi suspense.
Premiering to largely positive reviews, ABC’s new show The Whispers is based on Bradbury’s short story “Zero Hour” from his book The Illustrated Man. Both stories are about children finding a new imaginary friend, Drill, who wants to play a game called “Invasion” with them. The adults in their lives are dismissive of their behavior until the children start acting strangely and sinister events start to take place. Bradbury’s story is a relatively short read with just a few characters that ends on a chilling note, while The Whispers seeks to extend the plot over the course of at least one season, and to that end it features an expanded cast including journalists, policemen, and government agents.

The targeting of young, impressionable minds by malevolent forces is deeply disturbing, and it seems entirely plausible that parents would write off odd behavior or the presence of imaginary friends as a simple part of growing up. In both the story and the show, the adults do not realize that they are dealing with a very real and tangible threat until it’s too late. The dread escalates when the adults realize that children who don’t know each other are all talking to the same person. The fear of the unknown, merely hinted at in Bradbury’s story, will seem to be exploited to great effect during the show’s run.
When “Zero Hour” was written in 1951, America was in the midst of McCarthyism and the Red Scare, and the fear of Communism and homosexuality ran rampant. As the tensions of the Cold War grew, so too did the anxiety that Communists had infiltrated American society, with many of the most aggressively targeted individuals for “un-American” activities belonging to the Hollywood filmmaking and writing communities. Bradbury’s story shares with many other fictions of the time period a healthy dose of paranoia and fear around possession and mind control. Indeed, Fahrenheit 451, a parable about a futuristic world in which books are banned, is also a parable about the dangers of censorship and political hysteria.

The makers of The Whispers recognize that these concerns still permeate our collective consciousness, and have updated the story with modern subject matter, expanding the subject of our apprehension to state surveillance and abuse of authority. To wit, many recent films and shows have explored similar themes amidst the psychological ramifications of highly developed artificial intelligence and its ability to control and even harm humans. Our concurrent obsession with and fear of technology run amok is another topic explored by Ray Bradbury in many of his later works. The idea that those around us are participating in a grand scheme that will bring us harm still sows seeds of discontent and mistrust in our minds. For that reason, the concept continues to be used in suspense television and cinema to this day.
One of the reasons Bradbury’s work continues to serve as the inspiration for so much contemporary entertainment is his use of everyday situations and human oddities to create intrigue. One such example is a 5-issue series called Shadow Show based on Bradbury’s work, released in 2014 by comic book publisher IDW. Some of the best artists, writers and comics had agreed to participate in this project since Bradbury had such a huge influence in their writing and art. In this anthology, Harlan Ellison’s “Weariness” perfectly elicits Bradbury’s dystopia in which our main characters experience the universe’s end. The terrifying end of life as we know it is one of Bradbury’s recurring themes, depicted in writings like The Martian Chronicles. He rarely felt the need to set his stories in faraway galaxies or adorn them with futuristic gadgets. Most of his writing focussed on the frightening aspects of humans in quotidien surroundings, such as in the 2002 novel, Let’s All Kill Constance. Much of The Whispers takes place in an ordinary suburban neighborhood, and like many of his stories, what seems at first to be a simple curiosity, is hiding something much more complex and frightening.
Fiction that brings out the spookiness inherent in so many facets of human nature creates a stronger and more enduring bond with its audience, since we can easily deposit ourselves into the characters’ situations, and all of a sudden we find that we’re directly experiencing their plight on an emotional level. That’s always been, as Bradbury well knew, the key to great suspense.
Maria Ramos is a tech and sci-fi writer interested in comic books, cycling, and horror films. Her hobbies include cooking, doodling, and finding local shops around the city. She currently lives in Chicago with her two pet turtles, Franklin and Roy. You can follow her on Twitter @MariaRamos1889.
*****************
ScriptPhD.com covers science and technology in entertainment, media and advertising. Hire our consulting company for creative content development. Follow us on Twitter and Facebook. Subscribe to our podcast on SoundCloud or iTunes.

From a sci-fi and entertainment perspective, 2015 may undoubtedly be nicknamed “The Year of The Robot.” Several cinematic releases have already explored various angles of futuristic artificial intelligence (from the forgettable Chappie to the mainstream blockbuster Marvel’s Avengers: Age of Ultron to the intelligent sleeper indie hit Ex Machina), with several more on the way later this year. Two television series premiering this summer, limited series Humans on AMC and Mr. Robot on USA add thoughtful, layered (and very entertaining) discussions on the ethics and socio-economic impact of the technology affecting the age we live in. While Humans revolves around hyper-evolved robot companions, and Mr. Robot a singular shadowy eponymous cyberhacking organization, both represent enthusiastic Editor’s Selection recommendations from ScriptPhD. Reviews and an exclusive interview with Humans creators/writers Jonathan Brackley and Sam Vincent below.

Never in human history has technology and its potential reached a greater permeation of and importance in our daily lives than at the current moment. Indeed, it might even be changing the way our brains function! With entertainment often acting as a reflection of socially pertinent issues and zeitgeist motifs, it’s only natural to examine the depths to which robots (or any artificial technology) might subsume human life. Will they take over our jobs? Become smarter than us? Nefariously affect human society? These fears about the emotional lines between humans and their technology are at the heart of AMC’s new limited series Humans. It is set in the not-too-distant future, where the must have tech accessory is a ‘synth,’ a highly malleable, impeccably programmed robotic servant capable of providing any services – at the individual, family or macro-corporate level. It’s an idyllic ambition, fully realized. Busy, dysfunctional parents Joe and Laura obtain family android Anita to take care of basic housework and child rearing to free up time. Beat cop Pete’s rehabilitation android is indispensable to his paralyzed wife. And even though he doesn’t want a new synth, scientist George Millikan is thrust with a ‘care unit’ Vera by the Health Service to monitor his recovery from a stroke. They can pick fruit, clean up trash, work mindlessly in factories and sweat shops make meals, even provide service in brothels – an endless range of servile labor that we are uncomfortable or unwilling to do ourselves.

Humans brilliantly weaves the problems of this artificial intelligence narrative into multiple interweaving story lines. Anita may be the perfect house servant to Joe, but her omniscience and omnipresence borders on creepiness to wife Laura (and by proxy, the audience). Is Dr. Millikan (who helped craft the original synth technology) right that you can’t recycle them the way you would an old iPhone model? Or is he naive for loving his synth Odi like a son? And even if you create a Special Technologies Task Force to handle synth-related incidents, guaranteeing no harm to humans and minimal, if any, malfunctions, how can there be no nefarious downside to a piece of technology? They could, in theory, be obtained illegally and reprogrammed for subversive activity. If the original creator of the synths wanted to create a semblance of human life – “They were meant to feel,” he maintains – then are we culpable for their enslaved state? Should we feel relieved to see a synth break out of the brothel she’s forced to work in, or another mysterious group of synths that have somehow become sentient unite clandestinely to dream of a dimension where they’re free?
In reality, we already are in the midst of an age of artificial intelligence – computers. Powerful, fast, already capable of taking over our workforce and reshaping our society, they are the amorphous technological preamble to more specifically tailored robots, incurring all of the same trepidation and uncertainty. Mr. Robot, one of the smartest TV pilots in recent memory, is a cautionary tale about cyberhacking, socioeconomic vulnerability and the sheer reliance our society unknowingly places in computers. Its central themes are physically embodied in the central character of Elliot, a brilliant cybersecurity engineer by day/vigilante cyberhacker by night, battling schizophrenia and extreme social anxiety. To Elliott, the ubiquitous nature of computer power is simultaneously appealing and repulsive. Everything is electronic today – money, corporate transactions, even the way we communicate socially. As a hacker, he manipulates these elements with ease to get close to people and to solve injustice (carrying a Dexter-style digital cemetery of his conquests). But as someone who craves human contact he loathes the way technology has deteriorated human interaction and encouraged nameless, faceless corporate greed.

Elliot works for Allstate Security, whose biggest client is an emblem of corporate evil and economic diffidence. When they are hacked, Elliot discovers that it’s a private digital call to arms by a mysterious underground group called Mr. Robot (resembling the cybervigilante group Anonymous). They’ve hatched a plan to to concoct a wide-scale economic cyber attack that will result in the single biggest redistribution of wealth and debt forgiveness in history, and recruited Elliot into their organization. The question, and intriguing premise of the series, is whether Elliot can juggle his clean-cut day job, subversive underground hacking and protecting society one cyberterrorist act at a time, or if they will collapse under the burden of his conscience and mental illness.

Humans is a purview into the inevitable future, albeit one that may be creeping on us faster than we want it to. Even if hyper-advanced artificial intelligence is not an imminent reality and our fears might be overblown, the impact of technology on economics and human evolution is a reality we will have to grapple with eventually. And one that must inform the bioethics of any advanced sentient computing technology we create and release into the world. Mr. Robot is a stark reminder of our current present, that cyberterrorism is the new normal, that its global impact is immense, and (as with the case of artificial robots), our advancement of and reliance on technology is outpacing humans’ ability to control it.
ScriptPhD.com was extremely fortunate to chat directly with Humans writers Jonathan Brackley and Sam Vincent about the premise and thematic implications of their show. Here’s what they had to say:
ScriptPhD.com: Is “Humans” meant to be a cautionary tale about the dangers of complex artificial intelligence run amok or a hypothetical bioethical exploration of how such technology would permeate and affect human society?
Jonathan and Sam: Both! On one level, the synths are a metaphor for our real technology, and what it’s doing to us, as it becomes ever more human-like and user-friendly – but also more powerful and mysterious. It’s not so much hypothesising as it is extrapolating real world trends. But on a deeper story level, we play with the question – could these machines become more, and if so, what would happen? Though “run amok” has negative connotations – we’re trying to be more balanced. Who says a complex AI given free rein wouldn’t make things better?
SPhD: I found it interesting that there’s a tremendous range of emotions in how the humans related to and felt about their “synths.” George has a familial affection for his, Laura is creeped out/jealous of hers while her husband Joe is largely indifferent, policeman Peter grudgingly finds his synth to be a useful rehabilitation tool for his wife after an accident. Isn’t this reflective of the range of emotions in how humans react to the current technology in our lives, and maybe always will?
J&S: There’s always a wide range of attitudes towards any new technology – some adopt enthusiastically, others are suspicious. But maybe it’s become a more emotive question as we increasingly use our technology to conduct every aspect of our existence, including our emotional lives. Our feelings are already tangled up in our tech, and we can’t see that changing any time soon.
SPhD: Like many recent works exploring Artificial Intelligence, at the root of “Humans” is a sense of fear. Which is greater – the fear of losing our flaws and imperfections (the very things that make us human) or the genuine fear that the sentient “synths” have of us and their enslavement?
J&S: Though we show that synths certainly can’t take their continued existence for granted, there’s as much love as fear in the relationships between our characters. For us, the fear of how our technology is changing us is more powerful – purely because it’s really happening, and has been for a long time. But maybe it’s not to be feared – or not all of it at least…
Catch a trailer and closer series look at the making of Humans here:
And catch the FULL first episode of Mr. Robot here:
Mr. Robot airs on USA Network with full episodes available online.
Humans premieres on June 28, 2015 on AMC Television (USA) and airs on Channel 4 (UK).
*****************
ScriptPhD.com covers science and technology in entertainment, media and advertising. Hire our consulting company for creative content development. Follow us on Twitter and Facebook. Subscribe to our podcast on SoundCloud or iTunes.
Every so often, a seminal film comes out that ends up being the hallmark of its genre. 2001: A Space Odyssey redefined space and technology in science fiction. Star Wars proved sci-fi could provide blockbuster material, while Blade Runner remains the standard-bearer for post-apocalyptic dystopia. A slate of recent films have broached varying scenarios involving artificial intelligence – from talking robots to sentient computers to re-engineered human capacity. But Ex Machina, the latest film from Alex Garland (writer of the pandemic horror film 28 Days Later and the astro-thriller Sunshine) is the cream of the crop. A stylish, stripped-down, cerebral film, Ex Machina weaves through the psychological implications of an experimental AI robot named Ava possessing preternatural emotional intelligence and free will. It’s a Hitchcockian sci-fi thriller for the geek chic gadget-bearing age, a vulnerable expository inquiry into the isolated meaning of “sentience” (something we will surely contend with in our time) and an honest reproach of technology’s boundless capabilities that somehow manages to celebrate them at the same time.

ScriptPhD.com’s enthusiastic review of this visionary new sci-fi film includes an exclusive Q&A with writer and director Alex Garland from a recent Los Angeles screening.
The preoccupation with superior artificial intelligence as a thematic idea is not a recent phenomenon. After all, Frankenstein is one of the pillars of science fiction – an ode to hypothetical human engineering gone awry. Terminator and its many offshoots gave rise to robotics engineering, whether as saviors or disruptors of humanity. But over the last 16 months, a proliferation of films centered around the incorporation of artificial intelligence in the ongoing microevolution of humanity has signaled a mainstream arrival into the zeitgeist consciousness. 2014 was highlighted with stylish and ambitious but ultimately overmatched digital reincarnation film Transcendence to the understated yet brilliant digital love story Her to the surprisingly smart Disney film Big Hero 6. This year amplifies that trend, with Avengers: Age of Ultron and Chappie marching out robots Elon Musk could only dream about among many other later releases. Wedged in-between is Ex Machina, taking its title from the Latin Deus Ex Machina (God from the machine), a film that prefers to focus on the bioethics and philosophy of scientific limits rather than the razzle-dazzle technology itself. There is still a tendency for sci-fi films concerning AI to engross themselves in presenting over-the-top science, with ensuing wholesale consequences based on theoretical technology, which ultimately hinders storytelling. Ex Machina is a simple story about two male humans, a very advanced-intelligence generated AI robot named Ava, confined in a remote space together, and the life-changing consequences that their interactions engender as a parable for the meaning of humanity. It will be looked back on as one of the hallmark films about AI.
When computer programmer Caleb Smith (Domhall Gleeson) wins an exclusive private week with his search engine company’s CEO Nathan Bateman (Oscar Isaac) it seems like a dream come true. He is helicoptered to the middle of a verdant paradise, where Nathan lives as a recluse in a locked-down, self-sufficient compound. Only Nathan plans to let Caleb be the first to perform a Turing Test on an advanced humanistic robot named Ava (Alicia Vikander). (Incidentally, the technology of creating a completely new robot for cinema was a remarkable process, as the filmmakers discussed in-depth in the New York Times.) The opportunity sounds like a geek’s dream come true, only as the layers slowly peel back, it is apparent that Caleb’s presence is no accident; indeed, the methodology for how Nathan chose him is directly related to the engineering of Ava. Nathan is, depending on your viewpoint, at best a lonely eccentric and at worst an alcoholic lunatic.

For two thirds of the movie, tension is primarily ratcheted through Caleb’s increasingly tense interviews with Ava. She’s smart, witty, curious and clearly has a crush on him. Is something like Ava even possible? Depending on who you ask, maybe not or maybe it already happened. But no matter. The latter third of the movie provides one breathtaking twist after another. Who is testing and manipulating whom? Who is really the “intelligent being” of the three? Are we right to be cautionary and fear AI, even stop it in its tracks before it happens? With seemingly anodyne versions of “helpful robots” already in existence, and social media looking into implementing AI to track our every move, it may be a matter of when, not if.
The brilliance of Alex Garland’s sci-fi writing is his understanding that understated simplicity drives (and even heightens) dramatic tension. Too many AI and techno-futuristic films collapse under the crushing weight of over-imagined technological aspirations, which leave little room for exploring the ramifications thereof. We start Ex Machina with the simple premise that a sentient, advanced, highly programmed robot has been made. She’s here. The rest of the film deftly explores the introspective “what now?” scenarios that will grapple scientists and bio-ethicists should this technology come to pass. What is sentience and can a machine even possess self-awareness? Is their desire to be free of the grasp of their creators wrong and should we allow it? Most importantly, is disruptive AI already here in the amorphous form of social media, search history and private data collected by big technology companies?

The vast majority of Ex Machina consists of the triumvirate of Nathan, Caleb and Ava, toggling between scenes with Nathan and Caleb and Caleb interviewing (experimenting on?) Ava between a glass facade. The progression of intensity in the numbered interviews that comprise the Turing Test are probably the most compelling of the whole film, and nicely set-up the shocking conclusion. In its themes of the human/AI dichotomy and dialogue-heavy tone, Ex Machina compares a lot to last year’s brilliant sci-fi film Her, which rightfully won Spike Jonze the Oscar for Best Original Screenplay. In the former, a lonely professional letter writer becomes attached to and eventually falls in love with his computer operating system Samantha. Eventually, we see the limitations of a relationship void of human contact and the peculiar idiosyncrasies that make us so distinct, the very elusive elements that Samantha seeks to know and understand. (Think this scenario is far off? Many tech developers feel it is not only inevitable but not too far away.To that degree, both of these films show two kinds of sentient future technology chasing after human-ness, yearning for it, yet caution against a bleak future where they supplant it. But whereas Her does so in a sweetly melancholy sentimental fashion, Ex Machina plants a much darker, psychologically prohibitive conclusion.
It turns out that the most terrifying scenario isn’t a world in which artificial intelligence disrupts our lives through a drastic shift in technology. It’s a world in which technology seamlessly integrates itself into the lives we already know.
View the official Ex Machina trailer here:
Alex Garland, writer and director of Ex Machina, stayed after a recent Los Angeles press screening to give an insightful, profound question and answer session about the artificial intelligence as portrayed in the film and its relationship to the recent slew of works depicting interactive technology.
Ava [the robot created by Nathan Bateman] knew what a “good person” was. Why wasn’t she programmed by Nathan to just obey the commandments and not commit certain terrible acts that she does in the film?
AG: The same reason that we aren’t programmed that way. We are asked not to [sin] by social conventions, but no one instructs or programs us not to do it. And yet, a lot of us do bad things. Also, I think what you’re asking is – is Ava bad? Has she done something wrong? And I think that depends on how you choose to look at the movie. I’ve been doing stories for a while, and you hand the story over and you’ve got your intentions but I’ve been doing it for long enough to know that people bring their own [bias] into it.
The way I saw this movie was it was all about this robot – the secret protagonist of the movie. It’s not about these two guys. That’s a trick; an expectation based on the way it’s set up. And if you see the story from her point of view, if her is the right word, she’s in a prison, and there’s the jailer and the jailer’s friend and what she wants to do is get out. And I think if you look at it from that perspective what she does isn’t bad, it’s practical. Yes, she tricks them, but that’s okay. They shouldn’t have been dumb. If you arrive in life in this place, and desire to get out, I think her actions are quite legitimate.
So, that’s a very human-like quality. So let’s say that you’re confronted with a life or death situation with artificial intelligence. Do you have any tricks that you would use [to survive]?

AG: If I’m hypothetically attacked by an AI, I don’t know… run. I think the real question is whether AI is scary. Should we fear them? There’s a lot of people who say we should. Some smarter people than me such as Elon Musk, Stephen Dawkins, and I understand that. This film draws parallels with nuclear power and [Oppenheimer’s caution]. There’s a latent danger there in both. Yet, again, I think it depends on how you frame it. One version of this story is Frankenstein, and that story is a cautionary tale – a religious one at that. It’s saying “Man, don’t mess with God’s creationary work. It’s the wrong thing to do.”
And I framed this differently in my mind. It’s an act of parenthood. We create new conciousnesses on this planet all the time – everyone in this room, everyone on the planet is a product of other people having created this consciousness. If you see it that way, then the AI is the extension of us, not separate from us. A product of us, of something we’ve chosen to do. What would you expect or want of your child? At the bare minimum, you’d want for them to outlive you. The next expectation is that their life is at least as good as yours and hopefully better. All of these things are a matter of perspective. I’m not anti-AI. I think they’re going to be more reasonable than us, potentially in some key respects. We do a lot of unreasonable stuff and they may be fairer.
On the subject of reproduction, in this film, Ava was anatomically correct. Had it been a male, would he have been likewise built correctly?
AG: If you made the male AI in accordance with the experiment that this guy is trying to conduct, then yes. This film is an “ideas movie.” Sometimes it’s asking a question and then presenting an answer, like “Does she have empathy?” or “Is she sentient?”. Sometimes, there isn’t an answer to the question, either because I don’t know the answer or because no one does. The question you’re framing is not “Can you [have sex] with these AI?” it’s “Where does the gender reside?” Where does gender exist in all of us. Is it in the mind, or in the body? It would be easy to construct an argument that Ava has no gender and it would seem reasonable in many respects. You could take her mind and put it in a male body and say “Well, nothing is substantially changed. This is a cosmetic difference between the two.” And yet, then you start to think about how you talk about her and how you perceive her. And to say “he” of Ava just seems wrong. And to say “it” seems weirdly disrespectful. And you end up having this genderless thing coming back to she.
In addition, if you’re going to say gender is in the mind, then demonstrate it. That’s the question I’m trying to provoke. When they have that conversation halfway through the film, these implicit questions, if gender is in the mind, then what is it? Does a man think differently from a woman? Is that really true? Think of something that a man would always think, and you’ll find a man that doesn’t always think that, and you’ll find a woman that does. These are the implicit questions in the film. They don’t all have answers. The key thing about the gender thing isn’t about who is having sex with whom. It’s that this young man is tasked with thinking about what’s going on inside of this machine’s head. That’s his job is to figure that out. And at a certain point he stops thinking about her and he gets it wrong. That’s the issue – why does he stop thinking about it? If the plot shifts in this worked on the audience or any of you in the same way as they worked on the young man, why was that?
Was one of your implicit messages in the film for people to be more conscientious about what they’re sharing on the internet, whether in their searches or social media, and thereby identifying their interests “out there” and how that might be potentially used?
AG: Yes, absolutely. It’s a strange thing, what zeitgeist is. Movies take ages [to make] sometimes – like two and a half years at least. I first wrote this script about four years ago. And then, I find out as we go through production that we’re actually late to the party. There are a whole bunch of films about AI – Transcendance, Automator, Big Hero 6, Age of Ultron [coming out next month], Chappie. Why is that? There hasn’t been any breakthrough in AI, so why are all these people doing this at the same time? And I think it’s not AIs, I think it’s search engines. I think it’s because we’ve got laptops and phones and we, those of us outside of tech, don’t really understand how they work. But we have a strong sense that “they” understand how “we” work. They anticipate stuff about us, they target us with advertising, and I think that makes us uneasy. And I think that these AI stories that are around are symptomatic of that.
That bit in the film about [the dangers of internet identity], in a way it obliquely relates to Edward Snowden, and drawing attention to what the government is doing. But if people get sufficiently angry, they can vote out the government. That is within the power of an electorate. Theoretically, in capitalist terms, consumers have that power over tech companies, but we don’t really. Because that means not having a mobile phone, not having a tablet, a computer, a credit card, a television, and so on. There is something in me that is worried about that. I actually like the tech companies, because I think they’re kind of like NASA in the 1960s. They’re the people going to the moon. That’s great – we wanted to go to the moon. But I’m also scared of them, because they’ve got so much power and we tend not to cope well with a lot of power. So yes, that’s all in the film.
You mentioned Elon Musk earlier, who looks a little bit like [Google co-founder] Sergei Brin. Which tech executive would you say CEO Nathan Batemn is most modeled after?
AG: He wasn’t exactly modeled after an exec. He was modeled more like the companies in some respect. All that “dude, bro” stuff. I sometimes feel that’s what they’re doing. Not to generalize, but it’s a little bit like that – we’re all buddies, come on, dude. While it’s rifling through my wallet and my address book. It’s misleading, a mixed message. I don’t want to sound paranoid about tech companies. I do really like them, I think they’re great. But I think it’s correct to be ambivalent about them. Because anything which is that powerful and that unmarshalled you have to be suspicious of, not even for what we know they’re doing but for what they might do. So, Nathan is more [representative of] a vibe than a person.
For someone equally as scared of AI as Alex is of tech companies, what is the gap between human intelligence and AI intelligence that exists today? How long before we have AI as part of our daily lives?
AG: One of the great pleasures of working on this film was contacting and discussing with people who are at the edge of AI research. I don’t think we’re very close at all. It depends on what you’re talking about. General AI, yes, we’re getting closer. Sentient machines, it’s not even in the ballpark. It’s similar in my mind to a cure for cancer. You can make progress and move forward, but sometimes by going forward it highlights that the goal has receded by complexity. I know Ray Kurtzweil makes some sort of quantified predictions – in 20 years, we’ll be there. I don’t know how you can do that. He’s a smart guy, maybe he’s right. As far as I can tell, in talking to the people who are as close to knowing [about the subject] as I can encounter, it’s something that may or may not happen. And it will probably take a while.
One of the things that’s always bothered me about the Turing Test is that it’s not seeking to know whether or not the thing you’re dealing with is an artificial intelligence. It’s – can you tell that it is? And that’s always bothered me as a kind of weird test. You have a 20,000 question survey, and in the end this one decision comes from a binary point of view. It seems almost flawed.
AG: Yes, you’re completely right. Apart from the fact that it was configured quite a long time ago, it’s primarily a test to see if you can pass the Turing Test. It doesn’t carry information about sentience or potential intelligence. And you could certainly game it. But, it’s also incredibly difficult to pass. So in that respect it’s a really good test. It’s just not a test of what it’s perceived to be a test of, typically. This [experiment in the movie] was supposed to be like a post-Turing Turing Test. The guy says she passed with blind controls, he’s not interested in whether she’ll pass. He’s not interested in her language capacity, which is comparable to a chess computer that wants to win at chess, but doesn’t even know whether it’s playing chess or that it’s a computer. This is the thing you’d do after you pass the Turing Test. But I totally agree with everything you said.
In your research, is there a test that’s been developed that is the reverse of the Turing Test, that seeks to answer whether, in the face of so much technology development, we’ve lost some of our innate human-ness? Or that we’re more machine like?
AG: I think we are machine-like. As far as I know, no test exists like that. The argument at the heart of these things is: is there a significant difference between what a machine can do and what we are? I think how I see this is that we sometimes dignify our conciousness. We make it slightly metaphysical and we deify it because it’s so mysterious to us. An we think, are computers ever going to get up to the lofty heights where we exist in our conciousness? And I suspect that we should be repositioning it here, and we overstate us, in some respects. That’s probably the opposite of what you want to hear.
Do you think that some machine-like quality predates the technology?
AG: I do, yes. I suspect all our human aspects are through evolution, that’s how I think we got here. I can see how conciousness arises from needing to interact in a meaningful and helpful way with other sentient things. Our language develops, and as these things get more sophisticated, conciousness becomes more useful and things that have higher conciousness succeed better. Also, I heard someone talk about conciousness the other day and they were saying “One day, it’s possible that elephants will become sentient.” And that’s a really good example of how we misunderstand sentience. Elephants are already sentient. If you put a dog in front of a mirror, it recognizes its own reflection. It’s self-aware. It knows it’s not looking at another dog. So I put us on that spectrum.
Pertaining to that question, there’s a [critical] moment in the movie where Caleb cuts himself in front of a mirror to make sure that he’s bleeding. And I was going to ask if that’s symbolic of that evolution where conciousness can be undifferentiated between a human and a machine? I was wondering if that scene is a subtle hint that you don’t really know whether you’re the one that is being tested or you’re the tester?
AG: There’s two parts [to that scene]. One is film audiences are literate. I kind of assume that everyone who’s seen that has seen Blade Runner. So they’re going to be imagining to themselves, it’s not her [that is the AI] it’s him. He’s the robot. Here’s the thing. If someone asks of you, here’s a machine, test that machine’s conciousness, tell me if it’s concious or not, it turns out to be a very difficult thing to do. Because [the machine] could act convincingly that it’s concious, but that wouldn’t tell you that it is. Now, once you know that, that actually becomes true of us. You don’t know I’m concious. You think I’m probably concious, you’re not really questioning it. But you believe you are concious, and because I’m like you, I’m another human, you assume I’ve got it. But I’m doing anything that empirically demonstrates that I am concious. It’s an act of faith. And once you know that, you’ve figured that out about the machine and now you can figure it out about the other person. Weirdly, then you can ask it of yourself. That’s where the diminished sense of conciousness comes into it. The things that I believe are special about me are the things I’m feeling – love, fear. And then you think about electrochemicals floods in your brain and the things we’ve been taught and the things we’ve been born with and our behavior patterns and suddenly it gets more and more diminished. To the point that you can think something along the lines of “Am I like a complicated plant that thinks it’s a human?” It’s not such an unreasonable question. So cut your arm and have a look!
In thinking about being a complicated plant, that sounds very isolating. Nathan was really isolated in the movie as well. Do you think that this is indicative of where we’re going with our devices and internet and social media being our social outlet rather than actually socializing? Is AI taking us down that path of isolation?
AG: It may or may not. That could be the case. I’m not on Twitter, I’ve never been on Facebook, I’m not really too [fond of] that stuff. From the outside looking in, it looks like that’s the way people communicate – maybe in a limited way, but in a way I don’t really know. The thing about Nathan is we’re social animals, and our behavior is incredibly modified by people around us. And when we’re removed from modification, our behavior gets very eccentric very fast. I think of it like a kid holding on to a balloon and then they let it go and in a flash it’s gone. I know this because my job is I’m a writer and if I’m on a roll, I can spend six days where I don’t leave the house, I barely see my kids in the corridor, but I’m mainly interested in the fridge and the computer. And I get weird, fast. It’s amazing how quickly it happens. I think anyone who’s read Heart of Darkness or seen the adaptation Apocalypse Now, [Nathan] is like this character Kurtz. He spends too much time upriver, too much time unmodified by the influences that social interactions provide.
Ex Machina goes into wide release in theaters on April 10, 2015.
*****************
ScriptPhD.com covers science and technology in entertainment, media and advertising. Hire our consulting company for creative content development. Follow us on Twitter and Facebook. Subscribe to our podcast on SoundCloud or iTunes.
As part of an ongoing recommitment to its sci-fi genre roots, SyFy Channel is unveiling the original scripted drama Ascension, for now a six hour mini-series, and possible launch for a future series. It follows a crew aboard the starship Ascension, as part of a 1960s mission that sent 600 men, women and children on a 100 year planned voyage to populate a new world. In the midst of political unrest onboard the vessel, the approach of a critical juncture in the mission and the first-ever murder onboard the craft, the audience soon learns, there is more to the mission than meets the eye. Which can also be said of this multi-layered, ambitious, sophisticated mini-series. Full ScriptPhD review below.

In the late 1950s and early 1960s, largely fueled by the heigh of Cold War tensions with the Soviet Union and fears of mutual nuclear destruction, the United States government, in conjunction with NASA, launched a project that would have sent 150 people into various corners of space — from the Moon, to Mars and eventually Saturn. Code-named Orion, the project officially launched in 1958 at General Atomics in San Diego under the leadership of nuclear researcher Frederick deHoffman, Los Alamos weapons specialist Theodore Taylor and theoretical physicist Freeman Dyson. Largely fueled by Dyson, Orion’s aim was to build a spacecraft equipped with atomic bombs, that would propel the rocket further and further into space through a series of well-timed explosions (nuclear propulsion). The partial test ban treaty of 1963 ended the grandiose project, which remains classified to this day.

Ascension is the seamless fictional transition borne of asking “what if” questions about the erstwhile Project Orion. What if it never ended? What if it was still ongoing? What would be the psychological ramifications of entire generations of people born, raised and living on a closed vessel? Is human habitation of other planets an uncertainty or inevitability? And so Project Orion continued on as Project Ascension, under the hands of Abraham Enzmann. A crew of 600 was sent off into space not knowing the fate of humanity, frozen in time, and as far as they know — all that would be left of mankind.
Ascension carries on in the vein of stylish series such as Caprica, Helix and Defiance, with sleek sci-fi gadgetry and a spaceship capable of mimicking an entire world (including a beach!) for 100 years. This is no dilapidated, aging Battlestar Galactica. However, because time is frozen in the 1960s, all technology, clothes and cultural collections reflect that era — think Mad Men in space. Nostalgia reigns with references to the Space Race via speeches from President Kennedy, along with film and television cornerstones of that era.

51 years into the mission, on the evening of the annual launch party celebration, a kind of Ascension independence day, the unthinkable happens: the first ever murder onboard the ship. Captain William Denninger puts first officer Aaron Gault in charge of investigating. Soon, the motives for the murder become convoluted amidst internal politics and the looming “Insurrection,” a point of no return in which communication with Earth is no longer possible.
This year’s space epic Interstellar explored the science of traveling 10 billion light years away from Earth – ambitiously but not without factual fault. And to be sure, Ascension will address the challenges and physics of nuclear propulsion to the far reaches of space, starting with a radiation storm midway through the first episode. But rather than bogging itself down in the astrophysical minutiae of space travel, Ascension smartly focuses on the human drama and existential questions such a voyage would incur, precisely what made Battlestar Galactica such compelling sci-fi television. Would there be internal psychological ramifications to this journey? All residents of the ship seem to go through an adolescent period termed “The Crisis,” where they come to grips with the fact that they have no future, and a pre-determined fate. Furthermore, the murder victim’s young sister appears to be a “seer” with telekinetic insight into the nefarious inner workings of the ship.
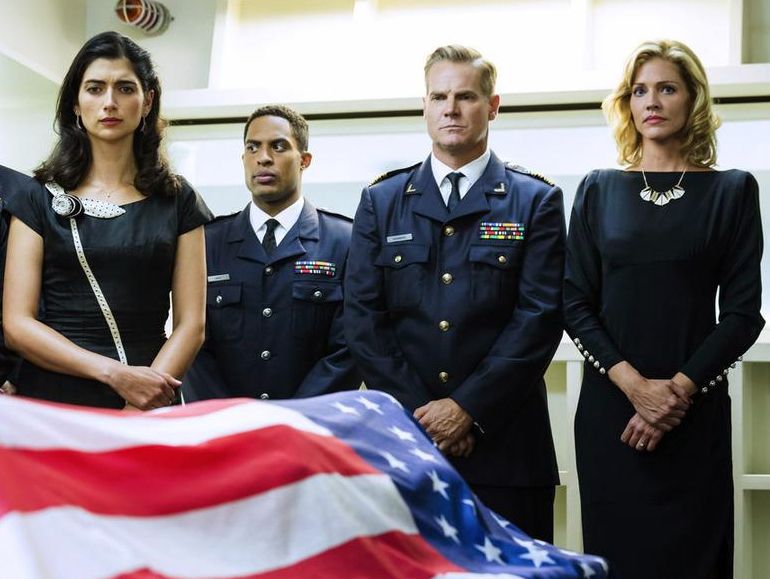

Would there be class division and political turmoil aboard such a confined community? There is a decidedly troublesome rift between the ranking officers of the upper quarters and the “Below Deckers”: butchers, steelworkers and other blue-collar craftsmen that appear on the edge of a revolt. Compounding their efforts are the Captain’s wife, Viondra Denninger (whom fans will recognize as Cylon Number Six from BSG), a cunning, manipulative power broker and the man seeking to wrestle control of the ship from her husband. Back on Earth, we meet Harris Enzmann, the son of the dying Project Ascension founder. Seemingly a low level government engineer, nor remotely interested in preserving his father’s legacy, his role in Project Ascension is convoluted yet significant.
Project Ascension is indeed an experiment critical for human survival — just not the one anyone onboard thinks it is. Amidst an awakened collective imagination about space exploration, including 2015’s IMAX Mars mission movie Journey To Space, this is one sci-fi mission worth taking.
View a trailer for Ascension:
Ascension is a three-day mini-series event on SyFy Channel, beginning Monday, December 15.
~*ScriptPhD*~
*****************
ScriptPhD.com covers science and technology in entertainment, media and advertising. Hire us for creative content development.
Subscribe to free email notifications of new posts on our home page.
]]>
Space movies are almost always grandiose in their storytelling aspirations. The enormity of space, the raw power of the shuttle, the existential quandary of whether we are alone in a vast Universe, and (as is the case in Gravity) an almost-inevitable crisis that must be resolved to steer the astronauts onboard to safety. There is one critical detail, however, that most fail to convey visually—solitude. Dr. Katherine Coleman, who spent thousands of hours aboard the shuttles Columbia and the International Space Station, and who was a primary mentor to star Sandra Bullock, recounts isolation—spatial separation, physical movements, zero gravity and a distant Earth—as the biggest challenge and reward she faced as an astronaut. With a tense, highly focused storyline centered almost entirely on one brave scientist, Gravity is a virtual space flight for the audience, but also a gripping examination of emotional and physical sequestration. Through this vista, we are able to perceive how beautiful, terrifying and enormous space truly is. Full ScriptPhD.com Gravity review under the “continue reading” cut.
It is in this backdrop that we are first introduced to Mission Specialist Ryan Stone (Bullock), a medical engineer turned novice astronaut sent to repair an arm of the Hubble Telescope, and ebullient, assertive veteran Mission Commander Matt Kowalski (Clooney), out on his last voyage in space. During a routine scanning system installation on the exterior of their shuttle, an intentional demolition of an obsolete satellite sends shrapnel debris unexpectedly hurling through space right in their direction. This nightmare scenario, called the Ablation Cascade, was first hypothesized back in 1978 by NASA scientist Donald J. Kessler. Once the density of objects flying in low Earth orbit became high enough (everything from space junk to satellites to intergalactic matter), a collision between two of those objects would lead to further collisions with other nearby objects, each creating more dangerous debris hurling through space. With catastrophic damage to their shuttle, Kowalski and Ryan are the sole survivors with no access to NASA Mission Control and no ability to steer their shuttle home. Limited oxygen supply and a series of tragic consequences soon leave the two astronauts to survival instincts and a last-ditch escape via an international space station as their only hope for returning to Earth.
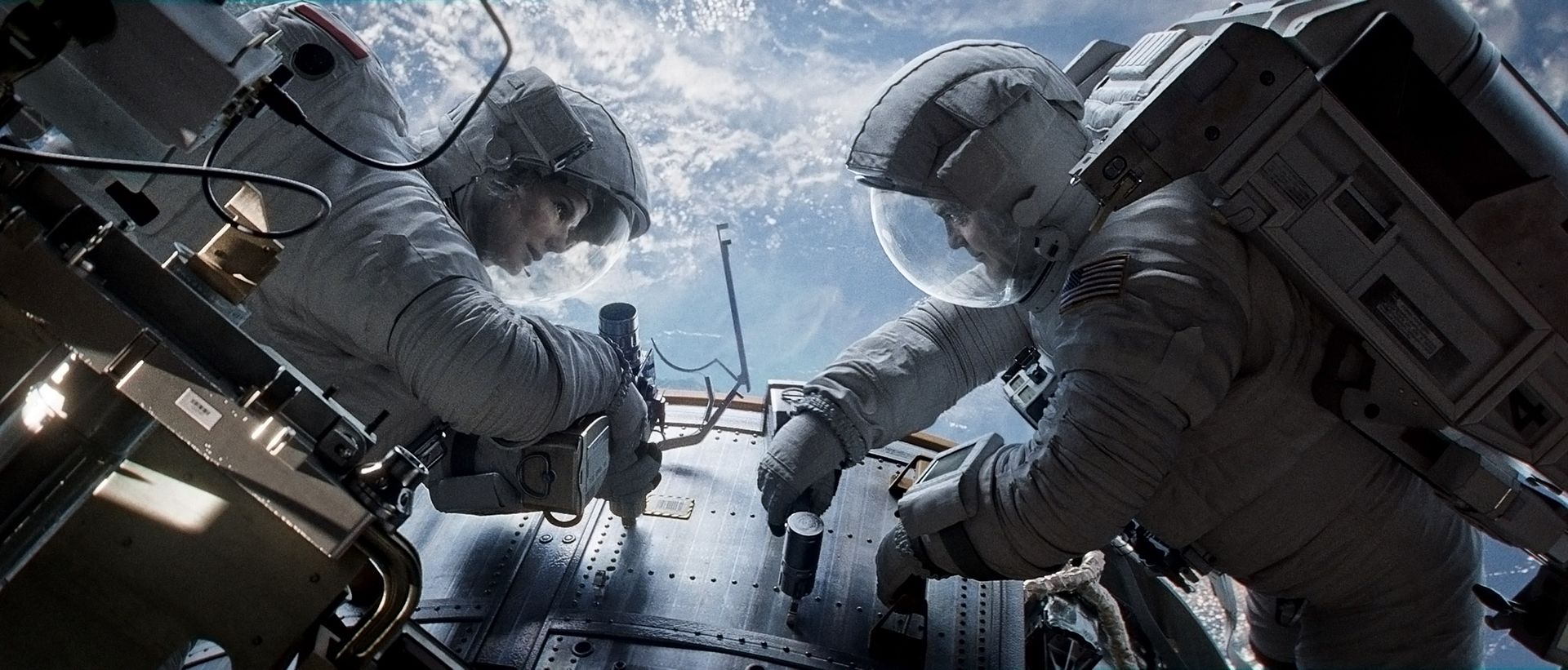

Much like its smart 2013 predecessor, Europa Report, Gravity is a highly technical, pinpoint-accurate movie that relied on input from NASA astronauts and physicists for every level of execution. Director Alfonso Cuarón, working on his first big screen film in seven years, worked painstakingly alongside a talented crew to implement previously-unproven digital technologies aimed at transporting audiences into weightless space.
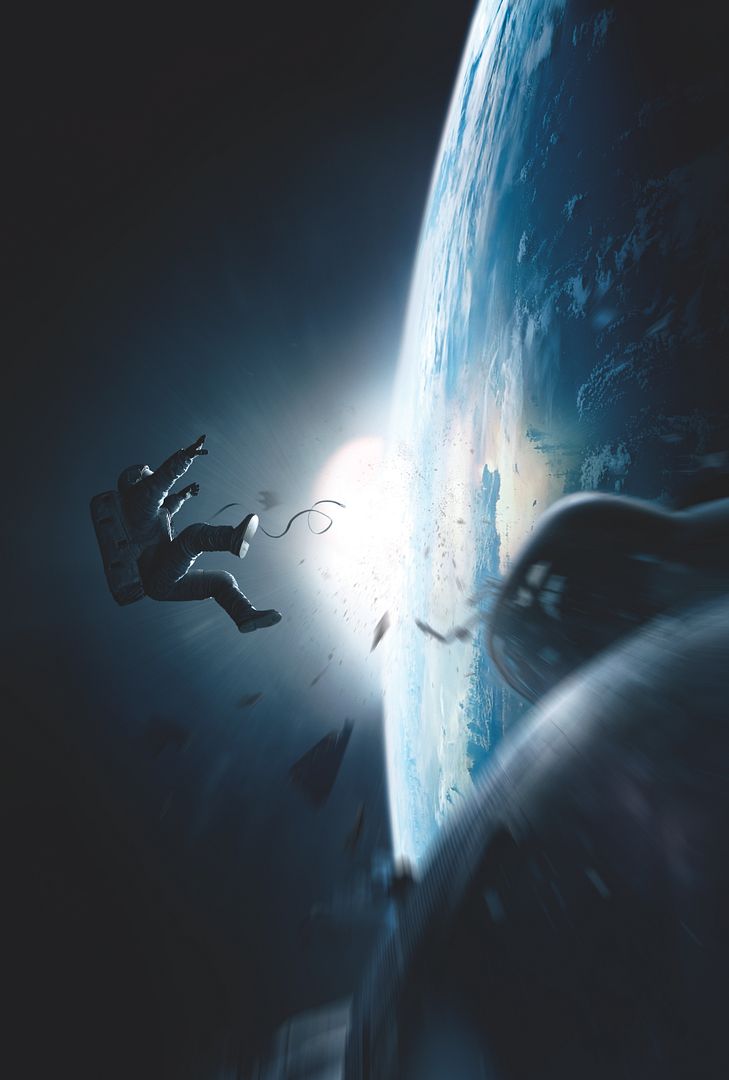

Dr. Michael Massimino, a Hubble service specialist with missions on Space Shuttles Columbia and Atlantis, provided insight into space travel and space walking. In addition, Clooney and Bullock spent hours training for zero gravity conditions, while artistic directors and technical crew built special stage-size light boxes and green screens to be able to create remarkable CGI renderings of space from all angles. “Even if [Gravity] was a work of fiction,” Cuarón remarked at a recent screening preview, “We wanted everything, especially the physics of space, to be as accurate as possible.”
Despite the thrilling story and technical fidelity, there is a stylistic beauty to Gravity rooted in simplicity, a silent abyss in the midst of intergalactic chaos. Cuarón’s desire to showcase space as a central physical and thematic piece of his movie is reflected in every frame. He perceived Gravity to be an existential film about “a woman drifting into the void and confronting adversity.” Rather than being tethered to the constraints of a time and place, however, the solar elements of space are the surge of life that inspires her to keep going.
“I used to think that astronauts wanted to go into space for the thrill and adventure,” Bullock reflected. “When I spoke to them, though, I was so moved by their deep love of that world and the beauty of Earth from their perspective. It’s amazing to realize how small we are in this massive universe.” These are the very details that are magnified on screen as the story unfolds – a tiny human being drifting in the enormity of space, a comforting human voice on the radio amid total abyss, a teardrop defying gravity, the magic of another sunrise viewed from millions of miles away.
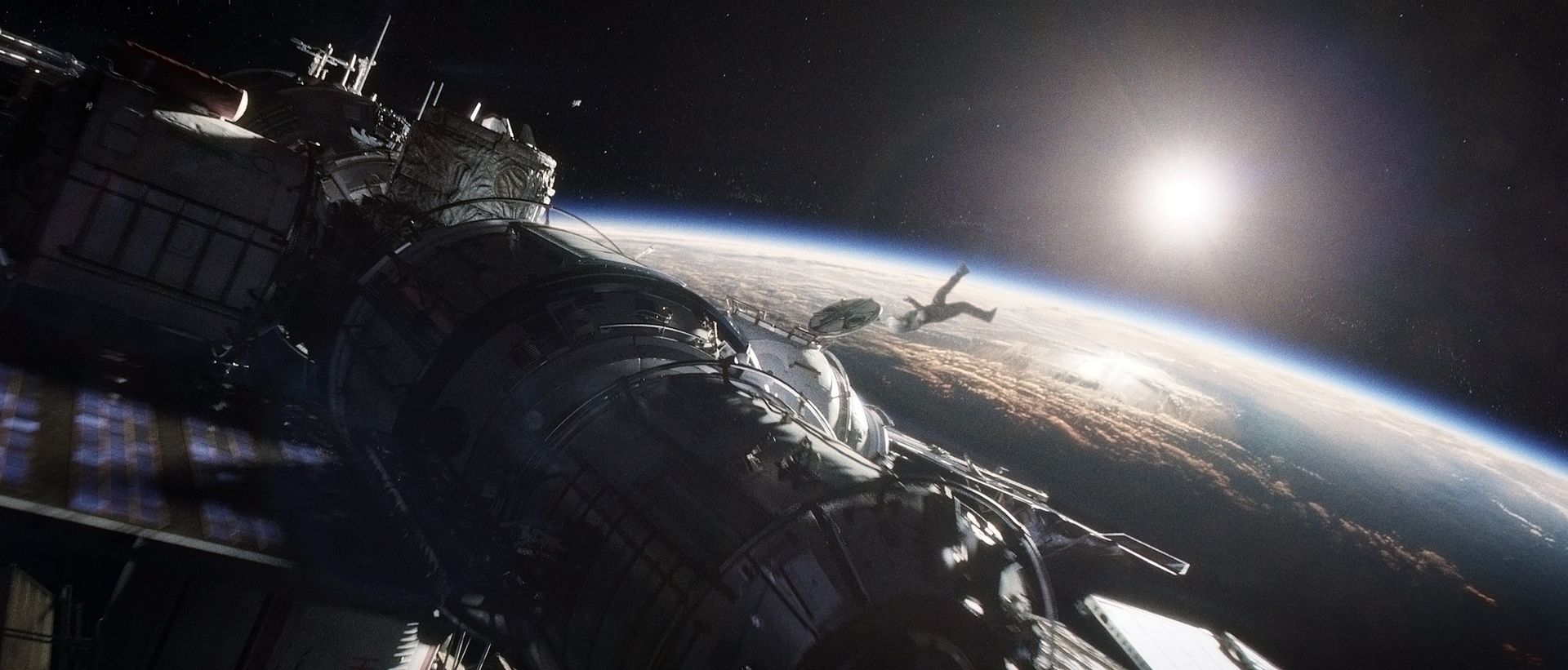

Far more than just a creative interpretation of space, Gravity is that rare piece of art that can inspire and entertain, a true game-changer in a crowded space film genre. As Dr. Massimino emotionally reminded the press during the preview screening, centers like NASA and the Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, CA are still doing important research as part of a space program that is very much thriving and as critical as it has ever been. Gravity is a magical way to bring the masses into space and inspire a new generation of support for NASA. “This movie will make folks understand what we do and why it is so important,” Massimino hopes.
As a love letter to space exploration and the sheer strength of human tenacity, Gravity exceeds all expectations.
Gravity goes into wide release in theaters and IMAX on October 4, 2013.
View an extended Gravity trailer:
~*ScriptPhD*~
*****************
ScriptPhD.com covers science and technology in entertainment, media and advertising. Hire us for creative content development.
Subscribe to free email notifications of new posts on our home page.
]]>
It has been three decades since Ridley Scott’s acclaimed sci-fi masterpiece Blade Runner practically reinvented the genre, and he has not made another sci-fi film since. “The reason I haven’t made another sci-fi film in so may years,” he says “is because I haven’t come across anything worthwhile for me to do with enough truth, originality and strength. Prometheus has all three.” With such heightened expectations, one would expect a bold, daring, all-encompassing storyline from Scott. Loosely based on elements from Alien, and originally intended as a prequel to that film, Prometheus meets many of those expectations, especially in visual and action content, while falling short on others. Full ScriptPhD review, under the “continue reading” cut.
Set 80 years in the future, a team of archaeologists discovers a series of cave etchings with a clue to the origins of mankind on Earth—a far-away planet in the darkest corners of the Universe. Commissioned by the corporate conglomerate Weyland Corporation, the $1 trillion scientific exploratory journey is originally intended to meet our makers in their native land. But when the team makes the shocking discovery that their makers’ paradise is a way station for a dangerous experiment in bioengineering, they begin the fight of their life to save humanity.

Interspersed within this non-stop intergalactic thrill ride are a series of conflicts between the crew members that challenge some of our most cherished scientific and philosophical ideas, conflicts we may ourselves be forced to address in the near future. The sterile, corporate (and somewhat surprisingly selfish) interests of the journey, funded by enigmatic Peter Weyland and carried out by Weyland Industries executive Meredith Vickers are in stark contrast to the spirit of scientific exploration for the sake of discovery and learning. The mission’s lead scientists are archetypes for the conflict of faith versus science. Elizabeth Shaw is deeply religious, and views the mission as a chance to meet the Gods, to affirm her faith and everything she believes in. Her partner, both in the lab and personally, Charlie Holloway is a classic adventurous scientist who is on the journey to push the envelope in the quest for answers. Finally, rounding out
the crew of 17 scientists is David, a human-replica android servant of superior intelligence created by the Weyland Corporation. David is an amalgamation of virtually every artificial intelligence character sci-fi has ever created, from Hal to C-3PO to the Terminator. Originally manufactured to tend to the ship during the two-year journey and to gather intelligence, David is nevertheless acutely aware of his superiority over his human charges. He even has the will to help them figure out the nefarious scheme of the alien predecessors and fight a battle for their survival. Responding to Holloway’s flippant response that humans made David simply because they could, he retorts: “Imagine how disappointed you’d be if your makers gave you the same response?”

Scott’s commitment to the grand scope of
Prometheus rewards the audience with a technological and engineering masterpiece of science fiction, starting with the visually arresting sets and action sequences. So extraordinary are the special effects of the scientific exploration of the alien planet and consequent battles, one would falsely assume they are CGI. But Scott built enormous sets and shot the majority of the film live in three dimensions. One production crew member called it the “greatest alien playground in the world.” The state-of-the-art spacecraft, modeled after current NASA and European Space Agency designs, was constructed with every piece of technology that would be necessary to probe the outer corners of the galaxy. Techno-geeks will salivate over sleek gadgetry like the self-operating medical pod, research labs capable of immediately isolating and sequencing single strands of DNA, travelling “mind pop” mapping devices that can isolate life, not to mention sleep-state pods where the scientists are suspended for their two-year journey. Prometheus gives a credible peek into what our science and technology capabilities will be like a hundred years from now.
Ultimately, for all of its ambition and far-reaching scope, Prometheus eventually buckles under its own weight of self-importance. The existential questions it is asking are sci-fi staples. Who are we? Where do we come from? How do we reconcile science and religion in our quest to define our identities? And finally, embodied by the advanced-technology android David, what are the parameters of responsibility in the creation of life? And what is the reason for the frailty about when and why it begins and ends? Unfortunately, the film only dabbles enough with each to titillate without ever providing fulfilling answers. The audience may finish the Prometheus quest philosophically unsatisfied, but the journey there is still an action-packed, viscerally stunning sci-fi ride.
Prometheus goes into theaters nationwide on June 11, 2012.
View the trailer:
~*ScriptPhD*~
*****************
ScriptPhD.com covers science and technology in entertainment, media and advertising. Hire our consulting company for creative content development.
Subscribe to free email notifications of new posts on our home page.
]]>
